Gourav Siddhad
Modified TSception for Analyzing Driver Drowsiness and Mental Workload from EEG
Dec 25, 2025Abstract:Driver drowsiness remains a primary cause of traffic accidents, necessitating the development of real-time, reliable detection systems to ensure road safety. This study presents a Modified TSception architecture designed for the robust assessment of driver fatigue using Electroencephalography (EEG). The model introduces a novel hierarchical architecture that surpasses the original TSception by implementing a five-layer temporal refinement strategy to capture multi-scale brain dynamics. A key innovation is the use of Adaptive Average Pooling, which provides the structural flexibility to handle varying EEG input dimensions, and a two - stage fusion mechanism that optimizes the integration of spatiotemporal features for improved stability. When evaluated on the SEED-VIG dataset and compared against established methods - including SVM, Transformer, EEGNet, ConvNeXt, LMDA-Net, and the original TSception - the Modified TSception achieves a comparable accuracy of 83.46% (vs. 83.15% for the original). Critically, the proposed model exhibits a substantially reduced confidence interval (0.24 vs. 0.36), signifying a marked improvement in performance stability. Furthermore, the architecture's generalizability is validated on the STEW mental workload dataset, where it achieves state-of-the-art results with 95.93% and 95.35% accuracy for 2-class and 3-class classification, respectively. These improvements in consistency and cross-task generalizability underscore the effectiveness of the proposed modifications for reliable EEG-based monitoring of drowsiness and mental workload.
Efficacy of Transformer Networks for Classification of Raw EEG Data
Feb 08, 2022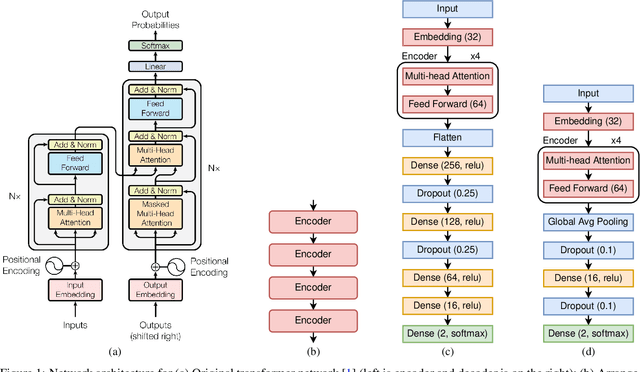
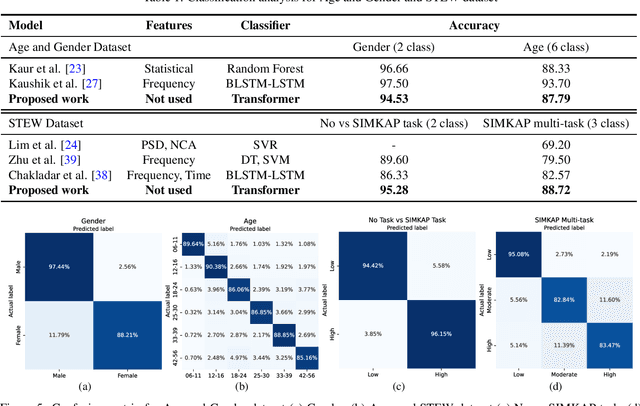
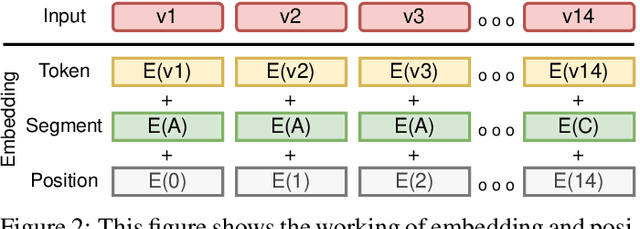
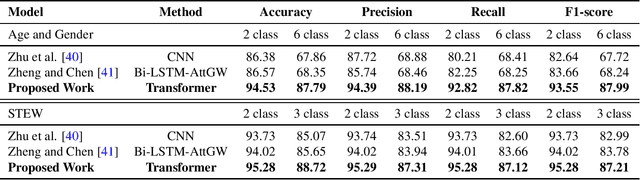
Abstract:With the unprecedented success of transformer networks in natural language processing (NLP), recently, they have been successfully adapted to areas like computer vision, generative adversarial networks (GAN), and reinforcement learning. Classifying electroencephalogram (EEG) data has been challenging and researchers have been overly dependent on pre-processing and hand-crafted feature extraction. Despite having achieved automated feature extraction in several other domains, deep learning has not yet been accomplished for EEG. In this paper, the efficacy of the transformer network for the classification of raw EEG data (cleaned and pre-processed) is explored. The performance of transformer networks was evaluated on a local (age and gender data) and a public dataset (STEW). First, a classifier using a transformer network is built to classify the age and gender of a person with raw resting-state EEG data. Second, the classifier is tuned for mental workload classification with open access raw multi-tasking mental workload EEG data (STEW). The network achieves an accuracy comparable to state-of-the-art accuracy on both the local (Age and Gender dataset; 94.53% (gender) and 87.79% (age)) and the public (STEW dataset; 95.28% (two workload levels) and 88.72% (three workload levels)) dataset. The accuracy values have been achieved using raw EEG data without feature extraction. Results indicate that the transformer-based deep learning models can successfully abate the need for heavy feature-extraction of EEG data for successful classification.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge