Giovanni Maria Biancofiore
Exploring Diversity, Novelty, and Popularity Bias in ChatGPT's Recommendations
Jan 05, 2026Abstract:ChatGPT has emerged as a versatile tool, demonstrating capabilities across diverse domains. Given these successes, the Recommender Systems (RSs) community has begun investigating its applications within recommendation scenarios primarily focusing on accuracy. While the integration of ChatGPT into RSs has garnered significant attention, a comprehensive analysis of its performance across various dimensions remains largely unexplored. Specifically, the capabilities of providing diverse and novel recommendations or exploring potential biases such as popularity bias have not been thoroughly examined. As the use of these models continues to expand, understanding these aspects is crucial for enhancing user satisfaction and achieving long-term personalization. This study investigates the recommendations provided by ChatGPT-3.5 and ChatGPT-4 by assessing ChatGPT's capabilities in terms of diversity, novelty, and popularity bias. We evaluate these models on three distinct datasets and assess their performance in Top-N recommendation and cold-start scenarios. The findings reveal that ChatGPT-4 matches or surpasses traditional recommenders, demonstrating the ability to balance novelty and diversity in recommendations. Furthermore, in the cold-start scenario, ChatGPT models exhibit superior performance in both accuracy and novelty, suggesting they can be particularly beneficial for new users. This research highlights the strengths and limitations of ChatGPT's recommendations, offering new perspectives on the capacity of these models to provide recommendations beyond accuracy-focused metrics.
Evaluating ChatGPT as a Recommender System: A Rigorous Approach
Sep 07, 2023



Abstract:Recent popularity surrounds large AI language models due to their impressive natural language capabilities. They contribute significantly to language-related tasks, including prompt-based learning, making them valuable for various specific tasks. This approach unlocks their full potential, enhancing precision and generalization. Research communities are actively exploring their applications, with ChatGPT receiving recognition. Despite extensive research on large language models, their potential in recommendation scenarios still needs to be explored. This study aims to fill this gap by investigating ChatGPT's capabilities as a zero-shot recommender system. Our goals include evaluating its ability to use user preferences for recommendations, reordering existing recommendation lists, leveraging information from similar users, and handling cold-start situations. We assess ChatGPT's performance through comprehensive experiments using three datasets (MovieLens Small, Last.FM, and Facebook Book). We compare ChatGPT's performance against standard recommendation algorithms and other large language models, such as GPT-3.5 and PaLM-2. To measure recommendation effectiveness, we employ widely-used evaluation metrics like Mean Average Precision (MAP), Recall, Precision, F1, normalized Discounted Cumulative Gain (nDCG), Item Coverage, Expected Popularity Complement (EPC), Average Coverage of Long Tail (ACLT), Average Recommendation Popularity (ARP), and Popularity-based Ranking-based Equal Opportunity (PopREO). Through thoroughly exploring ChatGPT's abilities in recommender systems, our study aims to contribute to the growing body of research on the versatility and potential applications of large language models. Our experiment code is available on the GitHub repository: https://github.com/sisinflab/Recommender-ChatGPT
Interactive Question Answering Systems: Literature Review
Sep 04, 2022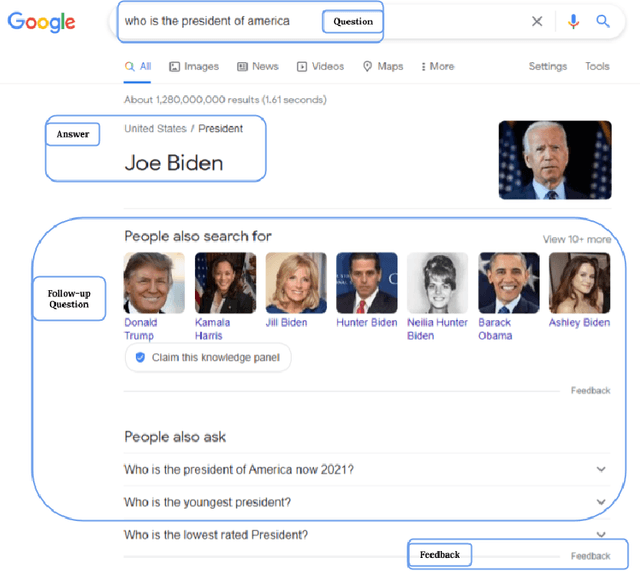
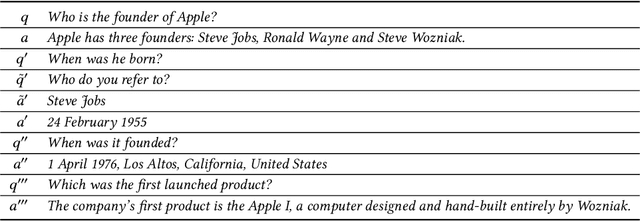
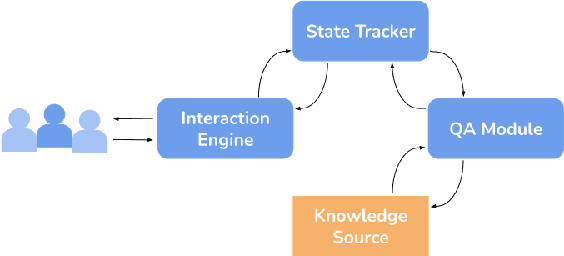
Abstract:Question answering systems are recognized as popular and frequently effective means of information seeking on the web. In such systems, information seekers can receive a concise response to their query by presenting their questions in natural language. Interactive question answering is a recently proposed and increasingly popular solution that resides at the intersection of question answering and dialogue systems. On the one hand, the user can ask questions in normal language and locate the actual response to her inquiry; on the other hand, the system can prolong the question-answering session into a dialogue if there are multiple probable replies, very few, or ambiguities in the initial request. By permitting the user to ask more questions, interactive question answering enables users to dynamically interact with the system and receive more precise results. This survey offers a detailed overview of the interactive question-answering methods that are prevalent in current literature. It begins by explaining the foundational principles of question-answering systems, hence defining new notations and taxonomies to combine all identified works inside a unified framework. The reviewed published work on interactive question-answering systems is then presented and examined in terms of its proposed methodology, evaluation approaches, and dataset/application domain. We also describe trends surrounding specific tasks and issues raised by the community, so shedding light on the future interests of scholars. Our work is further supported by a GitHub page with a synthesis of all the major topics covered in this literature study. https://sisinflab.github.io/interactive-question-answering-systems-survey/
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge