Haofei Wang
Jitter Does Matter: Adapting Gaze Estimation to New Domains
Oct 05, 2022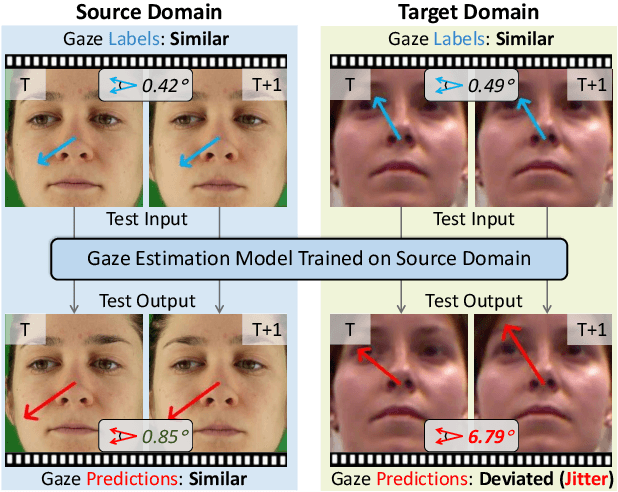
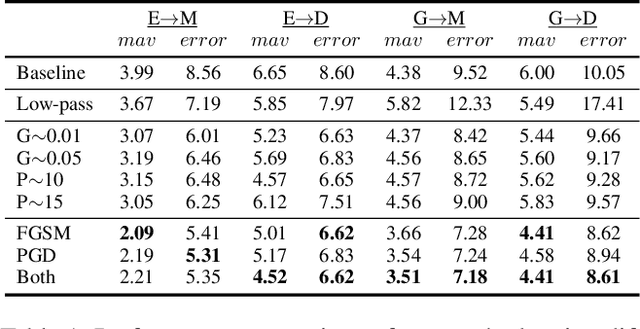
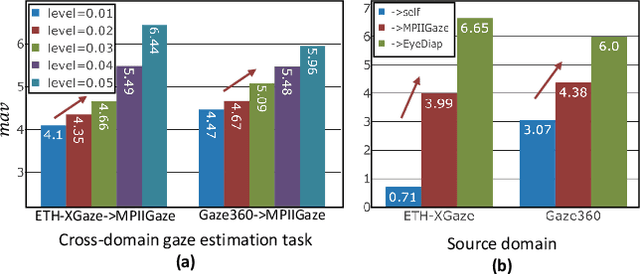
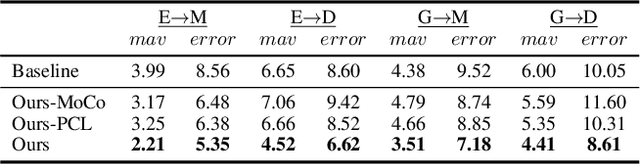
Abstract:Deep neural networks have demonstrated superior performance on appearance-based gaze estimation tasks. However, due to variations in person, illuminations, and background, performance degrades dramatically when applying the model to a new domain. In this paper, we discover an interesting gaze jitter phenomenon in cross-domain gaze estimation, i.e., the gaze predictions of two similar images can be severely deviated in target domain. This is closely related to cross-domain gaze estimation tasks, but surprisingly, it has not been noticed yet previously. Therefore, we innovatively propose to utilize the gaze jitter to analyze and optimize the gaze domain adaptation task. We find that the high-frequency component (HFC) is an important factor that leads to jitter. Based on this discovery, we add high-frequency components to input images using the adversarial attack and employ contrastive learning to encourage the model to obtain similar representations between original and perturbed data, which reduces the impacts of HFC. We evaluate the proposed method on four cross-domain gaze estimation tasks, and experimental results demonstrate that it significantly reduces the gaze jitter and improves the gaze estimation performance in target domains.
Separating Content and Style for Unsupervised Image-to-Image Translation
Oct 27, 2021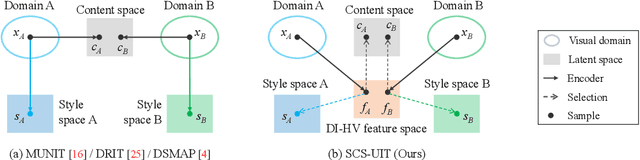
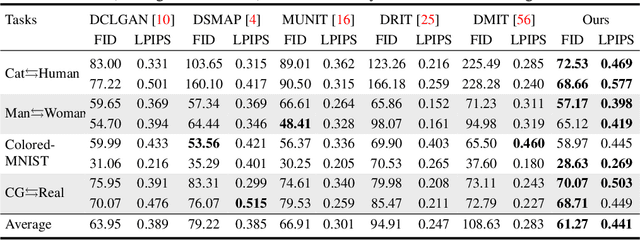
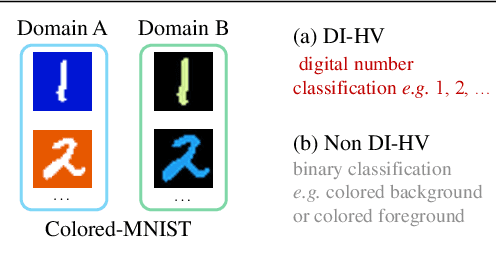
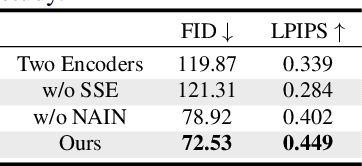
Abstract:Unsupervised image-to-image translation aims to learn the mapping between two visual domains with unpaired samples. Existing works focus on disentangling domain-invariant content code and domain-specific style code individually for multimodal purposes. However, less attention has been paid to interpreting and manipulating the translated image. In this paper, we propose to separate the content code and style code simultaneously in a unified framework. Based on the correlation between the latent features and the high-level domain-invariant tasks, the proposed framework demonstrates superior performance in multimodal translation, interpretability and manipulation of the translated image. Experimental results show that the proposed approach outperforms the existing unsupervised image translation methods in terms of visual quality and diversity.
Generalizing Gaze Estimation with Outlier-guided Collaborative Adaptation
Jul 30, 2021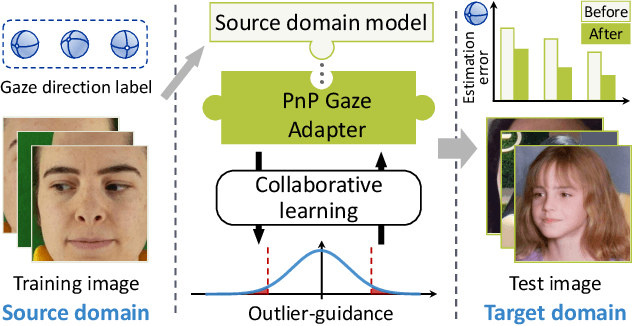
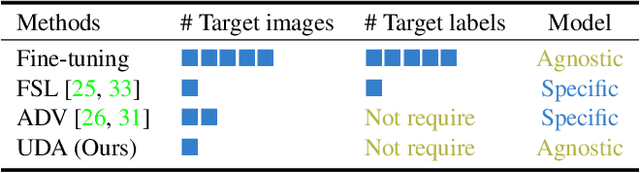
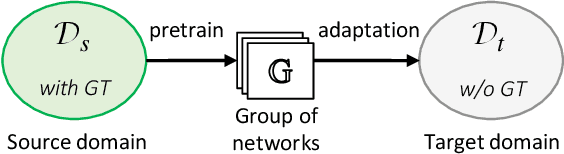
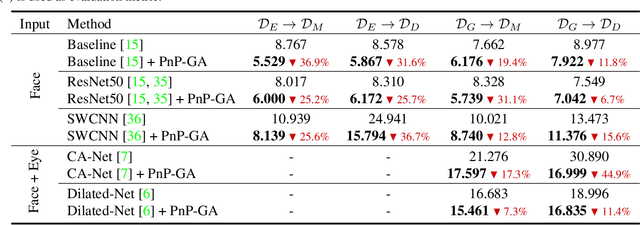
Abstract:Deep neural networks have significantly improved appearance-based gaze estimation accuracy. However, it still suffers from unsatisfactory performance when generalizing the trained model to new domains, e.g., unseen environments or persons. In this paper, we propose a plug-and-play gaze adaptation framework (PnP-GA), which is an ensemble of networks that learn collaboratively with the guidance of outliers. Since our proposed framework does not require ground-truth labels in the target domain, the existing gaze estimation networks can be directly plugged into PnP-GA and generalize the algorithms to new domains. We test PnP-GA on four gaze domain adaptation tasks, ETH-to-MPII, ETH-to-EyeDiap, Gaze360-to-MPII, and Gaze360-to-EyeDiap. The experimental results demonstrate that the PnP-GA framework achieves considerable performance improvements of 36.9%, 31.6%, 19.4%, and 11.8% over the baseline system. The proposed framework also outperforms the state-of-the-art domain adaptation approaches on gaze domain adaptation tasks.
Assessment of Deep Learning-based Heart Rate Estimation using Remote Photoplethysmography under Different Illuminations
Jul 28, 2021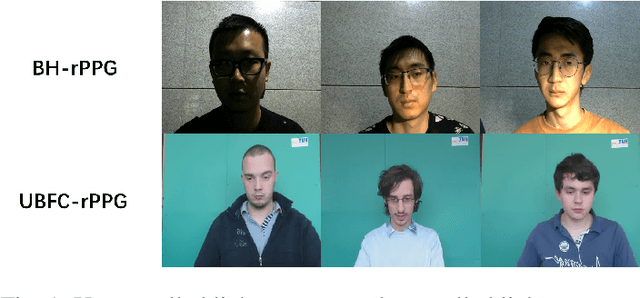
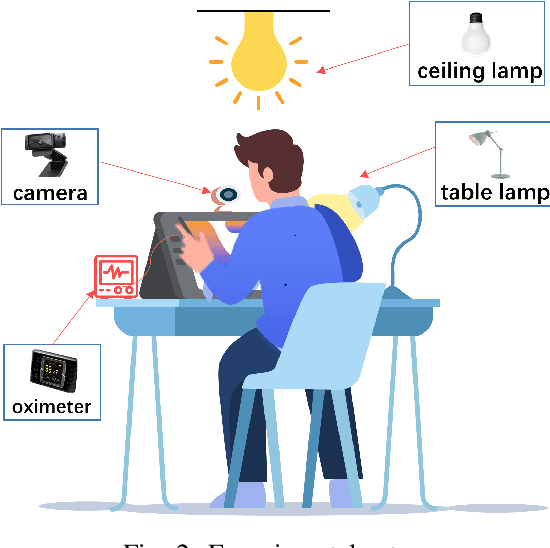
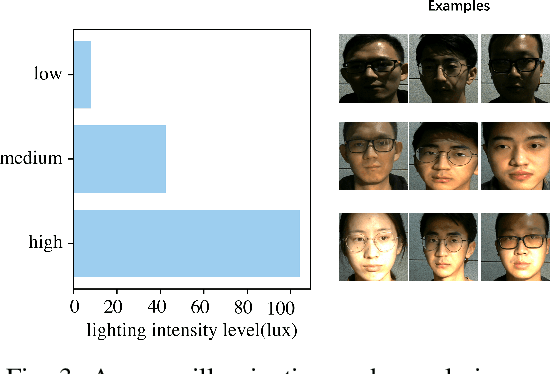
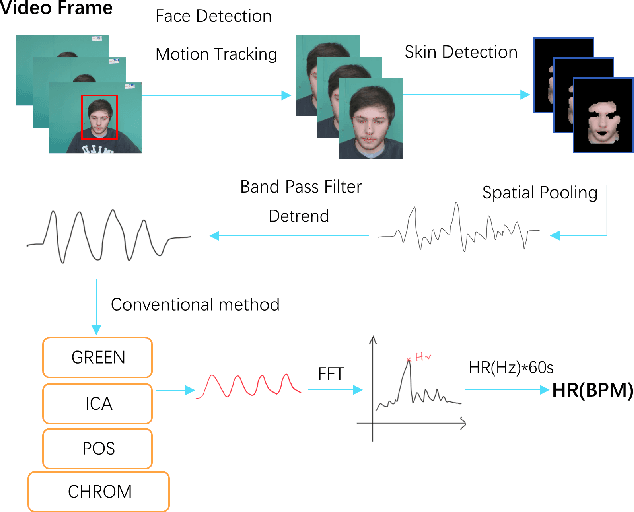
Abstract:Remote photoplethysmography (rPPG) monitors heart rate without requiring physical contact, which allows for a wide variety of applications. Deep learning-based rPPG have demonstrated superior performance over the traditional approaches in controlled context. However, the lighting situation in indoor space is typically complex, with uneven light distribution and frequent variations in illumination. It lacks a fair comparison of different methods under different illuminations using the same dataset. In this paper, we present a public dataset, namely the BH-rPPG dataset, which contains data from twelve subjects under three illuminations: low, medium, and high illumination. We also provide the ground truth heart rate measured by an oximeter. We evaluate the performance of three deep learning-based methods to that of four traditional methods using two public datasets: the UBFC-rPPG dataset and the BH-rPPG dataset. The experimental results demonstrate that traditional methods are generally more resistant to fluctuating illuminations. We found that the rPPGNet achieves lowest MAE among deep learning-based method under medium illumination, whereas the CHROM achieves 1.5 beats per minute (BPM), outperforming the rPPGNet by 60%. These findings suggest that while developing deep learning-based heart rate estimation algorithms, illumination variation should be taken into account. This work serves as a benchmark for rPPG performance evaluation and it opens a pathway for future investigation into deep learning-based rPPG under illumination variations.
Appearance-based Gaze Estimation With Deep Learning: A Review and Benchmark
Apr 26, 2021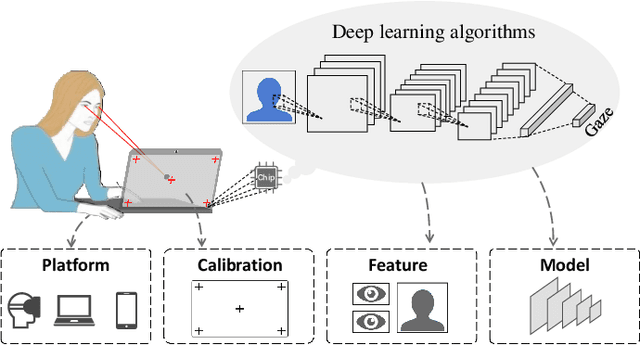
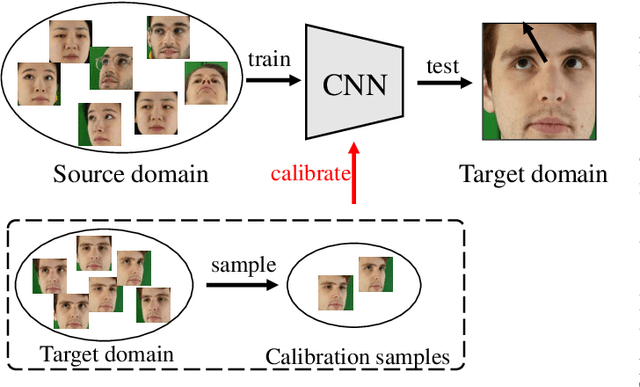
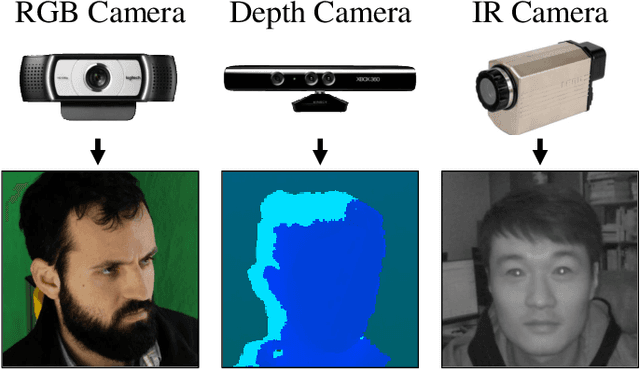

Abstract:Gaze estimation reveals where a person is looking. It is an important clue for understanding human intention. The recent development of deep learning has revolutionized many computer vision tasks, the appearance-based gaze estimation is no exception. However, it lacks a guideline for designing deep learning algorithms for gaze estimation tasks. In this paper, we present a comprehensive review of the appearance-based gaze estimation methods with deep learning. We summarize the processing pipeline and discuss these methods from four perspectives: deep feature extraction, deep neural network architecture design, personal calibration as well as device and platform. Since the data pre-processing and post-processing methods are crucial for gaze estimation, we also survey face/eye detection method, data rectification method, 2D/3D gaze conversion method, and gaze origin conversion method. To fairly compare the performance of various gaze estimation approaches, we characterize all the publicly available gaze estimation datasets and collect the code of typical gaze estimation algorithms. We implement these codes and set up a benchmark of converting the results of different methods into the same evaluation metrics. This paper not only serves as a reference to develop deep learning-based gaze estimation methods but also a guideline for future gaze estimation research. Implemented methods and data processing codes are available at http://phi-ai.org/GazeHub.
Vulnerability of Appearance-based Gaze Estimation
Mar 24, 2021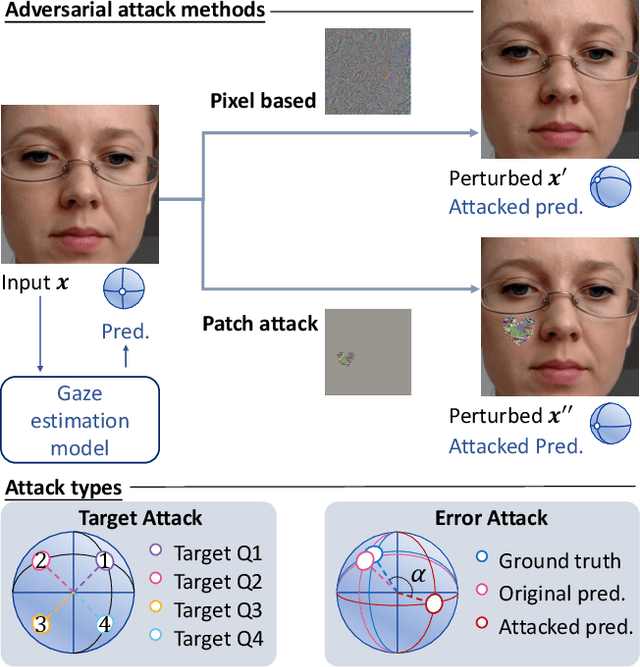
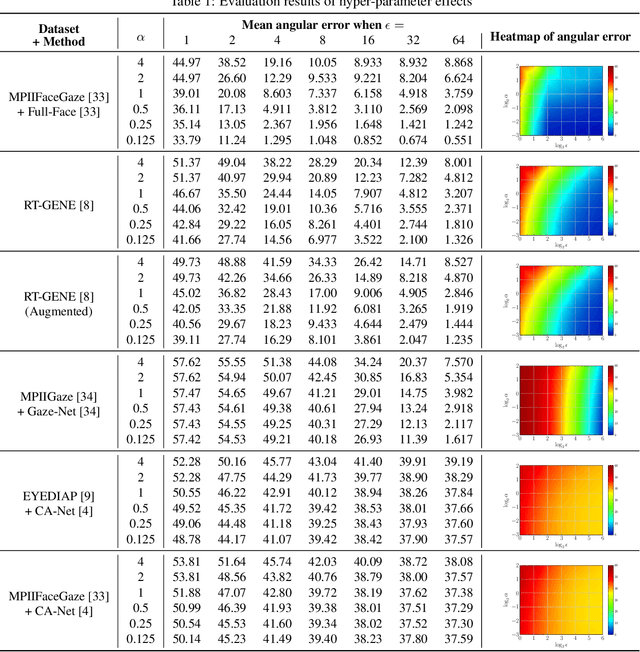
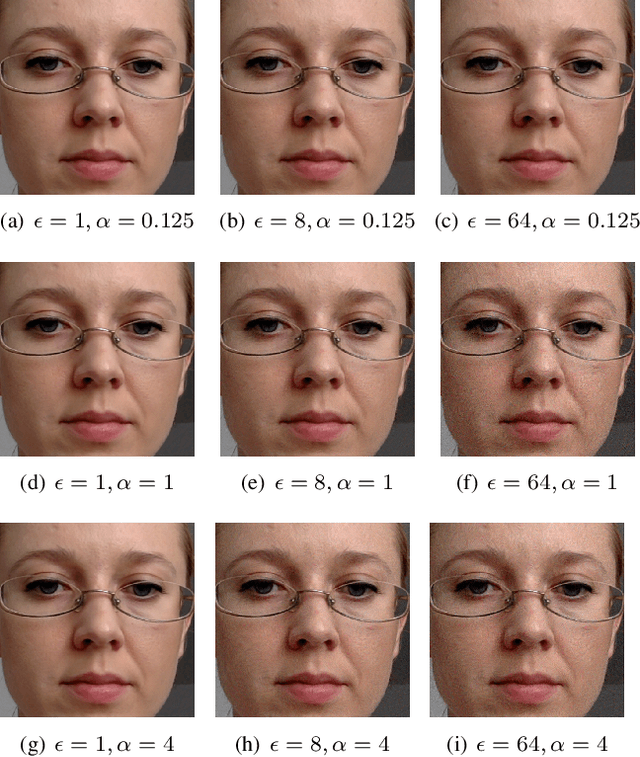
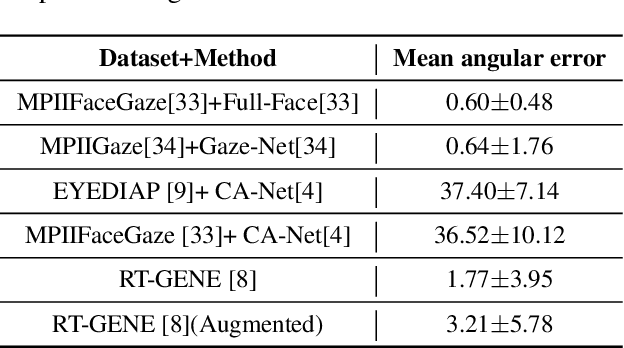
Abstract:Appearance-based gaze estimation has achieved significant improvement by using deep learning. However, many deep learning-based methods suffer from the vulnerability property, i.e., perturbing the raw image using noise confuses the gaze estimation models. Although the perturbed image visually looks similar to the original image, the gaze estimation models output the wrong gaze direction. In this paper, we investigate the vulnerability of appearance-based gaze estimation. To our knowledge, this is the first time that the vulnerability of gaze estimation to be found. We systematically characterized the vulnerability property from multiple aspects, the pixel-based adversarial attack, the patch-based adversarial attack and the defense strategy. Our experimental results demonstrate that the CA-Net shows superior performance against attack among the four popular appearance-based gaze estimation networks, Full-Face, Gaze-Net, CA-Net and RT-GENE. This study draws the attention of researchers in the appearance-based gaze estimation community to defense from adversarial attacks.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge