Guillaume Ausset
Individual Survival Curves with Conditional Normalizing Flows
Jul 27, 2021
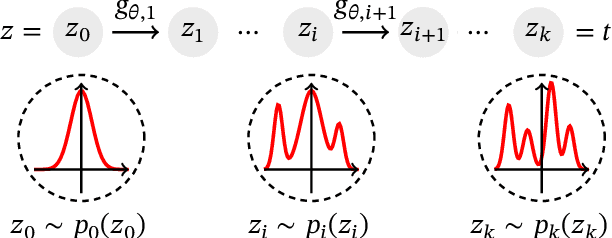
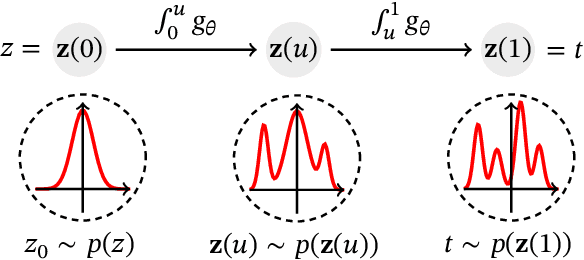

Abstract:Survival analysis, or time-to-event modelling, is a classical statistical problem that has garnered a lot of interest for its practical use in epidemiology, demographics or actuarial sciences. Recent advances on the subject from the point of view of machine learning have been concerned with precise per-individual predictions instead of population studies, driven by the rise of individualized medicine. We introduce here a conditional normalizing flow based estimate of the time-to-event density as a way to model highly flexible and individualized conditional survival distributions. We use a novel hierarchical formulation of normalizing flows to enable efficient fitting of flexible conditional distributions without overfitting and show how the normalizing flow formulation can be efficiently adapted to the censored setting. We experimentally validate the proposed approach on a synthetic dataset as well as four open medical datasets and an example of a common financial problem.
Nearest Neighbour Based Estimates of Gradients: Sharp Nonasymptotic Bounds and Applications
Jun 26, 2020
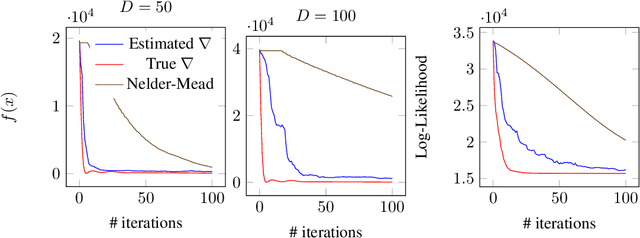
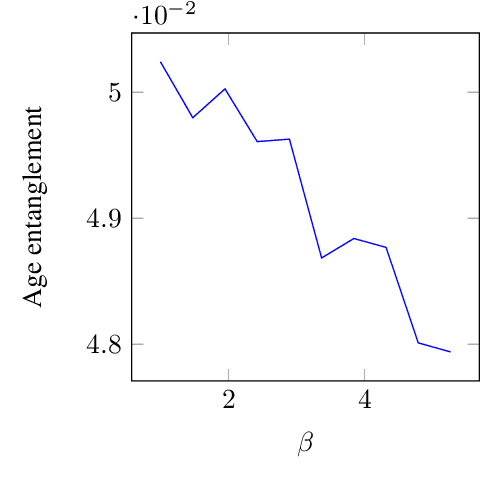
Abstract:Motivated by a wide variety of applications, ranging from stochastic optimization to dimension reduction through variable selection, the problem of estimating gradients accurately is of crucial importance in statistics and learning theory. We consider here the classic regression setup, where a real valued square integrable r.v. $Y$ is to be predicted upon observing a (possibly high dimensional) random vector $X$ by means of a predictive function $f(X)$ as accurately as possible in the mean-squared sense and study a nearest-neighbour-based pointwise estimate of the gradient of the optimal predictive function, the regression function $m(x)=\mathbb{E}[Y\mid X=x]$. Under classic smoothness conditions combined with the assumption that the tails of $Y-m(X)$ are sub-Gaussian, we prove nonasymptotic bounds improving upon those obtained for alternative estimation methods. Beyond the novel theoretical results established, several illustrative numerical experiments have been carried out. The latter provide strong empirical evidence that the estimation method proposed works very well for various statistical problems involving gradient estimation, namely dimensionality reduction, stochastic gradient descent optimization and quantifying disentanglement.
Empirical Risk Minimization under Random Censorship: Theory and Practice
Jun 05, 2019



Abstract:We consider the classic supervised learning problem, where a continuous non-negative random label $Y$ (i.e. a random duration) is to be predicted based upon observing a random vector $X$ valued in $\mathbb{R}^d$ with $d\geq 1$ by means of a regression rule with minimum least square error. In various applications, ranging from industrial quality control to public health through credit risk analysis for instance, training observations can be right censored, meaning that, rather than on independent copies of $(X,Y)$, statistical learning relies on a collection of $n\geq 1$ independent realizations of the triplet $(X, \; \min\{Y,\; C\},\; \delta)$, where $C$ is a nonnegative r.v. with unknown distribution, modeling censorship and $\delta=\mathbb{I}\{Y\leq C\}$ indicates whether the duration is right censored or not. As ignoring censorship in the risk computation may clearly lead to a severe underestimation of the target duration and jeopardize prediction, we propose to consider a plug-in estimate of the true risk based on a Kaplan-Meier estimator of the conditional survival function of the censorship $C$ given $X$, referred to as Kaplan-Meier risk, in order to perform empirical risk minimization. It is established, under mild conditions, that the learning rate of minimizers of this biased/weighted empirical risk functional is of order $O_{\mathbb{P}}(\sqrt{\log(n)/n})$ when ignoring model bias issues inherent to plug-in estimation, as can be attained in absence of censorship. Beyond theoretical results, numerical experiments are presented in order to illustrate the relevance of the approach developed.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge