Hanhan Deng
KST-GCN: A Knowledge-Driven Spatial-Temporal Graph Convolutional Network for Traffic Forecasting
Nov 26, 2020


Abstract:When considering the spatial and temporal features of traffic, capturing the impacts of various external factors on travel is an important step towards achieving accurate traffic forecasting. The impacts of external factors on the traffic flow have complex correlations. However, existing studies seldom consider external factors or neglecting the effect of the complex correlations among external factors on traffic. Intuitively, knowledge graphs can naturally describe these correlations, but knowledge graphs and traffic networks are essentially heterogeneous networks; thus, it is a challenging problem to integrate the information in both networks. We propose a knowledge representation-driven traffic forecasting method based on spatiotemporal graph convolutional networks. We first construct a city knowledge graph for traffic forecasting, then use KS-Cells to combine the information from the knowledge graph and the traffic network, and finally, capture the temporal changes of the traffic state with GRU. Testing on real-world datasets shows that the KST-GCN has higher accuracy than the baseline traffic forecasting methods at various prediction horizons. We provide a new way to integrate knowledge and the spatiotemporal features of data for traffic forecasting tasks. Without any loss of generality, the proposed method can also be extended to other spatiotemporal forecasting tasks.
AST-GCN: Attribute-Augmented Spatiotemporal Graph Convolutional Network for Traffic Forecasting
Nov 22, 2020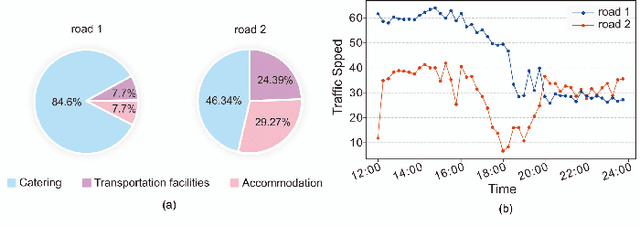
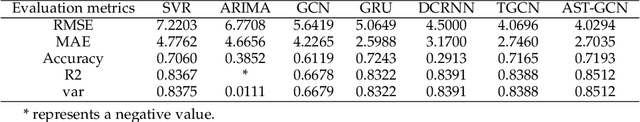
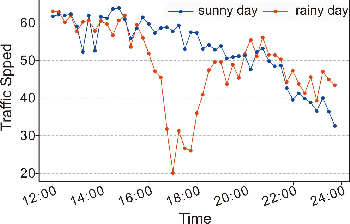
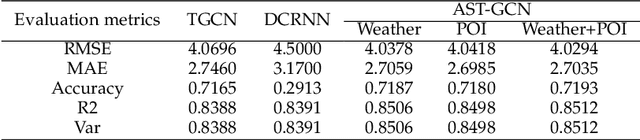
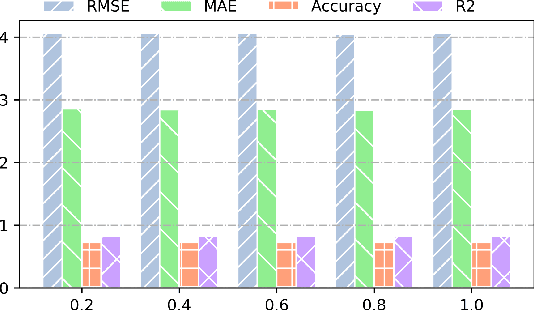
Abstract:Traffic forecasting is a fundamental and challenging task in the field of intelligent transportation. Accurate forecasting not only depends on the historical traffic flow information but also needs to consider the influence of a variety of external factors, such as weather conditions and surrounding POI distribution. Recently, spatiotemporal models integrating graph convolutional networks and recurrent neural networks have become traffic forecasting research hotspots and have made significant progress. However, few works integrate external factors. Therefore, based on the assumption that introducing external factors can enhance the spatiotemporal accuracy in predicting traffic and improving interpretability, we propose an attribute-augmented spatiotemporal graph convolutional network (AST-GCN). We model the external factors as dynamic attributes and static attributes and design an attribute-augmented unit to encode and integrate those factors into the spatiotemporal graph convolution model. Experiments on real datasets show the effectiveness of considering external information on traffic forecasting tasks when compared to traditional traffic prediction methods. Moreover, under different attribute-augmented schemes and prediction horizon settings, the forecasting accuracy of the AST-GCN is higher than that of the baselines.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge