Go-Eum Cha
A Robot That Listens: Enhancing Self-Disclosure and Engagement Through Sentiment-based Backchannels and Active Listening
Sep 09, 2025Abstract:As social robots get more deeply integrated intoour everyday lives, they will be expected to engage in meaningful conversations and exhibit socio-emotionally intelligent listening behaviors when interacting with people. Active listening and backchanneling could be one way to enhance robots' communicative capabilities and enhance their effectiveness in eliciting deeper self-disclosure, providing a sense of empathy,and forming positive rapport and relationships with people.Thus, we developed an LLM-powered social robot that can exhibit contextually appropriate sentiment-based backchannelingand active listening behaviors (active listening+backchanneling) and compared its efficacy in eliciting people's self-disclosurein comparison to robots that do not exhibit any of these listening behaviors (control) and a robot that only exhibitsbackchanneling behavior (backchanneling-only). Through ourexperimental study with sixty-five participants, we found theparticipants who conversed with the active listening robot per-ceived the interactions more positively, in which they exhibited the highest self-disclosures, and reported the strongest senseof being listened to. The results of our study suggest that the implementation of active listening behaviors in social robotshas the potential to improve human-robot communication andcould further contribute to the building of deeper human-robot relationships and rapport.
Implications of Personality on Cognitive Workload, Affect, and Task Performance in Robot Remote Control
Mar 08, 2023



Abstract:This paper explores how the personality traits of robot operators can impact their task performance during remote control of robots. The influence of personal dispositions on information processing, either directly or indirectly, needs to be examined when working with robots on specific tasks. To investigate this relationship, we utilize the open-access multi-modal dataset MOCAS to examine the operator's personality, affect, cognitive load, and task performance. Our objective is to confirm if personal traits have a total effect, including both direct and indirect effects, that could significantly impact operator performance level. We specifically examine the relationship between personality traits such as extroversion, conscientiousness, and agreeableness, and task performance. We analyze the correlation between cognitive load, self-ratings of workload and affect, and the quantified individual personality traits and their experimental scores. As a result, we confirm that personality traits have no total effect on task performance.
A ROS-based Framework for Monitoring Human and Robot Conditions in a Human-Multi-robot Team
Jun 06, 2020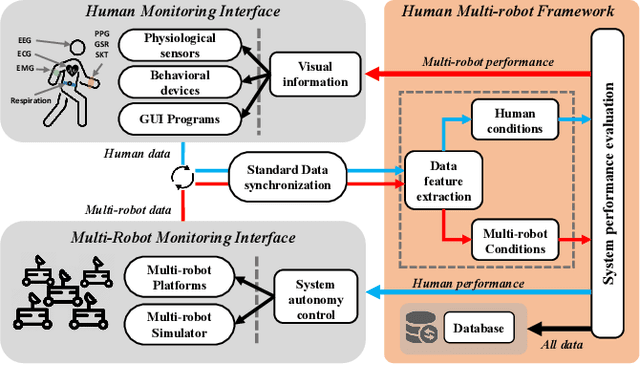
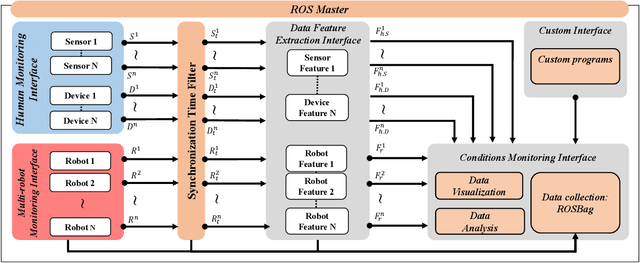
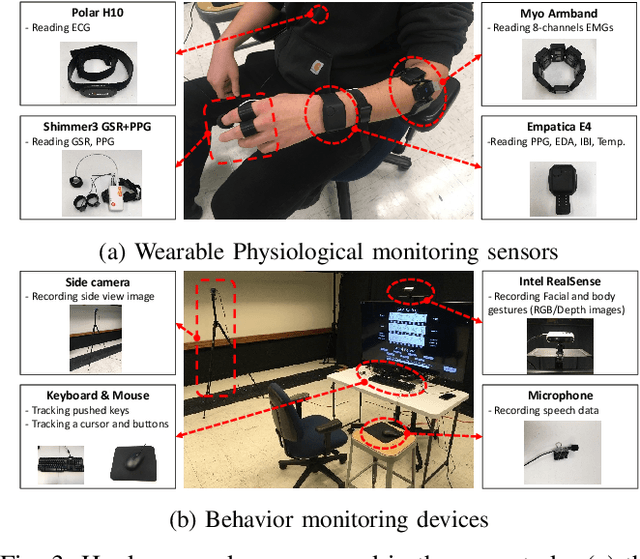
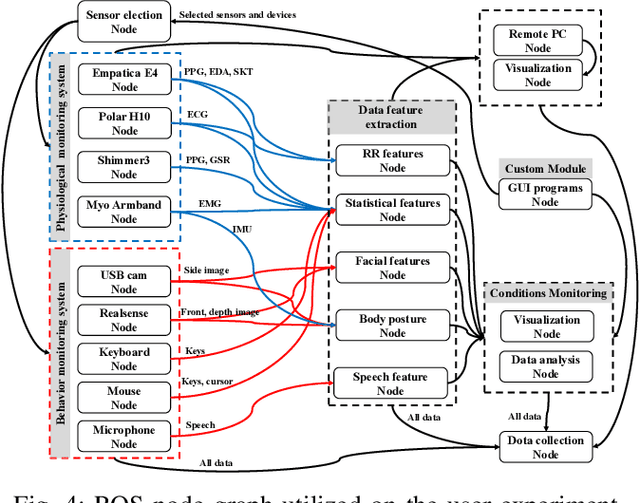
Abstract:This paper presents a framework for monitoring human and robot conditions in human multi-robot interactions. The proposed framework consists of four modules: 1) human and robot conditions monitoring interface, 2) synchronization time filter, 3) data feature extraction interface, and 4) condition monitoring interface. The framework is based on Robot Operating System (ROS), and it supports physiological and behavioral sensors and devices and robot systems, as well as custom programs. Furthermore, it allows synchronizing the monitoring conditions and sharing them simultaneously. In order to validate the proposed framework, we present experiment results and analysis obtained from the user study where 30 human subjects participated and simulated robot experiments.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge