Gyuri Byun
From Prediction to Application: Language Model-based Code Knowledge Tracing with Domain Adaptive Pre-Training and Automatic Feedback System with Pedagogical Prompting for Comprehensive Programming Education
Aug 31, 2024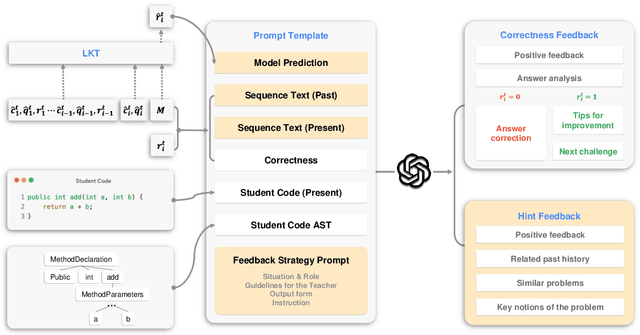
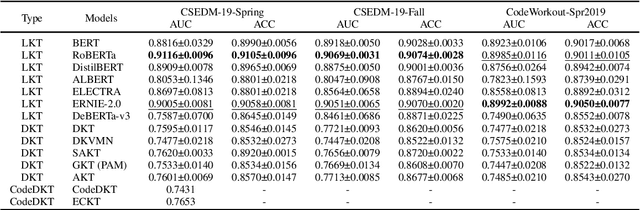
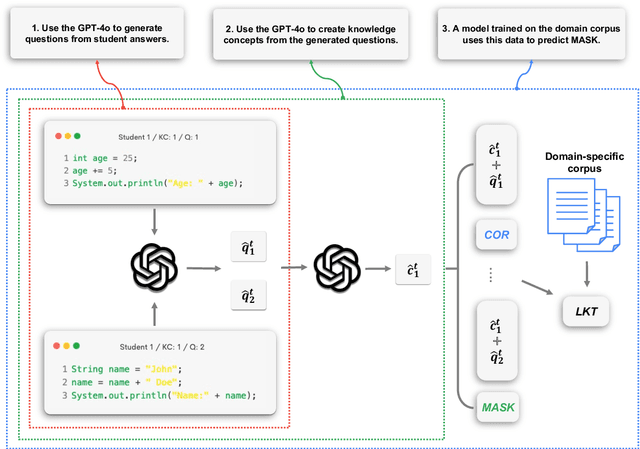
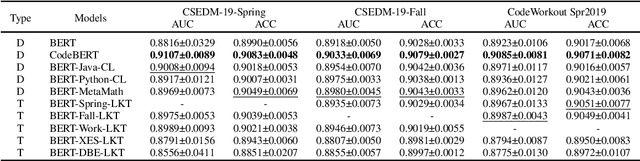
Abstract:Knowledge Tracing (KT) is a critical component in online learning, but traditional approaches face limitations in interpretability and cross-domain adaptability. This paper introduces Language Model-based Code Knowledge Tracing (CodeLKT), an innovative application of Language model-based Knowledge Tracing (LKT) to programming education. CodeLKT leverages pre-trained language models to process learning data, demonstrating superior performance over existing KT and Code KT models. We explore Domain Adaptive Pre-Training (DAPT) and Task Adaptive Pre-Training (TAPT), showing enhanced performance in the coding domain and investigating cross-domain transfer between mathematics and coding. Additionally, we present an theoretically-informed integrated system combining CodeLKT with large language models to generate personalized, in-depth feedback to support students' programming learning. This work advances the field of Code Knowledge Tracing by expanding the knowledge base with language model-based approach and offering practical implications for programming education through data-informed feedback.
LLaVA-Docent: Instruction Tuning with Multimodal Large Language Model to Support Art Appreciation Education
Feb 09, 2024



Abstract:Art appreciation is vital in nurturing critical thinking and emotional intelligence among learners. However, traditional art appreciation education has often been hindered by limited access to art resources, especially for disadvantaged students, and an imbalanced emphasis on STEM subjects in mainstream education. In response to these challenges, recent technological advancements have paved the way for innovative solutions. This study explores the application of multi-modal large language models (MLLMs) in art appreciation education, focusing on developing LLaVA-Docent, a model that leverages these advancements. Our approach involved a comprehensive literature review and consultations with experts in the field, leading to developing a robust data framework. Utilizing this framework, we generated a virtual dialogue dataset that was leveraged by GPT-4. This dataset was instrumental in training the MLLM, named LLaVA-Docent. Six researchers conducted quantitative and qualitative evaluations of LLaVA-Docent to assess its effectiveness, benchmarking it against the GPT-4 model in a few-shot setting. The evaluation process revealed distinct strengths and weaknesses of the LLaVA-Docent model. Our findings highlight the efficacy of LLaVA-Docent in enhancing the accessibility and engagement of art appreciation education. By harnessing the potential of MLLMs, this study makes a significant contribution to the field of art education, proposing a novel methodology that reimagines the way art appreciation is taught and experienced.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge