Grégoire Dhimoïla
Ho Wan
Cross-Modal Redundancy and the Geometry of Vision-Language Embeddings
Feb 05, 2026Abstract:Vision-language models (VLMs) align images and text with remarkable success, yet the geometry of their shared embedding space remains poorly understood. To probe this geometry, we begin from the Iso-Energy Assumption, which exploits cross-modal redundancy: a concept that is truly shared should exhibit the same average energy across modalities. We operationalize this assumption with an Aligned Sparse Autoencoder (SAE) that encourages energy consistency during training while preserving reconstruction. We find that this inductive bias changes the SAE solution without harming reconstruction, giving us a representation that serves as a tool for geometric analysis. Sanity checks on controlled data with known ground truth confirm that alignment improves when Iso-Energy holds and remains neutral when it does not. Applied to foundational VLMs, our framework reveals a clear structure with practical consequences: (i) sparse bimodal atoms carry the entire cross-modal alignment signal; (ii) unimodal atoms act as modality-specific biases and fully explain the modality gap; (iii) removing unimodal atoms collapses the gap without harming performance; (iv) restricting vector arithmetic to the bimodal subspace yields in-distribution edits and improved retrieval. These findings suggest that the right inductive bias can both preserve model fidelity and render the latent geometry interpretable and actionable.
Cluster-norm for Unsupervised Probing of Knowledge
Jul 26, 2024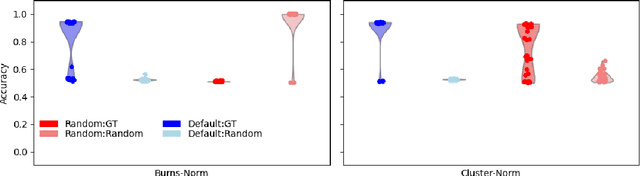

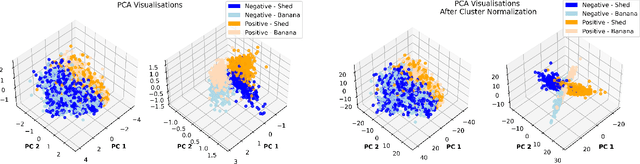

Abstract:The deployment of language models brings challenges in generating reliable information, especially when these models are fine-tuned using human preferences. To extract encoded knowledge without (potentially) biased human labels, unsupervised probing techniques like Contrast-Consistent Search (CCS) have been developed (Burns et al., 2022). However, salient but unrelated features in a given dataset can mislead these probes (Farquhar et al., 2023). Addressing this, we propose a cluster normalization method to minimize the impact of such features by clustering and normalizing activations of contrast pairs before applying unsupervised probing techniques. While this approach does not address the issue of differentiating between knowledge in general and simulated knowledge - a major issue in the literature of latent knowledge elicitation (Christiano et al., 2021) - it significantly improves the ability of unsupervised probes to identify the intended knowledge amidst distractions.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge