Haanvid Lee
Kernel Metric Learning for In-Sample Off-Policy Evaluation of Deterministic RL Policies
May 29, 2024



Abstract:We consider off-policy evaluation (OPE) of deterministic target policies for reinforcement learning (RL) in environments with continuous action spaces. While it is common to use importance sampling for OPE, it suffers from high variance when the behavior policy deviates significantly from the target policy. In order to address this issue, some recent works on OPE proposed in-sample learning with importance resampling. Yet, these approaches are not applicable to deterministic target policies for continuous action spaces. To address this limitation, we propose to relax the deterministic target policy using a kernel and learn the kernel metrics that minimize the overall mean squared error of the estimated temporal difference update vector of an action value function, where the action value function is used for policy evaluation. We derive the bias and variance of the estimation error due to this relaxation and provide analytic solutions for the optimal kernel metric. In empirical studies using various test domains, we show that the OPE with in-sample learning using the kernel with optimized metric achieves significantly improved accuracy than other baselines.
Local Metric Learning for Off-Policy Evaluation in Contextual Bandits with Continuous Actions
Oct 25, 2022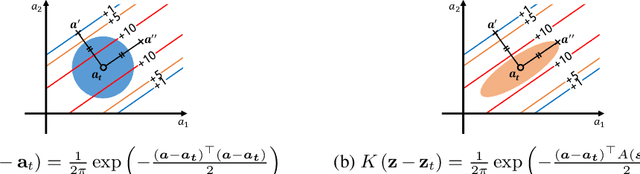
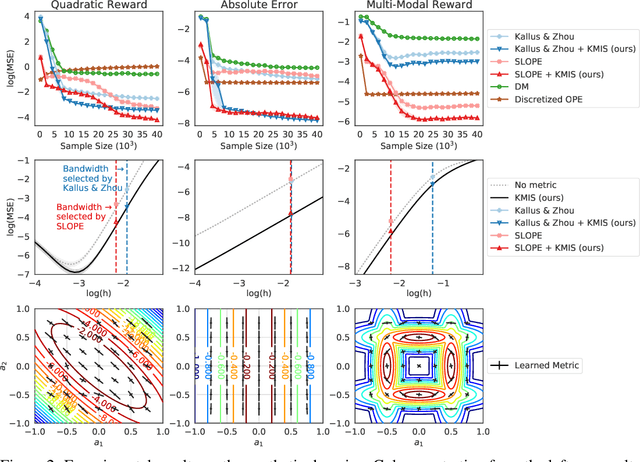
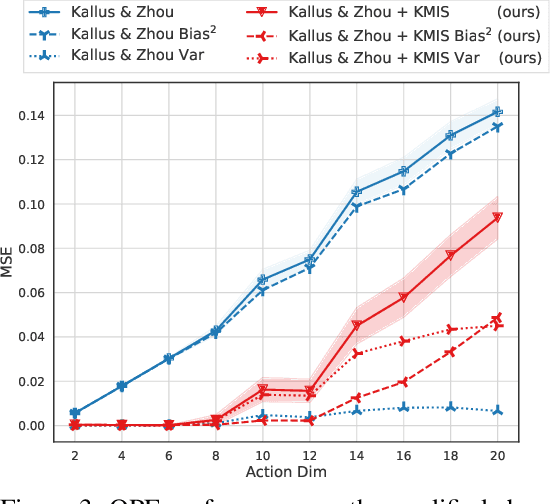
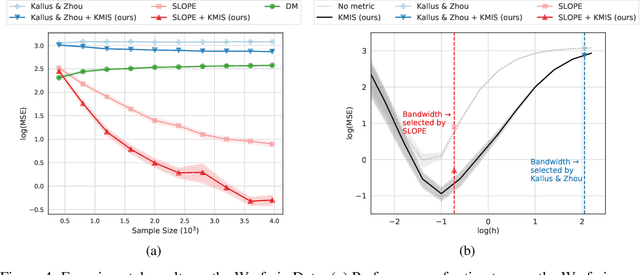
Abstract:We consider local kernel metric learning for off-policy evaluation (OPE) of deterministic policies in contextual bandits with continuous action spaces. Our work is motivated by practical scenarios where the target policy needs to be deterministic due to domain requirements, such as prescription of treatment dosage and duration in medicine. Although importance sampling (IS) provides a basic principle for OPE, it is ill-posed for the deterministic target policy with continuous actions. Our main idea is to relax the target policy and pose the problem as kernel-based estimation, where we learn the kernel metric in order to minimize the overall mean squared error (MSE). We present an analytic solution for the optimal metric, based on the analysis of bias and variance. Whereas prior work has been limited to scalar action spaces or kernel bandwidth selection, our work takes a step further being capable of vector action spaces and metric optimization. We show that our estimator is consistent, and significantly reduces the MSE compared to baseline OPE methods through experiments on various domains.
Adaptive Detrending to Accelerate Convolutional Gated Recurrent Unit Training for Contextual Video Recognition
May 24, 2017



Abstract:Based on the progress of image recognition, video recognition has been extensively studied recently. However, most of the existing methods are focused on short-term but not long-term video recognition, called contextual video recognition. To address contextual video recognition, we use convolutional recurrent neural networks (ConvRNNs) having a rich spatio-temporal information processing capability, but ConvRNNs requires extensive computation that slows down training. In this paper, inspired by the normalization and detrending methods, we propose adaptive detrending (AD) for temporal normalization in order to accelerate the training of ConvRNNs, especially for convolutional gated recurrent unit (ConvGRU). AD removes internal covariate shift within a sequence of each neuron in recurrent neural networks (RNNs) by subtracting a trend. In the experiments for contextual recognition on ConvGRU, the results show that (1) ConvGRU clearly outperforms the feed-forward neural networks, (2) AD consistently offers a significant training acceleration and generalization improvement, and (3) AD is further improved by collaborating with the existing normalization methods.
Recognition of Visually Perceived Compositional Human Actions by Multiple Spatio-Temporal Scales Recurrent Neural Networks
Feb 22, 2017



Abstract:The current paper proposes a novel neural network model for recognizing visually perceived human actions. The proposed multiple spatio-temporal scales recurrent neural network (MSTRNN) model is derived by introducing multiple timescale recurrent dynamics to the conventional convolutional neural network model. One of the essential characteristics of the MSTRNN is that its architecture imposes both spatial and temporal constraints simultaneously on the neural activity which vary in multiple scales among different layers. As suggested by the principle of the upward and downward causation, it is assumed that the network can develop meaningful structures such as functional hierarchy by taking advantage of such constraints during the course of learning. To evaluate the characteristics of the model, the current study uses three types of human action video dataset consisting of different types of primitive actions and different levels of compositionality on them. The performance of the MSTRNN in testing with these dataset is compared with the ones by other representative deep learning models used in the field. The analysis of the internal representation obtained through the learning with the dataset clarifies what sorts of functional hierarchy can be developed by extracting the essential compositionality underlying the dataset.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge