Gerhard Bauch
Turbo Equalization with Coarse Quantization using the Information Bottleneck Method
Sep 13, 2024Abstract:This paper proposes a turbo equalizer for intersymbol interference channels (ISI) that uses coarsely quantized messages across all receiver components. Lookup tables (LUTs) carry out compression operations designed with the information bottleneck method aiming to maximize relevant mutual information. The turbo setup consists of an equalizer and a decoder that provide extrinsic information to each other over multiple turbo iterations. We develop simplified LUT structures to incorporate the decoder feedback in the equalizer with significantly reduced complexity. The proposed receiver is optimized for selected ISI channels. A conceptual hardware implementation is developed to compare the area efficiency and error correction performance. A thorough analysis reveals that LUT-based configurations with very coarse quantization can achieve higher area efficiency than conventional equalizers. Moreover, the proposed turbo setups can outperform the respective non-turbo setups regarding area efficiency and error correction capability.
Reconstruction-Computation-Quantization (RCQ): A Paradigm for Low Bit Width LDPC Decoding
Nov 17, 2021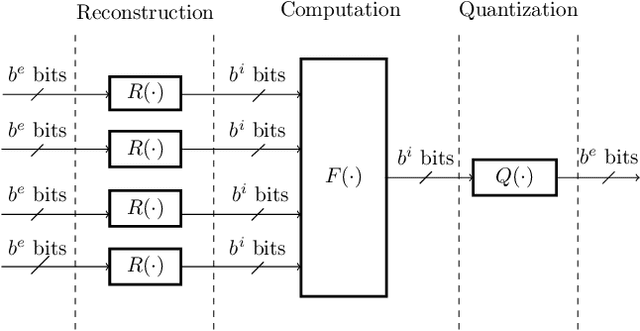
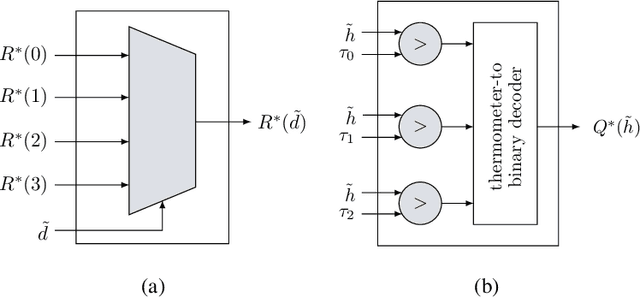
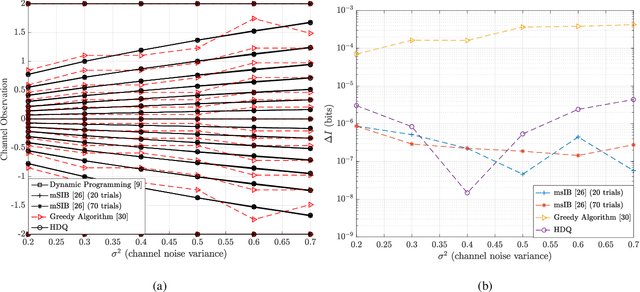
Abstract:This paper uses the reconstruction-computation-quantization (RCQ) paradigm to decode low-density parity-check (LDPC) codes. RCQ facilitates dynamic non-uniform quantization to achieve good frame error rate (FER) performance with very low message precision. For message-passing according to a flooding schedule, the RCQ parameters are designed by discrete density evolution (DDE). Simulation results on an IEEE 802.11 LDPC code show that for 4-bit messages, a flooding MinSum RCQ decoder outperforms table-lookup approaches such as information bottleneck (IB) or Min-IB decoding, with significantly fewer parameters to be stored. Additionally, this paper introduces layer-specific RCQ (LS-RCQ), an extension of RCQ decoding for layered architectures. LS-RCQ uses layer-specific message representations to achieve the best possible FER performance. For LS-RCQ, this paper proposes using layered DDE featuring hierarchical dynamic quantization (HDQ) to design LS-RCQ parameters efficiently. Finally, this paper studies field-programmable gate array (FPGA) implementations of RCQ decoders. Simulation results for a (9472, 8192) quasi-cyclic (QC) LDPC code show that a layered MinSum RCQ decoder with 3-bit messages achieves more than a $10\%$ reduction in LUTs and routed nets and more than a $6\%$ decrease in register usage while maintaining comparable decoding performance, compared to a 5-bit offset MinSum decoder.
Decoding of Non-Binary LDPC Codes Using the Information Bottleneck Method
Oct 21, 2018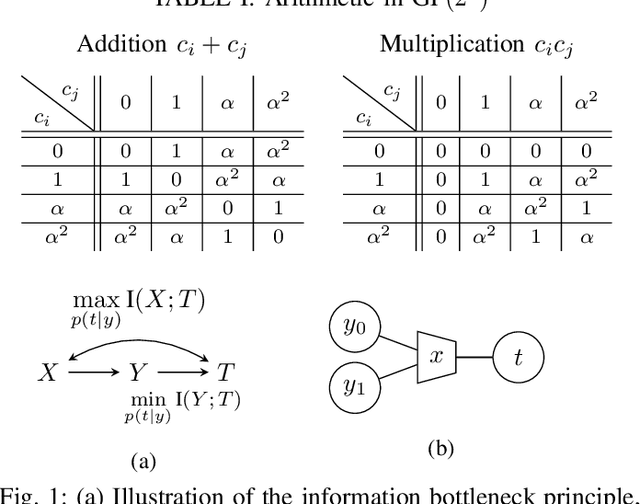
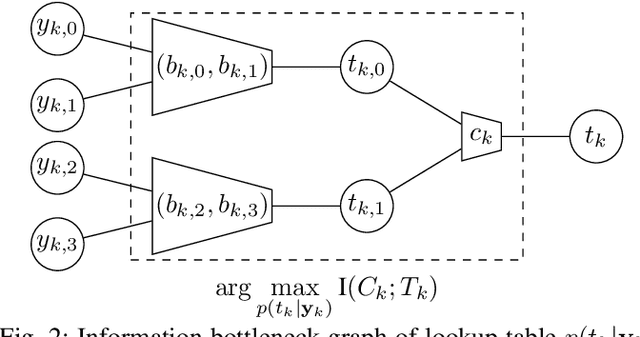
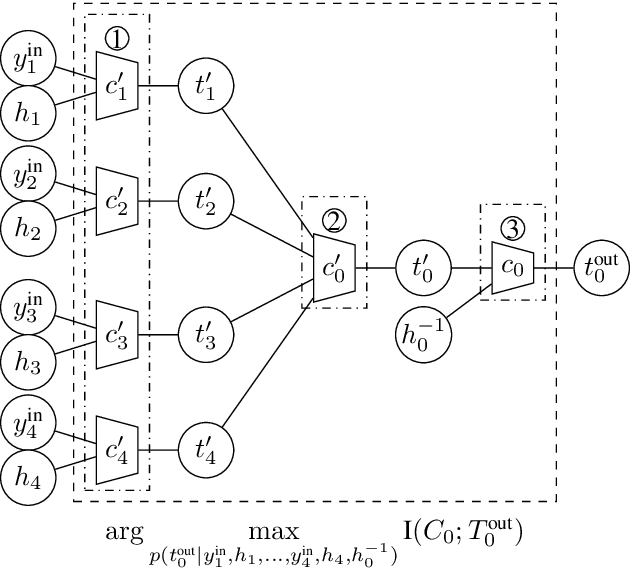
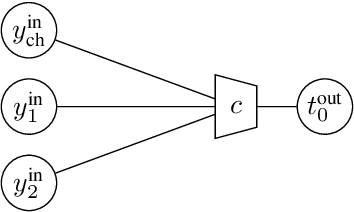
Abstract:Recently, a novel lookup table based decoding method for binary low-density parity-check codes has attracted considerable attention. In this approach, mutual-information maximizing lookup tables replace the conventional operations of the variable nodes and the check nodes in message passing decoding. Moreover, the exchanged messages are represented by integers with very small bit width. A machine learning framework termed the information bottleneck method is used to design the corresponding lookup tables. In this paper, we extend this decoding principle from binary to non-binary codes. This is not a straightforward extension, but requires a more sophisticated lookup table design to cope with the arithmetic in higher order Galois fields. Provided bit error rate simulations show that our proposed scheme outperforms the log-max decoding algorithm and operates close to sum-product decoding.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge