Hai-Hang Sun
DIDA: Denoised Imitation Learning based on Domain Adaptation
Apr 04, 2024
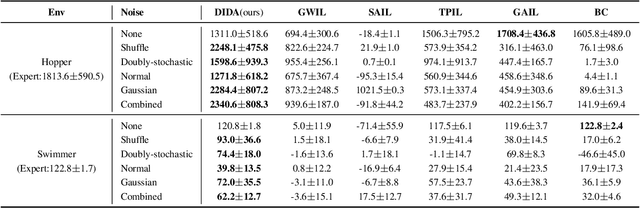
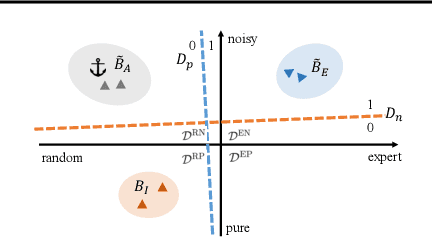
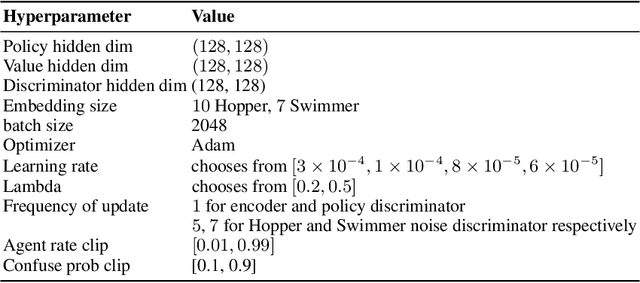
Abstract:Imitating skills from low-quality datasets, such as sub-optimal demonstrations and observations with distractors, is common in real-world applications. In this work, we focus on the problem of Learning from Noisy Demonstrations (LND), where the imitator is required to learn from data with noise that often occurs during the processes of data collection or transmission. Previous IL methods improve the robustness of learned policies by injecting an adversarially learned Gaussian noise into pure expert data or utilizing additional ranking information, but they may fail in the LND setting. To alleviate the above problems, we propose Denoised Imitation learning based on Domain Adaptation (DIDA), which designs two discriminators to distinguish the noise level and expertise level of data, facilitating a feature encoder to learn task-related but domain-agnostic representations. Experiment results on MuJoCo demonstrate that DIDA can successfully handle challenging imitation tasks from demonstrations with various types of noise, outperforming most baseline methods.
SENSOR: Imitate Third-Person Expert's Behaviors via Active Sensoring
Apr 04, 2024



Abstract:In many real-world visual Imitation Learning (IL) scenarios, there is a misalignment between the agent's and the expert's perspectives, which might lead to the failure of imitation. Previous methods have generally solved this problem by domain alignment, which incurs extra computation and storage costs, and these methods fail to handle the \textit{hard cases} where the viewpoint gap is too large. To alleviate the above problems, we introduce active sensoring in the visual IL setting and propose a model-based SENSory imitatOR (SENSOR) to automatically change the agent's perspective to match the expert's. SENSOR jointly learns a world model to capture the dynamics of latent states, a sensor policy to control the camera, and a motor policy to control the agent. Experiments on visual locomotion tasks show that SENSOR can efficiently simulate the expert's perspective and strategy, and outperforms most baseline methods.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge