Guanyao Li
A Multi-Scale Decomposition MLP-Mixer for Time Series Analysis
Oct 18, 2023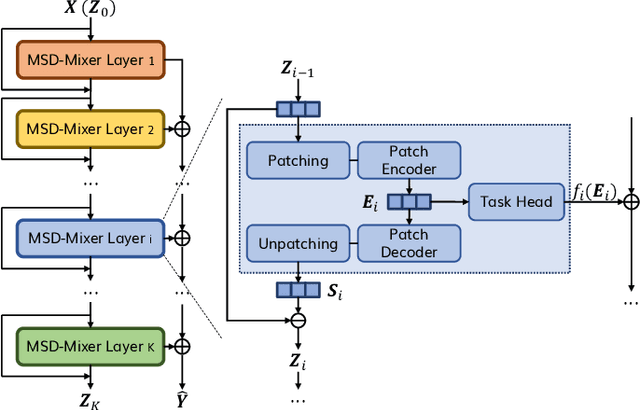
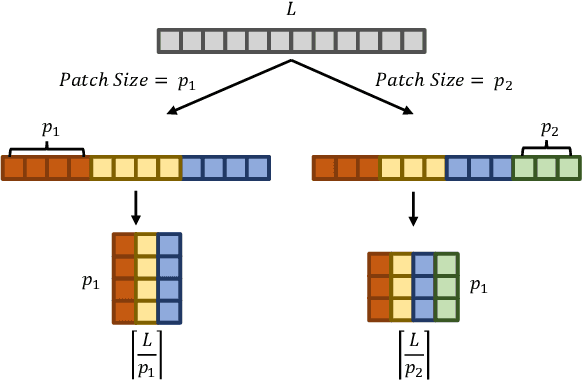
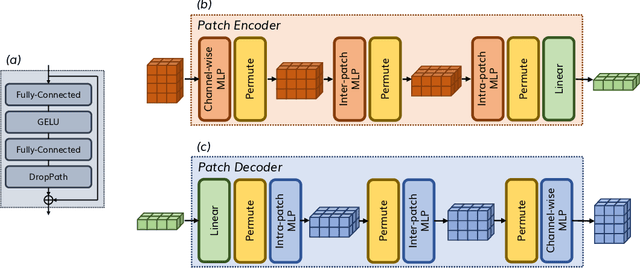
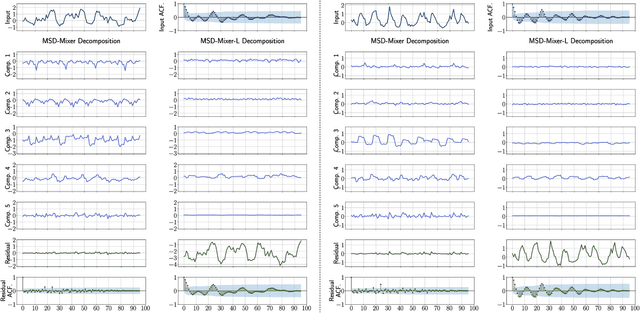
Abstract:Time series data, often characterized by unique composition and complex multi-scale temporal variations, requires special consideration of decomposition and multi-scale modeling in its analysis. Existing deep learning methods on this best fit to only univariate time series, and have not sufficiently accounted for sub-series level modeling and decomposition completeness. To address this, we propose MSD-Mixer, a Multi-Scale Decomposition MLP-Mixer which learns to explicitly decompose the input time series into different components, and represents the components in different layers. To handle multi-scale temporal patterns and inter-channel dependencies, we propose a novel temporal patching approach to model the time series as multi-scale sub-series, i.e., patches, and employ MLPs to mix intra- and inter-patch variations and channel-wise correlations. In addition, we propose a loss function to constrain both the magnitude and autocorrelation of the decomposition residual for decomposition completeness. Through extensive experiments on various real-world datasets for five common time series analysis tasks (long- and short-term forecasting, imputation, anomaly detection, and classification), we demonstrate that MSD-Mixer consistently achieves significantly better performance in comparison with other state-of-the-art task-general and task-specific approaches.
A Lightweight and Accurate Spatial-Temporal Transformer for Traffic Forecasting
Jan 04, 2022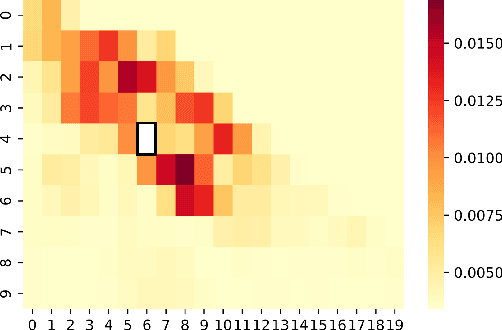
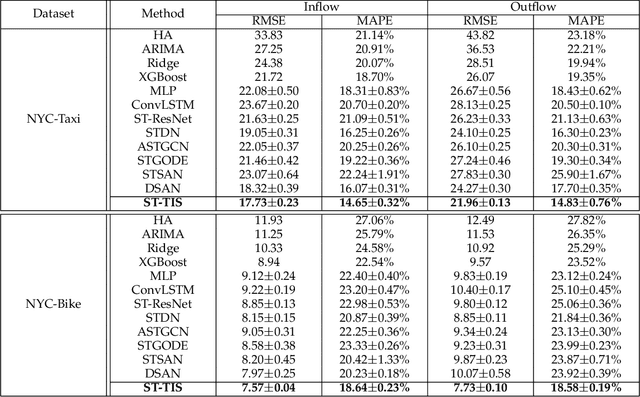
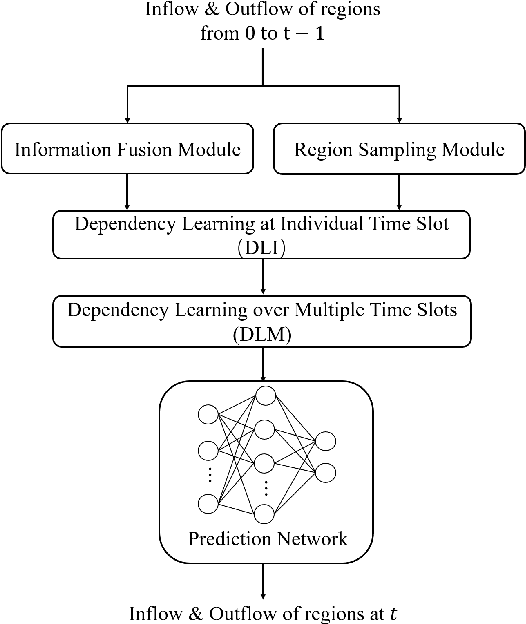
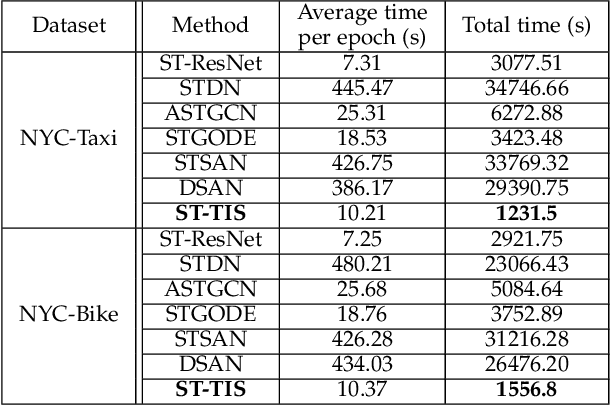
Abstract:We study the forecasting problem for traffic with dynamic, possibly periodical, and joint spatial-temporal dependency between regions. Given the aggregated inflow and outflow traffic of regions in a city from time slots 0 to t-1, we predict the traffic at time t at any region. Prior arts in the area often consider the spatial and temporal dependencies in a decoupled manner or are rather computationally intensive in training with a large number of hyper-parameters to tune. We propose ST-TIS, a novel, lightweight, and accurate Spatial-Temporal Transformer with information fusion and region sampling for traffic forecasting. ST-TIS extends the canonical Transformer with information fusion and region sampling. The information fusion module captures the complex spatial-temporal dependency between regions. The region sampling module is to improve the efficiency and prediction accuracy, cutting the computation complexity for dependency learning from $O(n^2)$ to $O(n\sqrt{n})$, where n is the number of regions. With far fewer parameters than state-of-the-art models, the offline training of our model is significantly faster in terms of tuning and computation (with a reduction of up to $90\%$ on training time and network parameters). Notwithstanding such training efficiency, extensive experiments show that ST-TIS is substantially more accurate in online prediction than state-of-the-art approaches (with an average improvement of up to $9.5\%$ on RMSE, and $12.4\%$ on MAPE).
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge