Fthi Abadi
Supervised Learning in the Presence of Concept Drift: A modelling framework
May 21, 2020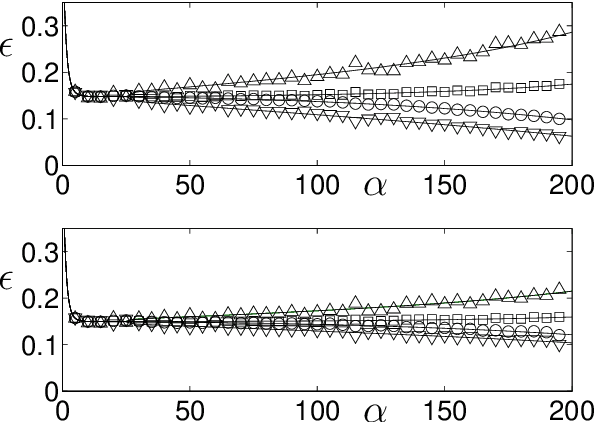

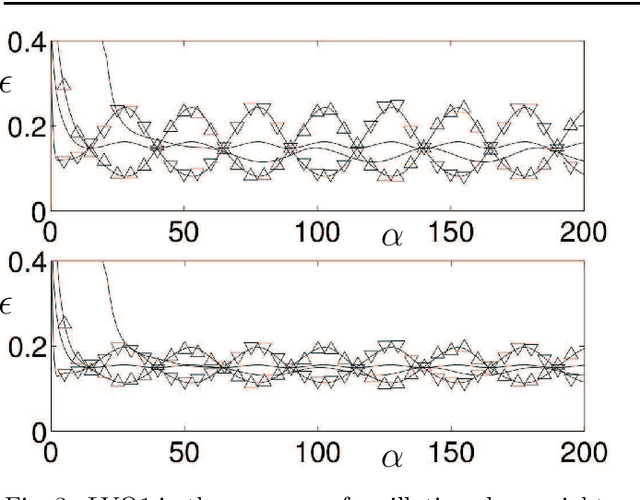
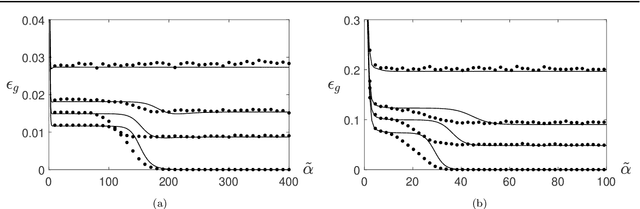
Abstract:We present a modelling framework for the investigation of supervised learning in non-stationary environments. Specifically, we model two example types of learning systems: prototype-based Learning Vector Quantization (LVQ) for classification and shallow, layered neural networks for regression tasks. We investigate so-called student teacher scenarios in which the systems are trained from a stream of high-dimensional, labeled data. Properties of the target task are considered to be non-stationary due to drift processes while the training is performed. Different types of concept drift are studied, which affect the density of example inputs only, the target rule itself, or both. By applying methods from statistical physics, we develop a modelling framework for the mathematical analysis of the training dynamics in non-stationary environments. Our results show that standard LVQ algorithms are already suitable for the training in non-stationary environments to a certain extent. However, the application of weight decay as an explicit mechanism of forgetting does not improve the performance under the considered drift processes. Furthermore, we investigate gradient-based training of layered neural networks with sigmoidal activation functions and compare with the use of rectified linear units (ReLU). Our findings show that the sensitivity to concept drift and the effectiveness of weight decay differs significantly between the two types of activation function.
Prototype-based classifiers in the presence of concept drift: A modelling framework
Mar 18, 2019
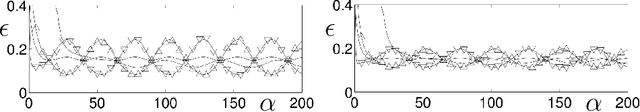
Abstract:We present a modelling framework for the investigation of prototype-based classifiers in non-stationary environments. Specifically, we study Learning Vector Quantization (LVQ) systems trained from a stream of high-dimensional, clustered data.We consider standard winner-takes-all updates known as LVQ1. Statistical properties of the input data change on the time scale defined by the training process. We apply analytical methods borrowed from statistical physics which have been used earlier for the exact description of learning in stationary environments. The suggested framework facilitates the computation of learning curves in the presence of virtual and real concept drift. Here we focus on timedependent class bias in the training data. First results demonstrate that, while basic LVQ algorithms are suitable for the training in non-stationary environments, weight decay as an explicit mechanism of forgetting does not improve the performance under the considered drift processes.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge