Gauri Pradhan
Hyperparameters in Score-Based Membership Inference Attacks
Feb 10, 2025



Abstract:Membership Inference Attacks (MIAs) have emerged as a valuable framework for evaluating privacy leakage by machine learning models. Score-based MIAs are distinguished, in particular, by their ability to exploit the confidence scores that the model generates for particular inputs. Existing score-based MIAs implicitly assume that the adversary has access to the target model's hyperparameters, which can be used to train the shadow models for the attack. In this work, we demonstrate that the knowledge of target hyperparameters is not a prerequisite for MIA in the transfer learning setting. Based on this, we propose a novel approach to select the hyperparameters for training the shadow models for MIA when the attacker has no prior knowledge about them by matching the output distributions of target and shadow models. We demonstrate that using the new approach yields hyperparameters that lead to an attack near indistinguishable in performance from an attack that uses target hyperparameters to train the shadow models. Furthermore, we study the empirical privacy risk of unaccounted use of training data for hyperparameter optimization (HPO) in differentially private (DP) transfer learning. We find no statistically significant evidence that performing HPO using training data would increase vulnerability to MIA.
Understanding Practical Membership Privacy of Deep Learning
Feb 07, 2024



Abstract:We apply a state-of-the-art membership inference attack (MIA) to systematically test the practical privacy vulnerability of fine-tuning large image classification models.We focus on understanding the properties of data sets and samples that make them vulnerable to membership inference. In terms of data set properties, we find a strong power law dependence between the number of examples per class in the data and the MIA vulnerability, as measured by true positive rate of the attack at a low false positive rate. For an individual sample, large gradients at the end of training are strongly correlated with MIA vulnerability.
Beyond PID Controllers: PPO with Neuralized PID Policy for Proton Beam Intensity Control in Mu2e
Dec 28, 2023
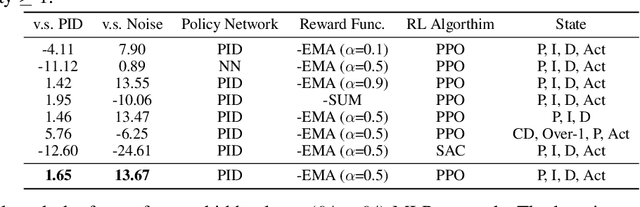
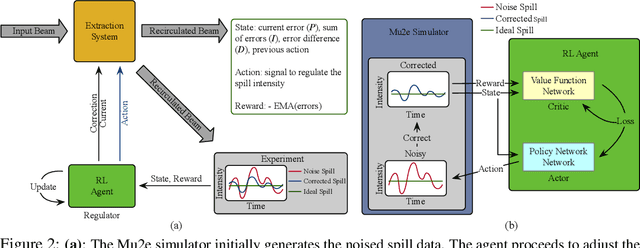

Abstract:We introduce a novel Proximal Policy Optimization (PPO) algorithm aimed at addressing the challenge of maintaining a uniform proton beam intensity delivery in the Muon to Electron Conversion Experiment (Mu2e) at Fermi National Accelerator Laboratory (Fermilab). Our primary objective is to regulate the spill process to ensure a consistent intensity profile, with the ultimate goal of creating an automated controller capable of providing real-time feedback and calibration of the Spill Regulation System (SRS) parameters on a millisecond timescale. We treat the Mu2e accelerator system as a Markov Decision Process suitable for Reinforcement Learning (RL), utilizing PPO to reduce bias and enhance training stability. A key innovation in our approach is the integration of a neuralized Proportional-Integral-Derivative (PID) controller into the policy function, resulting in a significant improvement in the Spill Duty Factor (SDF) by 13.6%, surpassing the performance of the current PID controller baseline by an additional 1.6%. This paper presents the preliminary offline results based on a differentiable simulator of the Mu2e accelerator. It paves the groundwork for real-time implementations and applications, representing a crucial step towards automated proton beam intensity control for the Mu2e experiment.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge