Frederik Faye
DermX: an end-to-end framework for explainable automated dermatological diagnosis
Feb 14, 2022
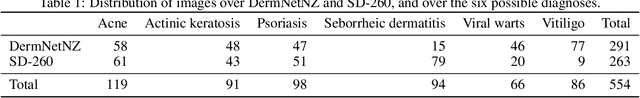

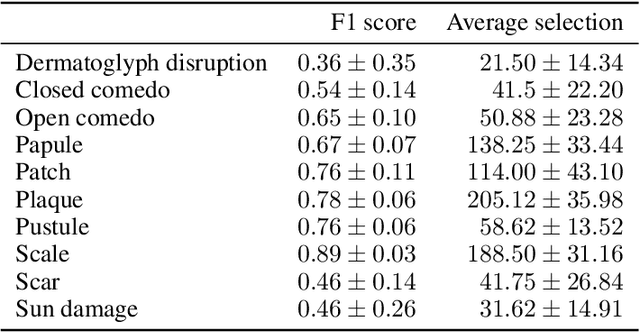
Abstract:Dermatological diagnosis automation is essential in addressing the high prevalence of skin diseases and critical shortage of dermatologists. Despite approaching expert-level diagnosis performance, convolutional neural network (ConvNet) adoption in clinical practice is impeded by their limited explainability, and by subjective, expensive explainability validations. We introduce DermX and DermX+, an end-to-end framework for explainable automated dermatological diagnosis. DermX is a clinically-inspired explainable dermatological diagnosis ConvNet, trained using DermXDB, a 554 images dataset annotated by eight dermatologists with diagnoses and supporting explanations. DermX+ extends DermX with guided attention training for explanation attention maps. Both methods achieve near-expert diagnosis performance, with DermX, DermX+, and dermatologist F1 scores of 0.79, 0.79, and 0.87, respectively. We assess the explanation plausibility in terms of identification and localization, by comparing model-selected with dermatologist-selected explanations, and gradient-weighted class-activation maps with dermatologist explanation maps. Both DermX and DermX+ obtain an identification F1 score of 0.78. The localization F1 score is 0.39 for DermX and 0.35 for DermX+. Explanation faithfulness is assessed through contrasting samples, DermX obtaining 0.53 faithfulness and DermX+ 0.25. These results show that explainability does not necessarily come at the expense of predictive power, as our high-performance models provide both plausible and faithful explanations for their diagnoses.
Uncertainty quantification in medical image segmentation with Normalizing Flows
Jun 04, 2020



Abstract:Medical image segmentation is inherently an ambiguous task due to factors such as partial volumes and variations in anatomical definitions. While in most cases the segmentation uncertainty is around the border of structures of interest, there can also be considerable inter-rater differences. The class of conditional variational autoencoders (cVAE) offers a principled approach to inferring distributions over plausible segmentations that are conditioned on input images. Segmentation uncertainty estimated from samples of such distributions can be more informative than using pixel level probability scores. In this work, we propose a novel conditional generative model that is based on conditional Normalizing Flow (cFlow). The basic idea is to increase the expressivity of the cVAE by introducing a cFlow transformation step after the encoder. This yields improved approximations of the latent posterior distribution, allowing the model to capture richer segmentation variations. With this we show that the quality and diversity of samples obtained from our conditional generative model is enhanced. Performance of our model, which we call cFlow Net, is evaluated on two medical imaging datasets demonstrating substantial improvements in both qualitative and quantitative measures when compared to a recent cVAE based model.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge