Grzegorz Czechmanowski
Beyond Constant Parameters: Hyper Prediction Models and HyperMPC
Aug 08, 2025Abstract:Model Predictive Control (MPC) is among the most widely adopted and reliable methods for robot control, relying critically on an accurate dynamics model. However, existing dynamics models used in the gradient-based MPC are limited by computational complexity and state representation. To address this limitation, we propose the Hyper Prediction Model (HyperPM) - a novel approach in which we project the unmodeled dynamics onto a time-dependent dynamics model. This time-dependency is captured through time-varying model parameters, whose evolution over the MPC prediction horizon is learned using a neural network. Such formulation preserves the computational efficiency and robustness of the base model while equipping it with the capacity to anticipate previously unmodeled phenomena. We evaluated the proposed approach on several challenging systems, including real-world F1TENTH autonomous racing, and demonstrated that it significantly reduces long-horizon prediction errors. Moreover, when integrated within the MPC framework (HyperMPC), our method consistently outperforms existing state-of-the-art techniques.
On learning racing policies with reinforcement learning
Apr 03, 2025Abstract:Fully autonomous vehicles promise enhanced safety and efficiency. However, ensuring reliable operation in challenging corner cases requires control algorithms capable of performing at the vehicle limits. We address this requirement by considering the task of autonomous racing and propose solving it by learning a racing policy using Reinforcement Learning (RL). Our approach leverages domain randomization, actuator dynamics modeling, and policy architecture design to enable reliable and safe zero-shot deployment on a real platform. Evaluated on the F1TENTH race car, our RL policy not only surpasses a state-of-the-art Model Predictive Control (MPC), but, to the best of our knowledge, also represents the first instance of an RL policy outperforming expert human drivers in RC racing. This work identifies the key factors driving this performance improvement, providing critical insights for the design of robust RL-based control strategies for autonomous vehicles.
One Policy to Run Them All: an End-to-end Learning Approach to Multi-Embodiment Locomotion
Sep 10, 2024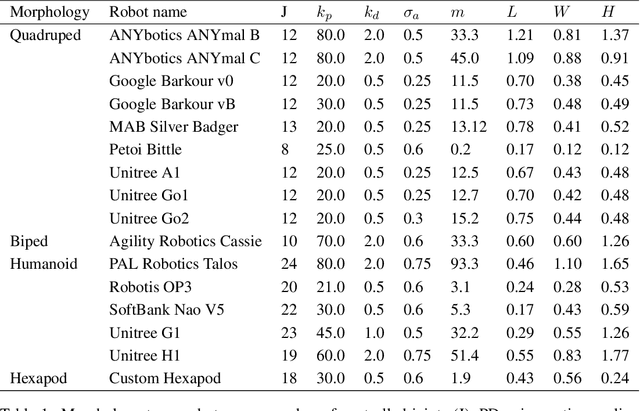
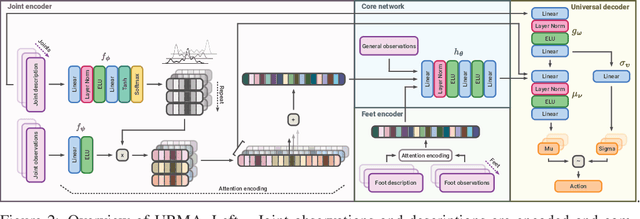
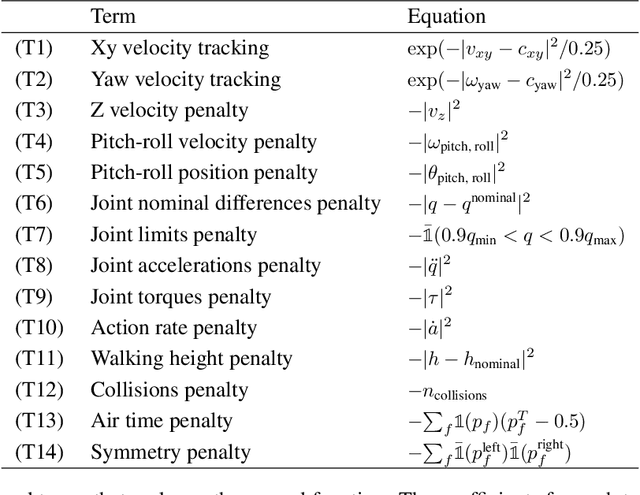
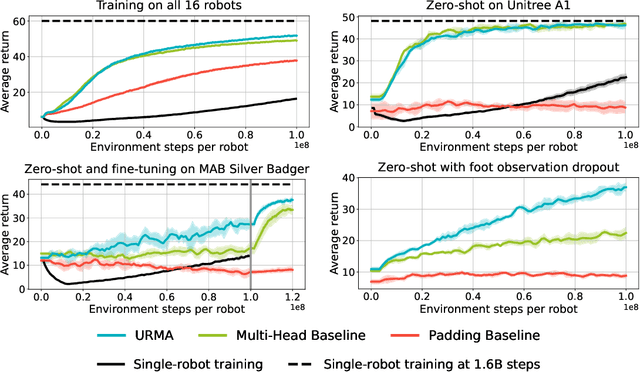
Abstract:Deep Reinforcement Learning techniques are achieving state-of-the-art results in robust legged locomotion. While there exists a wide variety of legged platforms such as quadruped, humanoids, and hexapods, the field is still missing a single learning framework that can control all these different embodiments easily and effectively and possibly transfer, zero or few-shot, to unseen robot embodiments. We introduce URMA, the Unified Robot Morphology Architecture, to close this gap. Our framework brings the end-to-end Multi-Task Reinforcement Learning approach to the realm of legged robots, enabling the learned policy to control any type of robot morphology. The key idea of our method is to allow the network to learn an abstract locomotion controller that can be seamlessly shared between embodiments thanks to our morphology-agnostic encoders and decoders. This flexible architecture can be seen as a potential first step in building a foundation model for legged robot locomotion. Our experiments show that URMA can learn a locomotion policy on multiple embodiments that can be easily transferred to unseen robot platforms in simulation and the real world.
Learning dynamics models for velocity estimation in autonomous racing
Aug 28, 2024
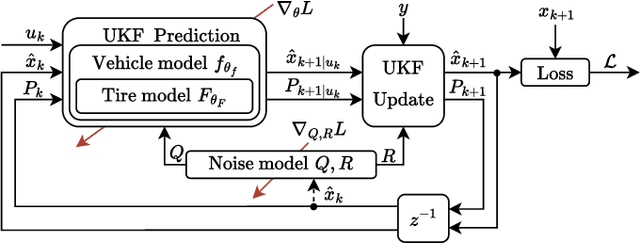
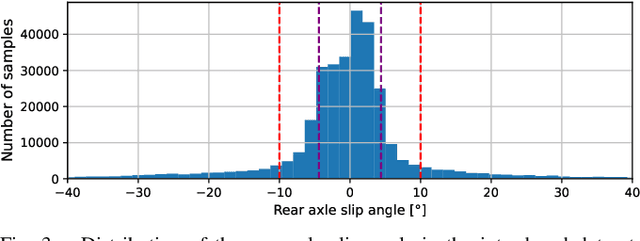
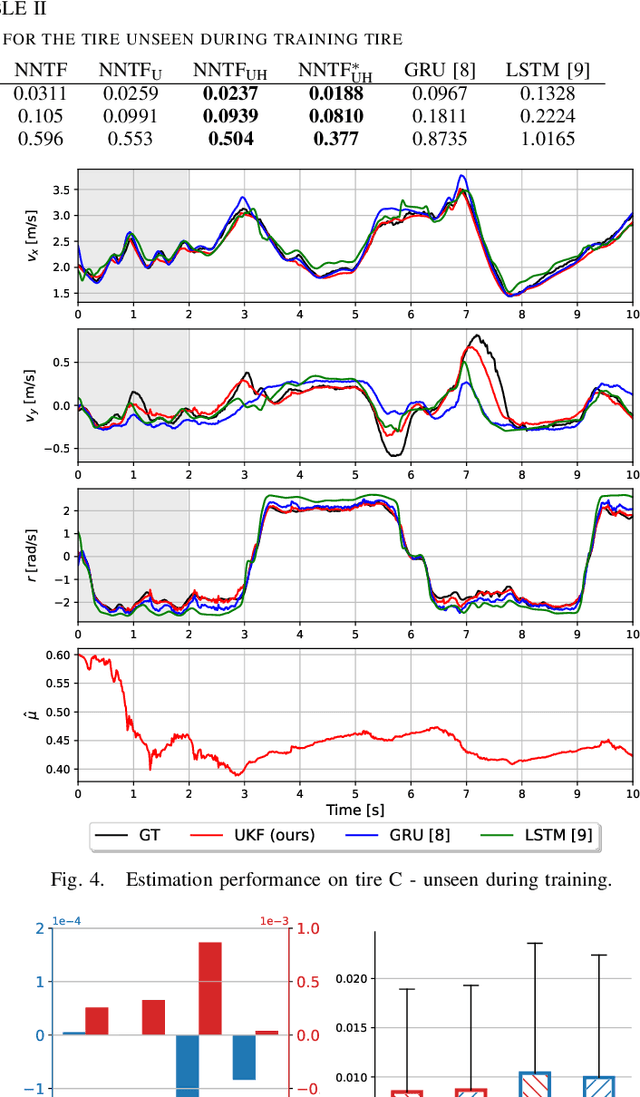
Abstract:Velocity estimation is of great importance in autonomous racing. Still, existing solutions are characterized by limited accuracy, especially in the case of aggressive driving or poor generalization to unseen road conditions. To address these issues, we propose to utilize Unscented Kalman Filter (UKF) with a learned dynamics model that is optimized directly for the state estimation task. Moreover, we propose to aid this model with the online-estimated friction coefficient, which increases the estimation accuracy and enables zero-shot adaptation to the new road conditions. To evaluate the UKF-based velocity estimator with the proposed dynamics model, we introduced a publicly available dataset of aggressive manoeuvres performed by an F1TENTH car, with sideslip angles reaching 40{\deg}. Using this dataset, we show that learning the dynamics model through UKF leads to improved estimation performance and that the proposed solution outperforms state-of-the-art learning-based state estimators by 17% in the nominal scenario. Moreover, we present unseen zero-shot adaptation abilities of the proposed method to the new road surface thanks to the use of the proposed learning-based tire dynamics model with online friction estimation.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge