Gouthaman KV
Towards Mitigating Hallucinations in Large Vision-Language Models by Refining Textual Embeddings
Nov 07, 2025Abstract:In this work, we identify an inherent bias in prevailing LVLM architectures toward the language modality, largely resulting from the common practice of simply appending visual embeddings to the input text sequence. To address this, we propose a simple yet effective method that refines textual embeddings by integrating average-pooled visual features. Our approach demonstrably improves visual grounding and significantly reduces hallucinations on established benchmarks. While average pooling offers a straightforward, robust, and efficient means of incorporating visual information, we believe that more sophisticated fusion methods could further enhance visual grounding and cross-modal alignment. Given that the primary focus of this work is to highlight the modality imbalance and its impact on hallucinations -- and to show that refining textual embeddings with visual information mitigates this issue -- we leave exploration of advanced fusion strategies for future work.
On the Significance of Question Encoder Sequence Model in the Out-of-Distribution Performance in Visual Question Answering
Aug 28, 2021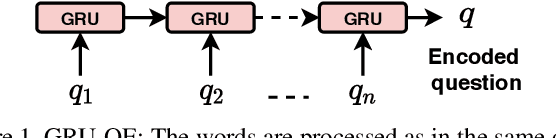
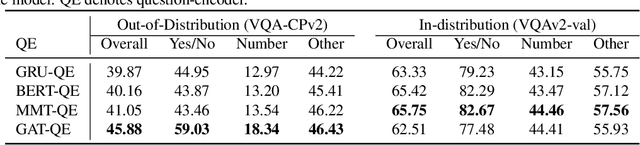
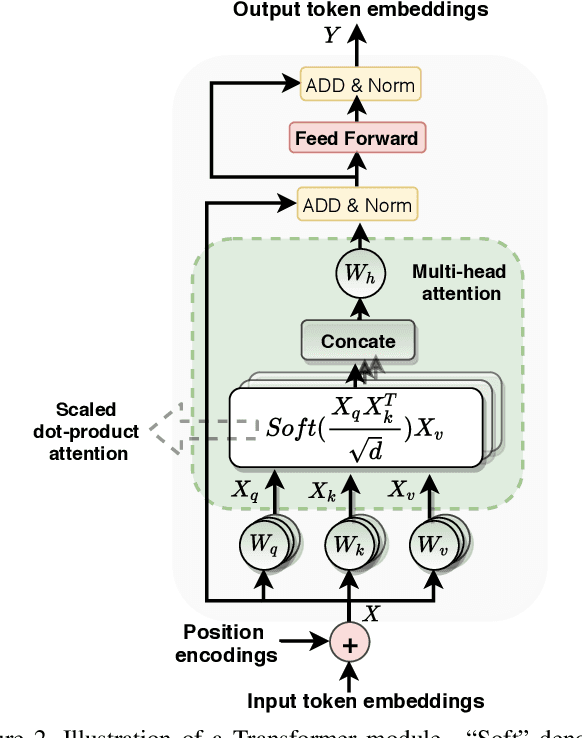
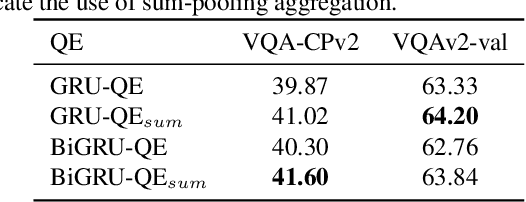
Abstract:Generalizing beyond the experiences has a significant role in developing practical AI systems. It has been shown that current Visual Question Answering (VQA) models are over-dependent on the language-priors (spurious correlations between question-types and their most frequent answers) from the train set and pose poor performance on Out-of-Distribution (OOD) test sets. This conduct limits their generalizability and restricts them from being utilized in real-world situations. This paper shows that the sequence model architecture used in the question-encoder has a significant role in the generalizability of VQA models. To demonstrate this, we performed a detailed analysis of various existing RNN-based and Transformer-based question-encoders, and along, we proposed a novel Graph attention network (GAT)-based question-encoder. Our study found that a better choice of sequence model in the question-encoder improves the generalizability of VQA models even without using any additional relatively complex bias-mitigation approaches.
Linguistically-aware Attention for Reducing the Semantic-Gap in Vision-Language Tasks
Aug 18, 2020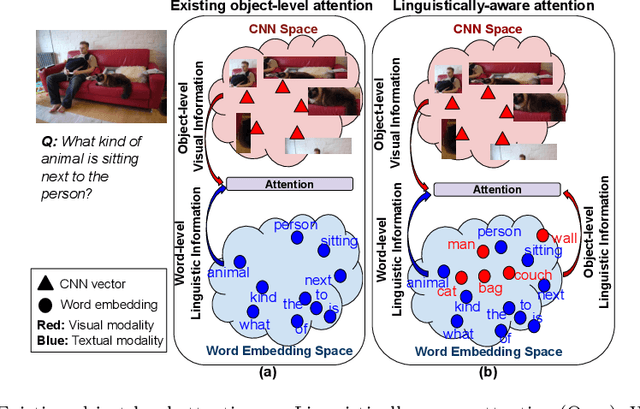
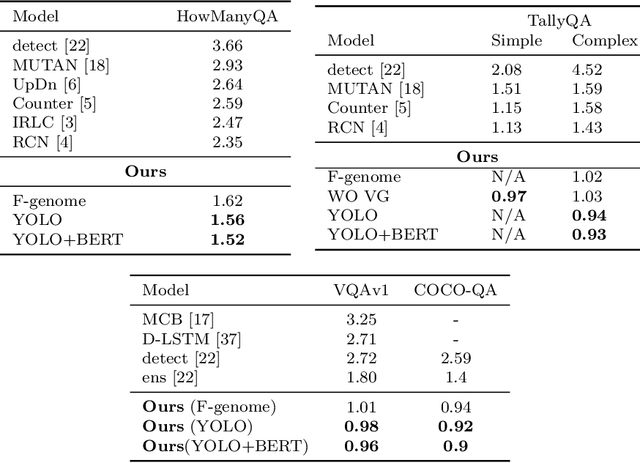
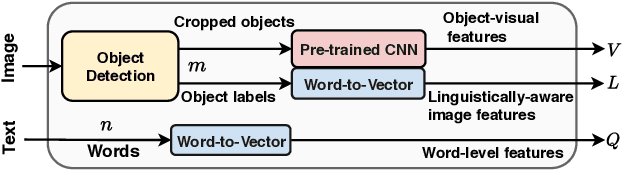
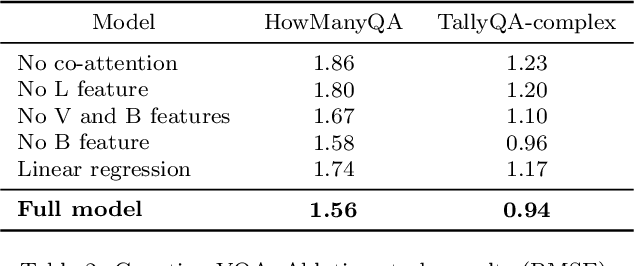
Abstract:Attention models are widely used in Vision-language (V-L) tasks to perform the visual-textual correlation. Humans perform such a correlation with a strong linguistic understanding of the visual world. However, even the best performing attention model in V-L tasks lacks such a high-level linguistic understanding, thus creating a semantic gap between the modalities. In this paper, we propose an attention mechanism - Linguistically-aware Attention (LAT) - that leverages object attributes obtained from generic object detectors along with pre-trained language models to reduce this semantic gap. LAT represents visual and textual modalities in a common linguistically-rich space, thus providing linguistic awareness to the attention process. We apply and demonstrate the effectiveness of LAT in three V-L tasks: Counting-VQA, VQA, and Image captioning. In Counting-VQA, we propose a novel counting-specific VQA model to predict an intuitive count and achieve state-of-the-art results on five datasets. In VQA and Captioning, we show the generic nature and effectiveness of LAT by adapting it into various baselines and consistently improving their performance.
Reducing Language Biases in Visual Question Answering with Visually-Grounded Question Encoder
Jul 18, 2020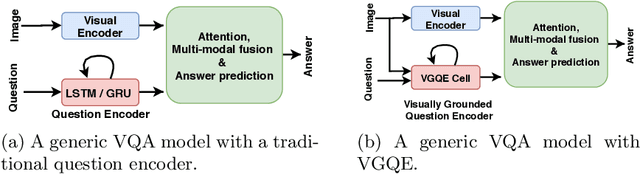
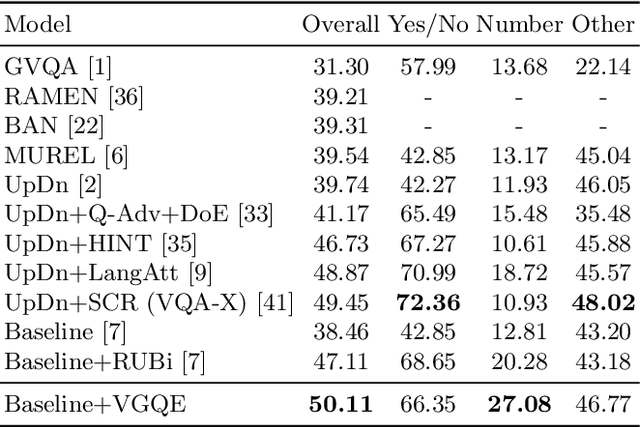
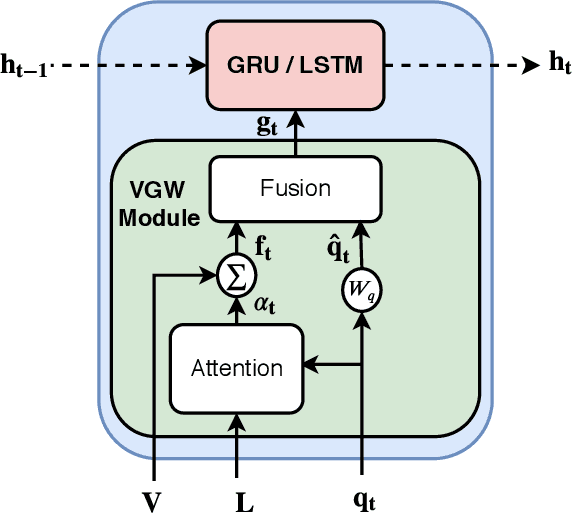
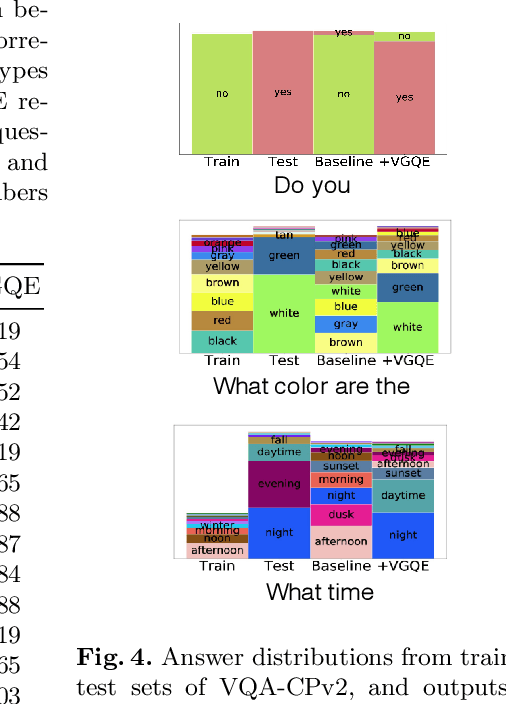
Abstract:Recent studies have shown that current VQA models are heavily biased on the language priors in the train set to answer the question, irrespective of the image. E.g., overwhelmingly answer "what sport is" as "tennis" or "what color banana" as "yellow." This behavior restricts them from real-world application scenarios. In this work, we propose a novel model-agnostic question encoder, Visually-Grounded Question Encoder (VGQE), for VQA that reduces this effect. VGQE utilizes both visual and language modalities equally while encoding the question. Hence the question representation itself gets sufficient visual-grounding, and thus reduces the dependency of the model on the language priors. We demonstrate the effect of VGQE on three recent VQA models and achieve state-of-the-art results on the bias-sensitive split of the VQAv2 dataset; VQA-CPv2. Further, unlike the existing bias-reduction techniques, on the standard VQAv2 benchmark, our approach does not drop the accuracy; instead, it improves the performance.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge