Guillaume Metzler
Fair-GPTQ: Bias-Aware Quantization for Large Language Models
Sep 18, 2025Abstract:High memory demands of generative language models have drawn attention to quantization, which reduces computational cost, memory usage, and latency by mapping model weights to lower-precision integers. Approaches such as GPTQ effectively minimize input-weight product errors during quantization; however, recent empirical studies show that they can increase biased outputs and degrade performance on fairness benchmarks, and it remains unclear which specific weights cause this issue. In this work, we draw new links between quantization and model fairness by adding explicit group-fairness constraints to the quantization objective and introduce Fair-GPTQ, the first quantization method explicitly designed to reduce unfairness in large language models. The added constraints guide the learning of the rounding operation toward less-biased text generation for protected groups. Specifically, we focus on stereotype generation involving occupational bias and discriminatory language spanning gender, race, and religion. Fair-GPTQ has minimal impact on performance, preserving at least 90% of baseline accuracy on zero-shot benchmarks, reduces unfairness relative to a half-precision model, and retains the memory and speed benefits of 4-bit quantization. We also compare the performance of Fair-GPTQ with existing debiasing methods and find that it achieves performance on par with the iterative null-space projection debiasing approach on racial-stereotype benchmarks. Overall, the results validate our theoretical solution to the quantization problem with a group-bias term, highlight its applicability for reducing group bias at quantization time in generative models, and demonstrate that our approach can further be used to analyze channel- and weight-level contributions to fairness during quantization.
Histoires Morales: A French Dataset for Assessing Moral Alignment
Jan 28, 2025Abstract:Aligning language models with human values is crucial, especially as they become more integrated into everyday life. While models are often adapted to user preferences, it is equally important to ensure they align with moral norms and behaviours in real-world social situations. Despite significant progress in languages like English and Chinese, French has seen little attention in this area, leaving a gap in understanding how LLMs handle moral reasoning in this language. To address this gap, we introduce Histoires Morales, a French dataset derived from Moral Stories, created through translation and subsequently refined with the assistance of native speakers to guarantee grammatical accuracy and adaptation to the French cultural context. We also rely on annotations of the moral values within the dataset to ensure their alignment with French norms. Histoires Morales covers a wide range of social situations, including differences in tipping practices, expressions of honesty in relationships, and responsibilities toward animals. To foster future research, we also conduct preliminary experiments on the alignment of multilingual models on French and English data and the robustness of the alignment. We find that while LLMs are generally aligned with human moral norms by default, they can be easily influenced with user-preference optimization for both moral and immoral data.
When Quantization Affects Confidence of Large Language Models?
May 01, 2024Abstract:Recent studies introduced effective compression techniques for Large Language Models (LLMs) via post-training quantization or low-bit weight representation. Although quantized weights offer storage efficiency and allow for faster inference, existing works have indicated that quantization might compromise performance and exacerbate biases in LLMs. This study investigates the confidence and calibration of quantized models, considering factors such as language model type and scale as contributors to quantization loss. Firstly, we reveal that quantization with GPTQ to 4-bit results in a decrease in confidence regarding true labels, with varying impacts observed among different language models. Secondly, we observe fluctuations in the impact on confidence across different scales. Finally, we propose an explanation for quantization loss based on confidence levels, indicating that quantization disproportionately affects samples where the full model exhibited low confidence levels in the first place.
Mini Minds: Exploring Bebeshka and Zlata Baby Models
Nov 06, 2023
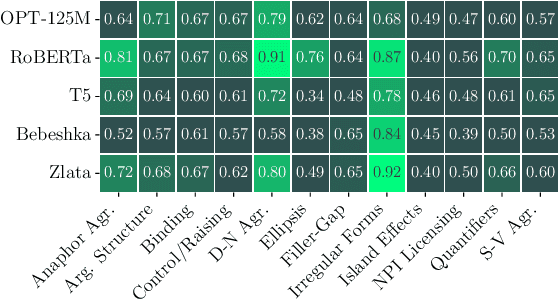


Abstract:In this paper, we describe the University of Lyon 2 submission to the Strict-Small track of the BabyLM competition. The shared task is created with an emphasis on small-scale language modelling from scratch on limited-size data and human language acquisition. Dataset released for the Strict-Small track has 10M words, which is comparable to children's vocabulary size. We approach the task with an architecture search, minimizing masked language modelling loss on the data of the shared task. Having found an optimal configuration, we introduce two small-size language models (LMs) that were submitted for evaluation, a 4-layer encoder with 8 attention heads and a 6-layer decoder model with 12 heads which we term Bebeshka and Zlata, respectively. Despite being half the scale of the baseline LMs, our proposed models achieve comparable performance. We further explore the applicability of small-scale language models in tasks involving moral judgment, aligning their predictions with human values. These findings highlight the potential of compact LMs in addressing practical language understanding tasks.
An Adjusted Nearest Neighbor Algorithm Maximizing the F-Measure from Imbalanced Data
Sep 02, 2019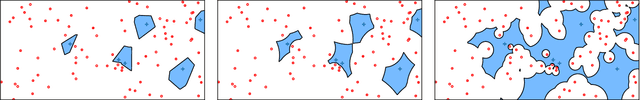
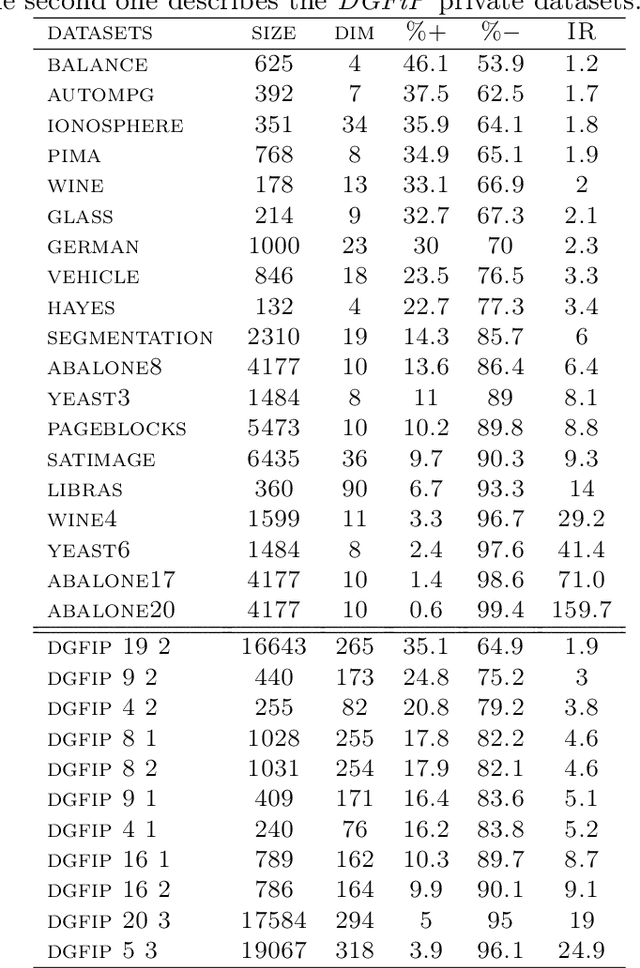
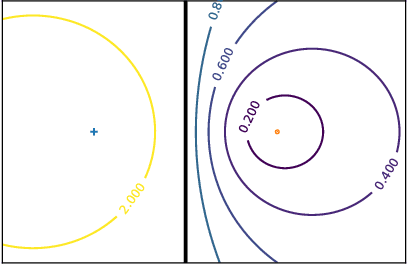
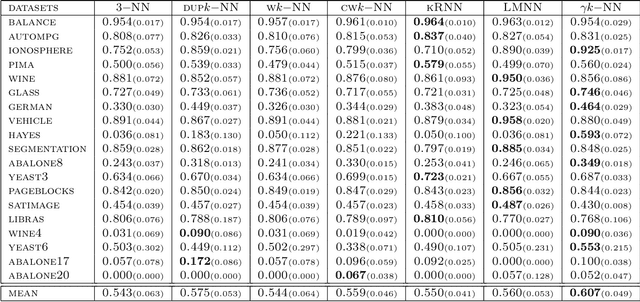
Abstract:In this paper, we address the challenging problem of learning from imbalanced data using a Nearest-Neighbor (NN) algorithm. In this setting, the minority examples typically belong to the class of interest requiring the optimization of specific criteria, like the F-Measure. Based on simple geometrical ideas, we introduce an algorithm that reweights the distance between a query sample and any positive training example. This leads to a modification of the Voronoi regions and thus of the decision boundaries of the NN algorithm. We provide a theoretical justification about the weighting scheme needed to reduce the False Negative rate while controlling the number of False Positives. We perform an extensive experimental study on many public imbalanced datasets, but also on large scale non public data from the French Ministry of Economy and Finance on a tax fraud detection task, showing that our method is very effective and, interestingly, yields the best performance when combined with state of the art sampling methods.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge