Gunnar Brehm
Automated Visual Monitoring of Nocturnal Insects with Light-based Camera Traps
Jul 28, 2023Abstract:Automatic camera-assisted monitoring of insects for abundance estimations is crucial to understand and counteract ongoing insect decline. In this paper, we present two datasets of nocturnal insects, especially moths as a subset of Lepidoptera, photographed in Central Europe. One of the datasets, the EU-Moths dataset, was captured manually by citizen scientists and contains species annotations for 200 different species and bounding box annotations for those. We used this dataset to develop and evaluate a two-stage pipeline for insect detection and moth species classification in previous work. We further introduce a prototype for an automated visual monitoring system. This prototype produced the second dataset consisting of more than 27,000 images captured on 95 nights. For evaluation and bootstrapping purposes, we annotated a subset of the images with bounding boxes enframing nocturnal insects. Finally, we present first detection and classification baselines for these datasets and encourage other scientists to use this publicly available data.
Fine-grained Recognition Datasets for Biodiversity Analysis
Jul 03, 2015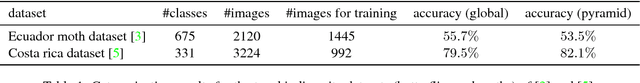


Abstract:In the following paper, we present and discuss challenging applications for fine-grained visual classification (FGVC): biodiversity and species analysis. We not only give details about two challenging new datasets suitable for computer vision research with up to 675 highly similar classes, but also present first results with localized features using convolutional neural networks (CNN). We conclude with a list of challenging new research directions in the area of visual classification for biodiversity research.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge