Haedam Oh
TreeLoc: 6-DoF LiDAR Global Localization in Forests via Inter-Tree Geometric Matching
Feb 03, 2026Abstract:Reliable localization is crucial for navigation in forests, where GPS is often degraded and LiDAR measurements are repetitive, occluded, and structurally complex. These conditions weaken the assumptions of traditional urban-centric localization methods, which assume that consistent features arise from unique structural patterns, necessitating forest-centric solutions to achieve robustness in these environments. To address these challenges, we propose TreeLoc, a LiDAR-based global localization framework for forests that handles place recognition and 6-DoF pose estimation. We represent scenes using tree stems and their Diameter at Breast Height (DBH), which are aligned to a common reference frame via their axes and summarized using the tree distribution histogram (TDH) for coarse matching, followed by fine matching with a 2D triangle descriptor. Finally, pose estimation is achieved through a two-step geometric verification. On diverse forest benchmarks, TreeLoc outperforms baselines, achieving precise localization. Ablation studies validate the contribution of each component. We also propose applications for long-term forest management using descriptors from a compact global tree database. TreeLoc is open-sourced for the robotics community at https://github.com/minwoo0611/TreeLoc.
Evaluation and Deployment of LiDAR-based Place Recognition in Dense Forests
Mar 21, 2024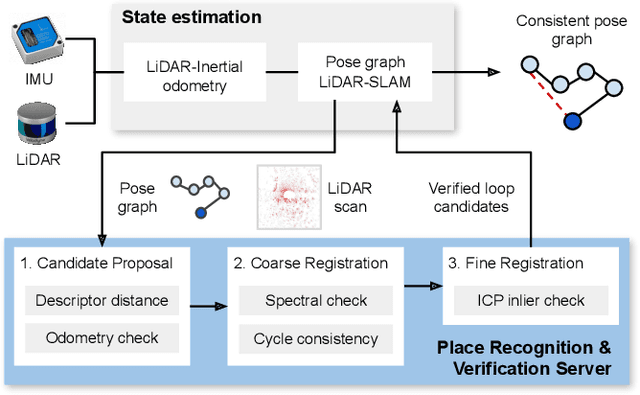
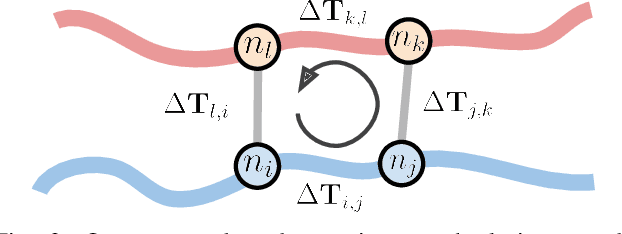
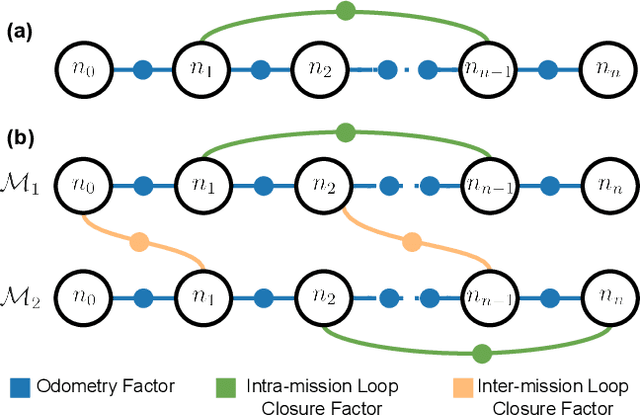
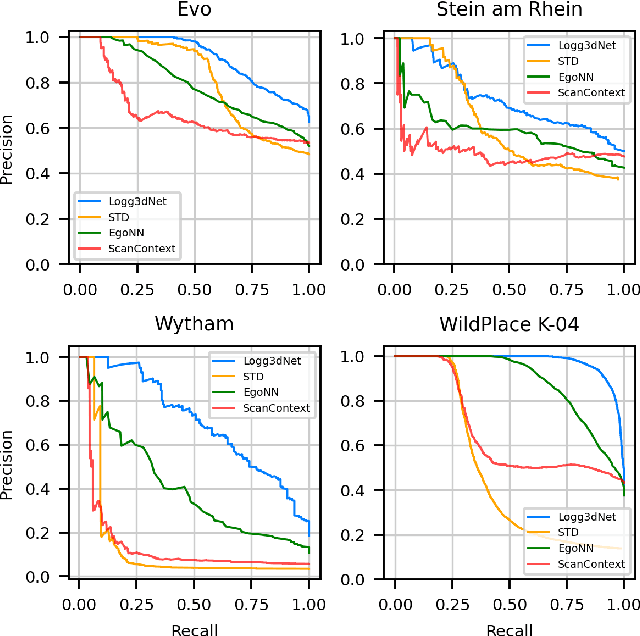
Abstract:Many LiDAR place recognition systems have been developed and tested specifically for urban driving scenarios. Their performance in natural environments such as forests and woodlands have been studied less closely. In this paper, we analyzed the capabilities of four different LiDAR place recognition systems, both handcrafted and learning-based methods, using LiDAR data collected with a handheld device and legged robot within dense forest environments. In particular, we focused on evaluating localization where there is significant translational and orientation difference between corresponding LiDAR scan pairs. This is particularly important for forest survey systems where the sensor or robot does not follow a defined road or path. Extending our analysis we then incorporated the best performing approach, Logg3dNet, into a full 6-DoF pose estimation system -- introducing several verification layers for precise registration. We demonstrated the performance of our methods in three operational modes: online SLAM, offline multi-mission SLAM map merging, and relocalization into a prior map. We evaluated these modes using data captured in forests from three different countries, achieving 80% of correct loop closures candidates with baseline distances up to 5m, and 60% up to 10m.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge