Gulsen Taskin
Explainable AI for Earth Observation: Current Methods, Open Challenges, and Opportunities
Nov 08, 2023Abstract:Deep learning has taken by storm all fields involved in data analysis, including remote sensing for Earth observation. However, despite significant advances in terms of performance, its lack of explainability and interpretability, inherent to neural networks in general since their inception, remains a major source of criticism. Hence it comes as no surprise that the expansion of deep learning methods in remote sensing is being accompanied by increasingly intensive efforts oriented towards addressing this drawback through the exploration of a wide spectrum of Explainable Artificial Intelligence techniques. This chapter, organized according to prominent Earth observation application fields, presents a panorama of the state-of-the-art in explainable remote sensing image analysis.
There Are No Data Like More Data- Datasets for Deep Learning in Earth Observation
Oct 30, 2023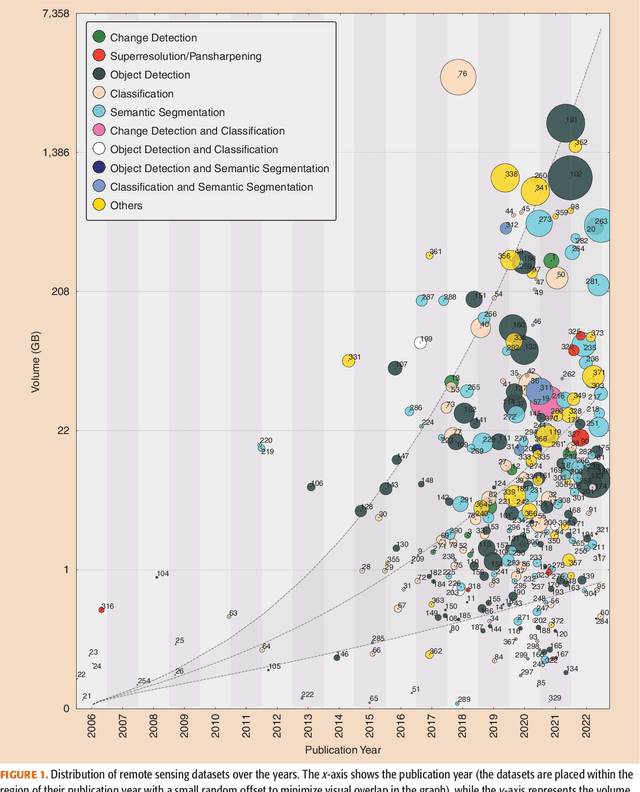

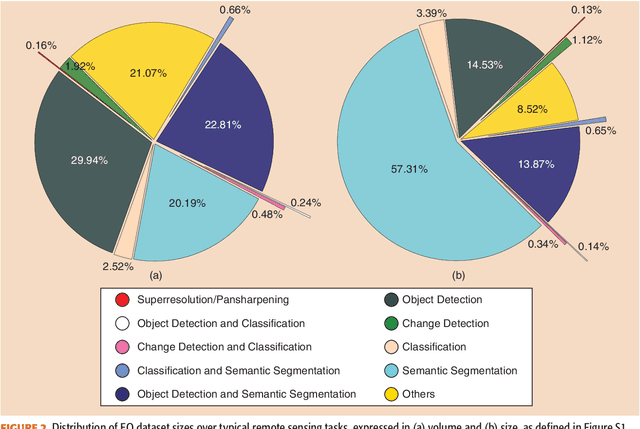
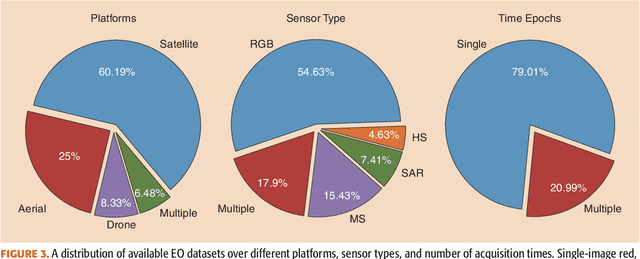
Abstract:Carefully curated and annotated datasets are the foundation of machine learning, with particularly data-hungry deep neural networks forming the core of what is often called Artificial Intelligence (AI). Due to the massive success of deep learning applied to Earth Observation (EO) problems, the focus of the community has been largely on the development of ever-more sophisticated deep neural network architectures and training strategies largely ignoring the overall importance of datasets. For that purpose, numerous task-specific datasets have been created that were largely ignored by previously published review articles on AI for Earth observation. With this article, we want to change the perspective and put machine learning datasets dedicated to Earth observation data and applications into the spotlight. Based on a review of the historical developments, currently available resources are described and a perspective for future developments is formed. We hope to contribute to an understanding that the nature of our data is what distinguishes the Earth observation community from many other communities that apply deep learning techniques to image data, and that a detailed understanding of EO data peculiarities is among the core competencies of our discipline.
Graph Embedding via High Dimensional Model Representation for Hyperspectral Images
Nov 29, 2021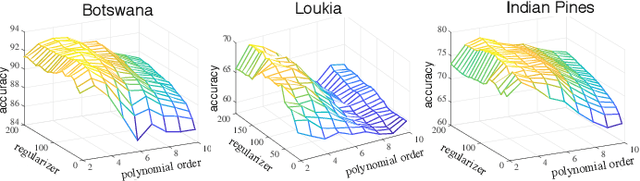
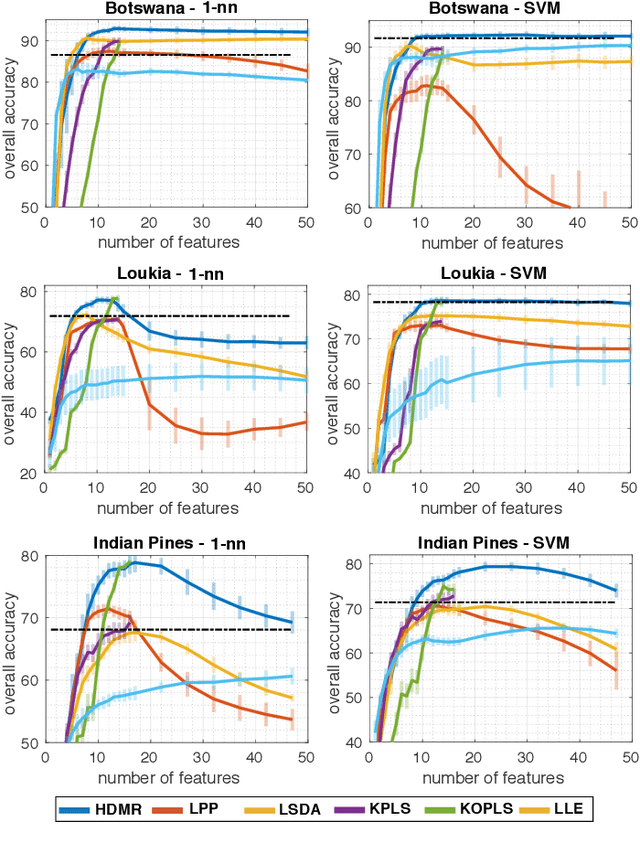
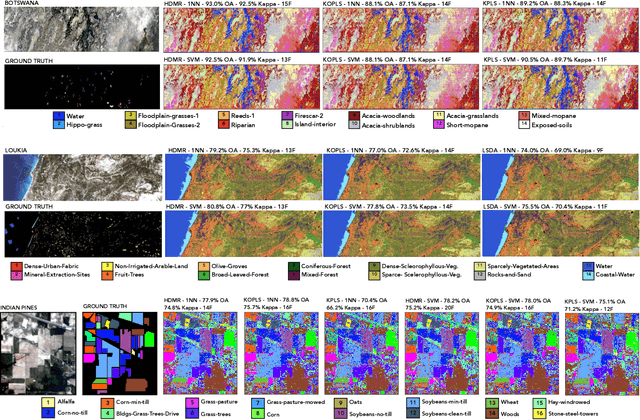
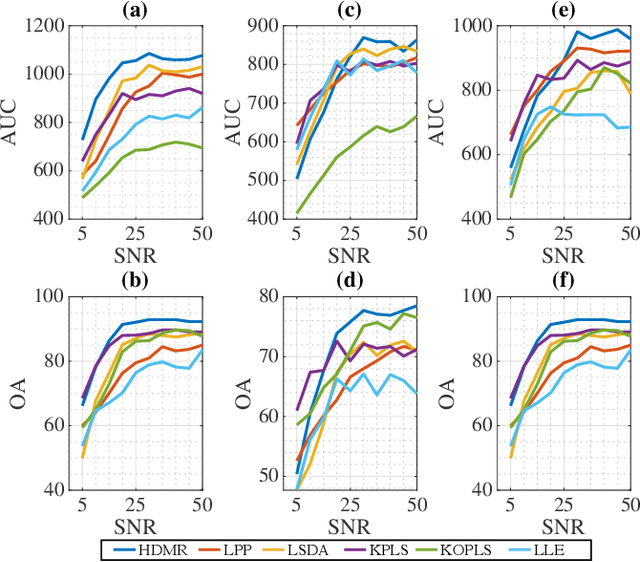
Abstract:Learning the manifold structure of remote sensing images is of paramount relevance for modeling and understanding processes, as well as to encapsulate the high dimensionality in a reduced set of informative features for subsequent classification, regression, or unmixing. Manifold learning methods have shown excellent performance to deal with hyperspectral image (HSI) analysis but, unless specifically designed, they cannot provide an explicit embedding map readily applicable to out-of-sample data. A common assumption to deal with the problem is that the transformation between the high-dimensional input space and the (typically low) latent space is linear. This is a particularly strong assumption, especially when dealing with hyperspectral images due to the well-known nonlinear nature of the data. To address this problem, a manifold learning method based on High Dimensional Model Representation (HDMR) is proposed, which enables to present a nonlinear embedding function to project out-of-sample samples into the latent space. The proposed method is compared to manifold learning methods along with its linear counterparts and achieves promising performance in terms of classification accuracy of a representative set of hyperspectral images.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge