Guolong Chen
An Intelligent CNN-VAE Text Representation Technology Based on Text Semantics for Comprehensive Big Data
Aug 28, 2020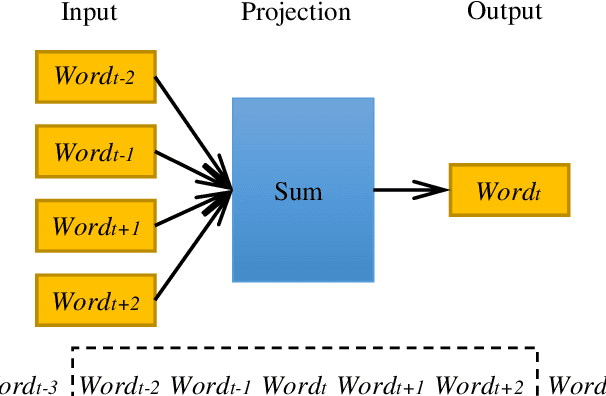
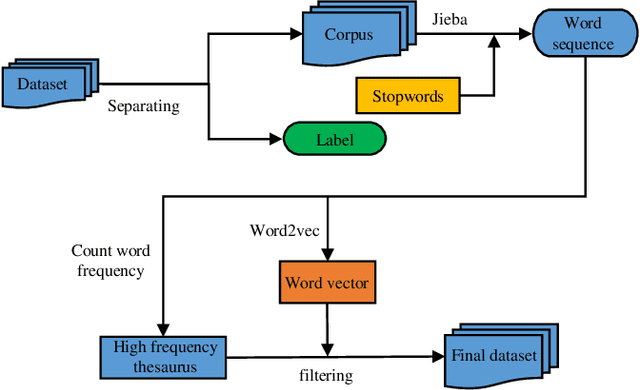
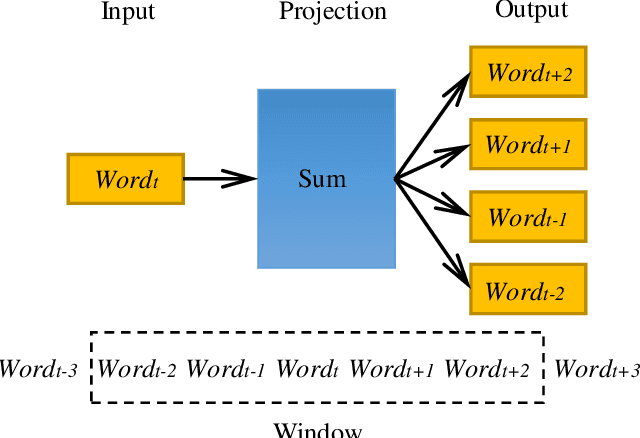
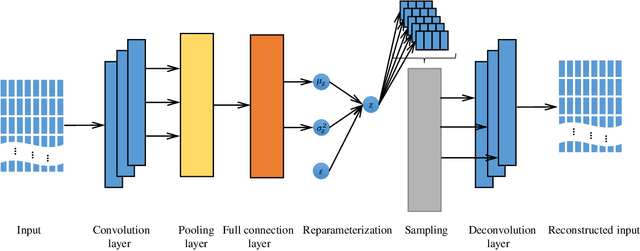
Abstract:In the era of big data, a large number of text data generated by the Internet has given birth to a variety of text representation methods. In natural language processing (NLP), text representation transforms text into vectors that can be processed by computer without losing the original semantic information. However, these methods are difficult to effectively extract the semantic features among words and distinguish polysemy in language. Therefore, a text feature representation model based on convolutional neural network (CNN) and variational autoencoder (VAE) is proposed to extract the text features and apply the obtained text feature representation on the text classification tasks. CNN is used to extract the features of text vector to get the semantics among words and VAE is introduced to make the text feature space more consistent with Gaussian distribution. In addition, the output of the improved word2vec model is employed as the input of the proposed model to distinguish different meanings of the same word in different contexts. The experimental results show that the proposed model outperforms in k-nearest neighbor (KNN), random forest (RF) and support vector machine (SVM) classification algorithms.
A novel particle swarm optimizer with multi-stage transformation and genetic operation for VLSI routing
Nov 26, 2018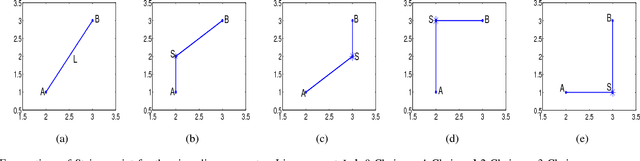
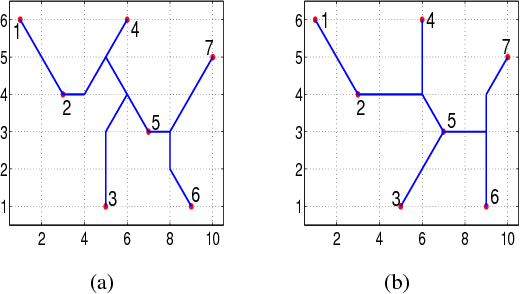
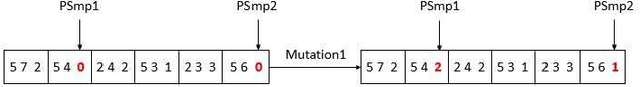
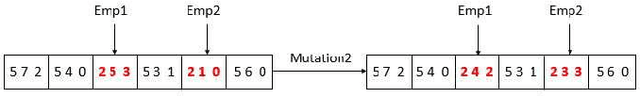
Abstract:As the basic model for very large scale integration (VLSI) routing, the Steiner minimal tree (SMT) can be used in various practical problems, such as wire length optimization, congestion, and time delay estimation. In this paper, a novel particle swarm optimization (PSO) algorithm based on multi-stage transformation and genetic operation is presented to construct two types of SMT, including non-Manhattan SMT and Manhattan SMT. Firstly, in order to be able to handle two types of SMT problems at the same time, an effective edge-vertex encoding strategy is proposed. Secondly, a multi-stage transformation strategy is proposed to both expand the algorithm search space and ensure the effective convergence. We have tested three types from two to four stages and various combinations under each type to highlight the best combination. Thirdly, the genetic operators combined with union-find partition are designed to construct the discrete particle update formula for discrete VLSI routing. Moreover, in order to introduce uncertainty and diversity into the search of PSO algorithm, we propose an improved mutation operation with edge transformation. Experimental results show that our algorithm from a global perspective of multilayer structure can achieve the best solution quality among the existing algorithms. Finally, to our best knowledge, it is the first work to address both manhattan and non-manhattan routing at the same time.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge