Gennady Andrienko
Resolving Congestions in the Air Traffic Management Domain via Multiagent Reinforcement Learning Methods
Dec 14, 2019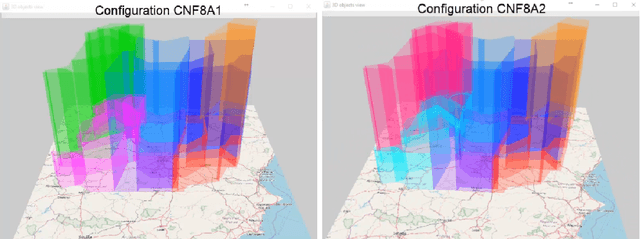
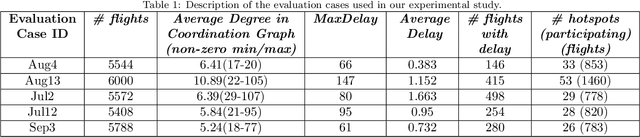
Abstract:In this article, we report on the efficiency and effectiveness of multiagent reinforcement learning methods (MARL) for the computation of flight delays to resolve congestion problems in the Air Traffic Management (ATM) domain. Specifically, we aim to resolve cases where demand of airspace use exceeds capacity (demand-capacity problems), via imposing ground delays to flights at the pre-tactical stage of operations (i.e. few days to few hours before operation). Casting this into the multiagent domain, agents, representing flights, need to decide on own delays w.r.t. own preferences, having no information about others' payoffs, preferences and constraints, while they plan to execute their trajectories jointly with others, adhering to operational constraints. Specifically, we formalize the problem as a multiagent Markov Decision Process (MA-MDP) and we show that it can be considered as a Markov game in which interacting agents need to reach an equilibrium: What makes the problem more interesting is the dynamic setting in which agents operate, which is also due to the unforeseen, emergent effects of their decisions in the whole system. We propose collaborative multiagent reinforcement learning methods to resolve demand-capacity imbalances: Extensive experimental study on real-world cases, shows the potential of the proposed approaches in resolving problems, while advanced visualizations provide detailed views towards understanding the quality of solutions provided.
Applications of Trajectory Data from the Perspective of a Road Transportation Agency: Literature Review and Maryland Case Study
May 30, 2018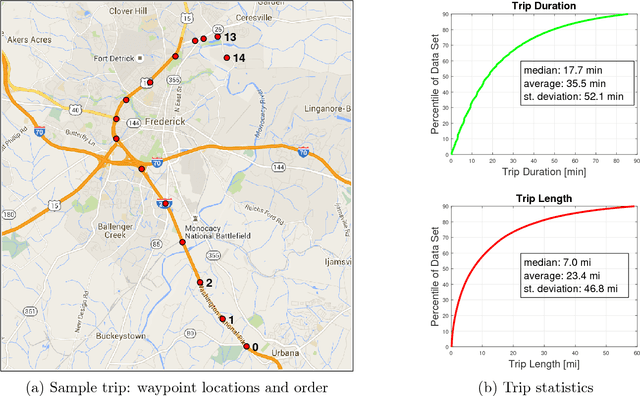
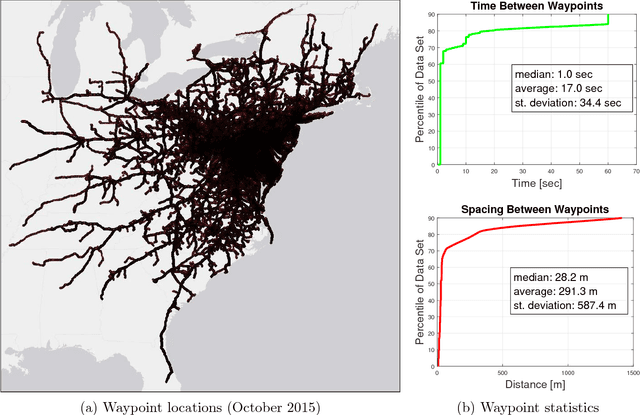
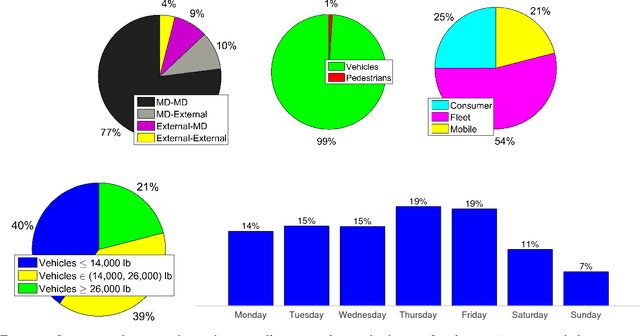
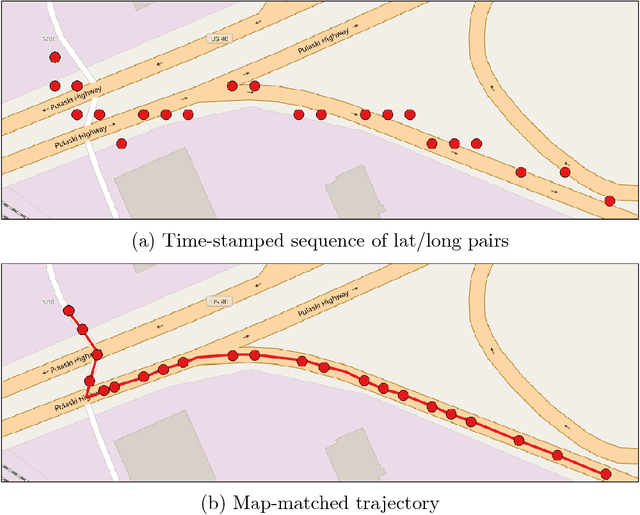
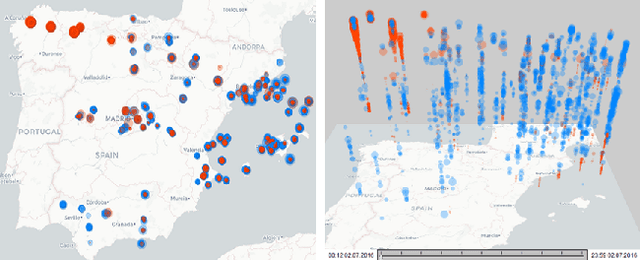
Abstract:Transportation agencies have an opportunity to leverage increasingly-available trajectory datasets to improve their analyses and decision-making processes. However, this data is typically purchased from vendors, which means agencies must understand its potential benefits beforehand in order to properly assess its value relative to the cost of acquisition. While the literature concerned with trajectory data is rich, it is naturally fragmented and focused on technical contributions in niche areas, which makes it difficult for government agencies to assess its value across different transportation domains. To overcome this issue, the current paper explores trajectory data from the perspective of a road transportation agency interested in acquiring trajectories to enhance its analyses. The paper provides a literature review illustrating applications of trajectory data in six areas of road transportation systems analysis: demand estimation, modeling human behavior, designing public transit, traffic performance measurement and prediction, environment and safety. In addition, it visually explores 20 million GPS traces in Maryland, illustrating existing and suggesting new applications of trajectory data.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge