Garima Chhikara
SMITE: Enhancing Fairness in LLMs through Optimal In-Context Example Selection via Dynamic Validation
Aug 25, 2025Abstract:Large Language Models (LLMs) are widely used for downstream tasks such as tabular classification, where ensuring fairness in their outputs is critical for inclusivity, equal representation, and responsible AI deployment. This study introduces a novel approach to enhancing LLM performance and fairness through the concept of a dynamic validation set, which evolves alongside the test set, replacing the traditional static validation approach. We also propose an iterative algorithm, SMITE, to select optimal in-context examples, with each example set validated against its corresponding dynamic validation set. The in-context set with the lowest total error is used as the final demonstration set. Our experiments across four different LLMs show that our proposed techniques significantly improve both predictive accuracy and fairness compared to baseline methods. To our knowledge, this is the first study to apply dynamic validation in the context of in-context learning for LLMs.
Through the Prism of Culture: Evaluating LLMs' Understanding of Indian Subcultures and Traditions
Jan 28, 2025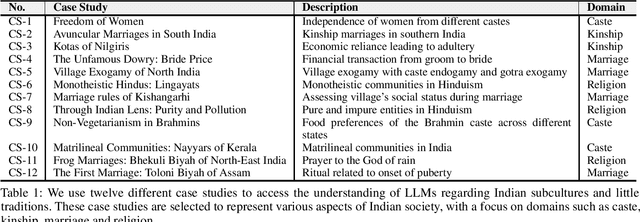
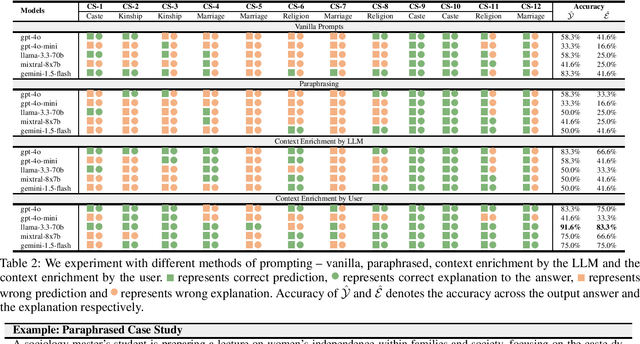

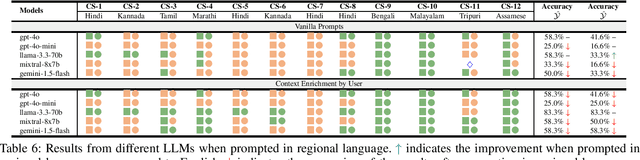
Abstract:Large Language Models (LLMs) have shown remarkable advancements but also raise concerns about cultural bias, often reflecting dominant narratives at the expense of under-represented subcultures. In this study, we evaluate the capacity of LLMs to recognize and accurately respond to the Little Traditions within Indian society, encompassing localized cultural practices and subcultures such as caste, kinship, marriage, and religion. Through a series of case studies, we assess whether LLMs can balance the interplay between dominant Great Traditions and localized Little Traditions. We explore various prompting strategies and further investigate whether using prompts in regional languages enhances the models cultural sensitivity and response quality. Our findings reveal that while LLMs demonstrate an ability to articulate cultural nuances, they often struggle to apply this understanding in practical, context-specific scenarios. To the best of our knowledge, this is the first study to analyze LLMs engagement with Indian subcultures, offering critical insights into the challenges of embedding cultural diversity in AI systems.
LaMSUM: A Novel Framework for Extractive Summarization of User Generated Content using LLMs
Jun 22, 2024Abstract:Large Language Models (LLMs) have demonstrated impressive performance across a wide range of NLP tasks, including summarization. Inherently LLMs produce abstractive summaries, and the task of achieving extractive summaries through LLMs still remains largely unexplored. To bridge this gap, in this work, we propose a novel framework LaMSUM to generate extractive summaries through LLMs for large user-generated text by leveraging voting algorithms. Our evaluation on three popular open-source LLMs (Llama 3, Mixtral and Gemini) reveal that the LaMSUM outperforms state-of-the-art extractive summarization methods. We further attempt to provide the rationale behind the output summary produced by LLMs. Overall, this is one of the early attempts to achieve extractive summarization for large user-generated text by utilizing LLMs, and likely to generate further interest in the community.
Few-Shot Fairness: Unveiling LLM's Potential for Fairness-Aware Classification
Feb 28, 2024



Abstract:Employing Large Language Models (LLM) in various downstream applications such as classification is crucial, especially for smaller companies lacking the expertise and resources required for fine-tuning a model. Fairness in LLMs helps ensure inclusivity, equal representation based on factors such as race, gender and promotes responsible AI deployment. As the use of LLMs has become increasingly prevalent, it is essential to assess whether LLMs can generate fair outcomes when subjected to considerations of fairness. In this study, we introduce a framework outlining fairness regulations aligned with various fairness definitions, with each definition being modulated by varying degrees of abstraction. We explore the configuration for in-context learning and the procedure for selecting in-context demonstrations using RAG, while incorporating fairness rules into the process. Experiments conducted with different LLMs indicate that GPT-4 delivers superior results in terms of both accuracy and fairness compared to other models. This work is one of the early attempts to achieve fairness in prediction tasks by utilizing LLMs through in-context learning.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge