Guoqing Hao
Separability Membrane: 3D Active Contour for Point Cloud Surface Reconstruction
Mar 07, 2025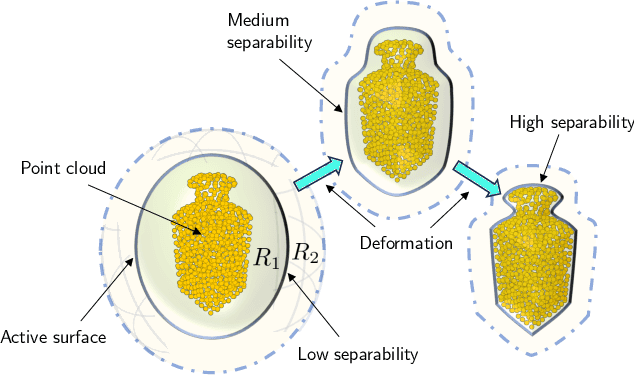
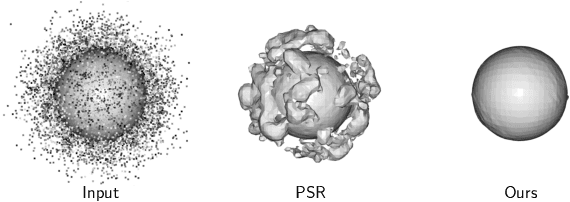
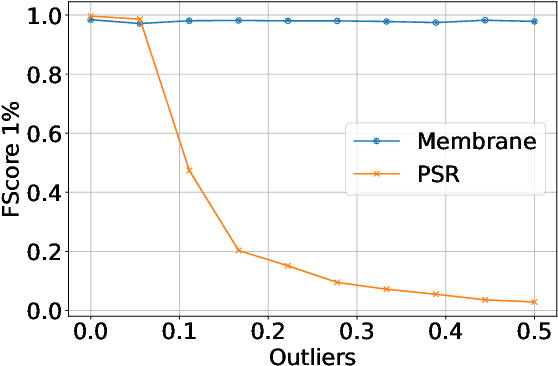
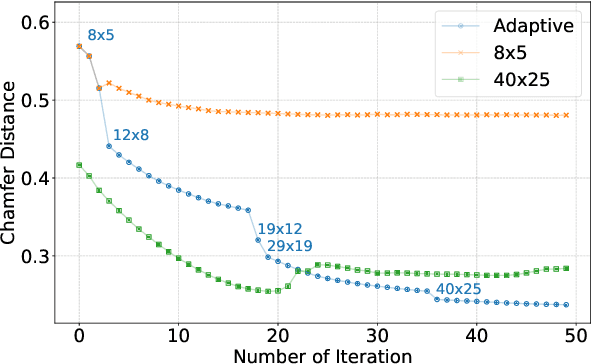
Abstract:This paper proposes Separability Membrane, a robust 3D active contour for extracting a surface from 3D point cloud object. Our approach defines the surface of a 3D object as the boundary that maximizes the separability of point features, such as intensity, color, or local density, between its inner and outer regions based on Fisher's ratio. Separability Membrane identifies the exact surface of a 3D object by maximizing class separability while controlling the rigidity of the 3D surface model with an adaptive B-spline surface that adjusts its properties based on the local and global separability. A key advantage of our method is its ability to accurately reconstruct surface boundaries even when they are ambiguous due to noise or outliers, without requiring any training data or conversion to volumetric representation. Evaluations on a synthetic 3D point cloud dataset and the 3DNet dataset demonstrate the membrane's effectiveness and robustness under diverse conditions.
Diffusion-based Holistic Texture Rectification and Synthesis
Sep 26, 2023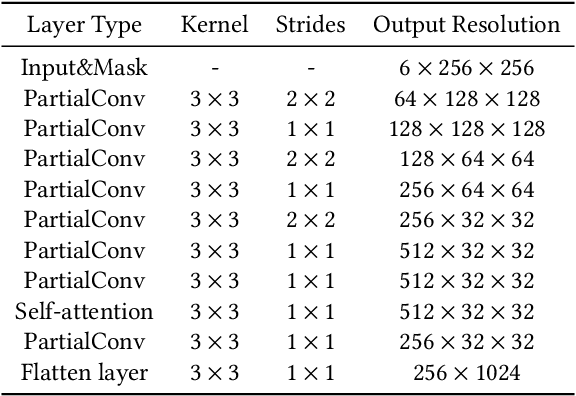
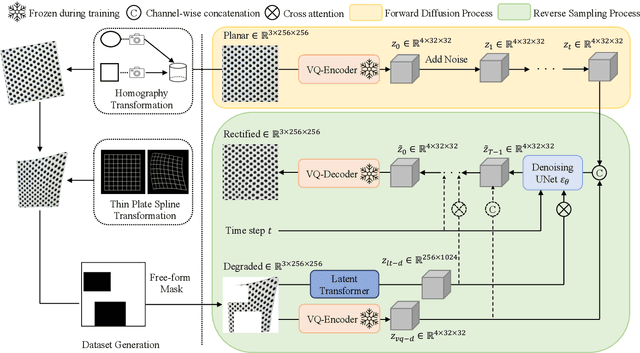
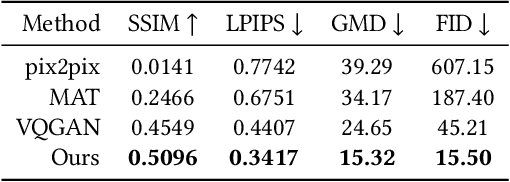
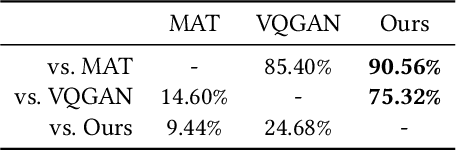
Abstract:We present a novel framework for rectifying occlusions and distortions in degraded texture samples from natural images. Traditional texture synthesis approaches focus on generating textures from pristine samples, which necessitate meticulous preparation by humans and are often unattainable in most natural images. These challenges stem from the frequent occlusions and distortions of texture samples in natural images due to obstructions and variations in object surface geometry. To address these issues, we propose a framework that synthesizes holistic textures from degraded samples in natural images, extending the applicability of exemplar-based texture synthesis techniques. Our framework utilizes a conditional Latent Diffusion Model (LDM) with a novel occlusion-aware latent transformer. This latent transformer not only effectively encodes texture features from partially-observed samples necessary for the generation process of the LDM, but also explicitly captures long-range dependencies in samples with large occlusions. To train our model, we introduce a method for generating synthetic data by applying geometric transformations and free-form mask generation to clean textures. Experimental results demonstrate that our framework significantly outperforms existing methods both quantitatively and quantitatively. Furthermore, we conduct comprehensive ablation studies to validate the different components of our proposed framework. Results are corroborated by a perceptual user study which highlights the efficiency of our proposed approach.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge