Gabriel Gordon-Hall
$α$VIL: Learning to Leverage Auxiliary Tasks for Multitask Learning
May 13, 2024



Abstract:Multitask Learning is a Machine Learning paradigm that aims to train a range of (usually related) tasks with the help of a shared model. While the goal is often to improve the joint performance of all training tasks, another approach is to focus on the performance of a specific target task, while treating the remaining ones as auxiliary data from which to possibly leverage positive transfer towards the target during training. In such settings, it becomes important to estimate the positive or negative influence auxiliary tasks will have on the target. While many ways have been proposed to estimate task weights before or during training they typically rely on heuristics or extensive search of the weighting space. We propose a novel method called $\alpha$-Variable Importance Learning ($\alpha$VIL) that is able to adjust task weights dynamically during model training, by making direct use of task-specific updates of the underlying model's parameters between training epochs. Experiments indicate that $\alpha$VIL is able to outperform other Multitask Learning approaches in a variety of settings. To our knowledge, this is the first attempt at making direct use of model updates for task weight estimation.
Learning Dialog Policies from Weak Demonstrations
Apr 23, 2020
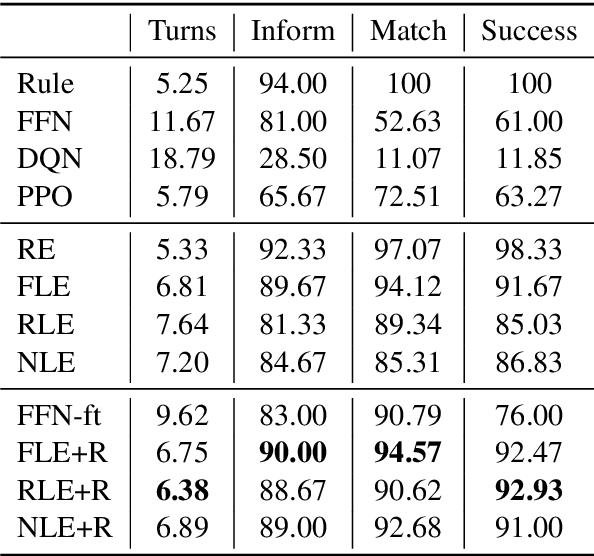
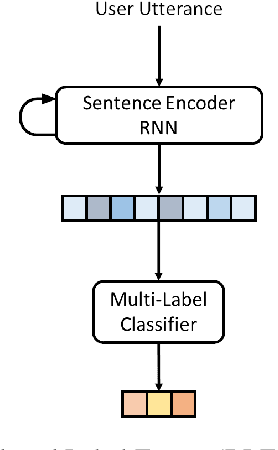
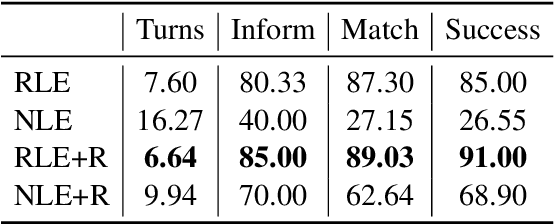
Abstract:Deep reinforcement learning is a promising approach to training a dialog manager, but current methods struggle with the large state and action spaces of multi-domain dialog systems. Building upon Deep Q-learning from Demonstrations (DQfD), an algorithm that scores highly in difficult Atari games, we leverage dialog data to guide the agent to successfully respond to a user's requests. We make progressively fewer assumptions about the data needed, using labeled, reduced-labeled, and even unlabeled data to train expert demonstrators. We introduce Reinforced Fine-tune Learning, an extension to DQfD, enabling us to overcome the domain gap between the datasets and the environment. Experiments in a challenging multi-domain dialog system framework validate our approaches, and get high success rates even when trained on out-of-domain data.
Show Us the Way: Learning to Manage Dialog from Demonstrations
Apr 17, 2020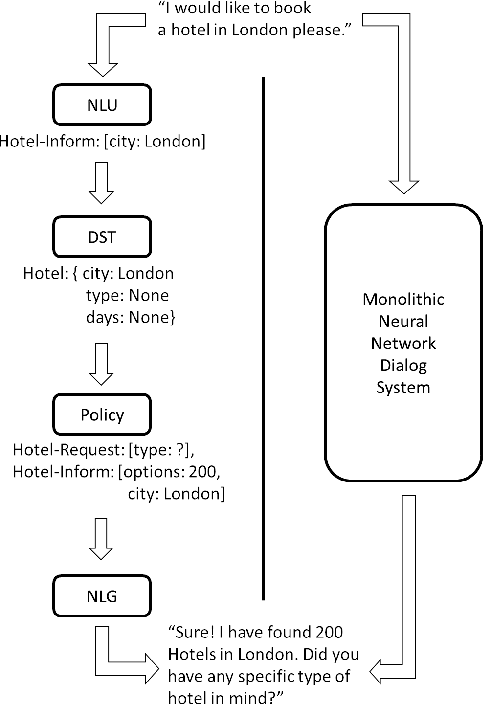
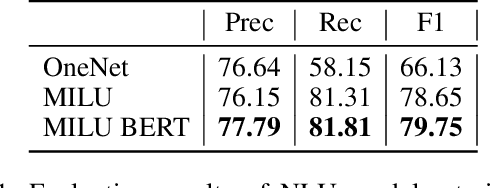
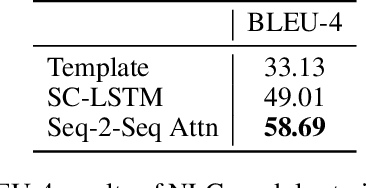
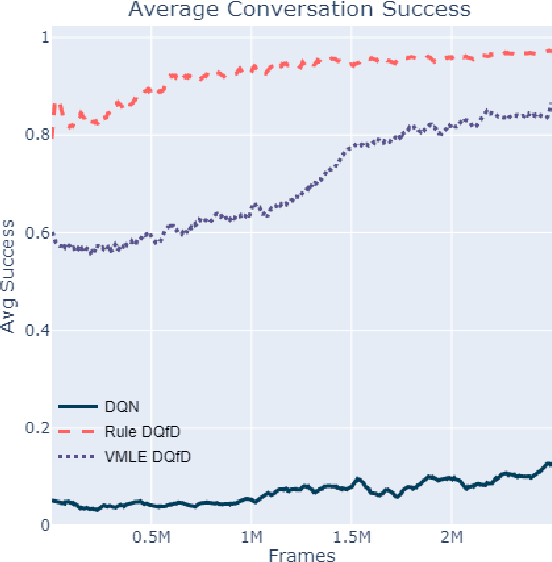
Abstract:We present our submission to the End-to-End Multi-Domain Dialog Challenge Track of the Eighth Dialog System Technology Challenge. Our proposed dialog system adopts a pipeline architecture, with distinct components for Natural Language Understanding, Dialog State Tracking, Dialog Management and Natural Language Generation. At the core of our system is a reinforcement learning algorithm which uses Deep Q-learning from Demonstrations to learn a dialog policy with the help of expert examples. We find that demonstrations are essential to training an accurate dialog policy where both state and action spaces are large. Evaluation of our Dialog Management component shows that our approach is effective - beating supervised and reinforcement learning baselines.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge