Frank Yeung
Multi-modal AI for comprehensive breast cancer prognostication
Oct 28, 2024Abstract:Treatment selection in breast cancer is guided by molecular subtypes and clinical characteristics. Recurrence risk assessment plays a crucial role in personalizing treatment. Current methods, including genomic assays, have limited accuracy and clinical utility, leading to suboptimal decisions for many patients. We developed a test for breast cancer patient stratification based on digital pathology and clinical characteristics using novel AI methods. Specifically, we utilized a vision transformer-based pan-cancer foundation model trained with self-supervised learning to extract features from digitized H&E-stained slides. These features were integrated with clinical data to form a multi-modal AI test predicting cancer recurrence and death. The test was developed and evaluated using data from a total of 8,161 breast cancer patients across 15 cohorts originating from seven countries. Of these, 3,502 patients from five cohorts were used exclusively for evaluation, while the remaining patients were used for training. Our test accurately predicted our primary endpoint, disease-free interval, in the five external cohorts (C-index: 0.71 [0.68-0.75], HR: 3.63 [3.02-4.37, p<0.01]). In a direct comparison (N=858), the AI test was more accurate than Oncotype DX, the standard-of-care 21-gene assay, with a C-index of 0.67 [0.61-0.74] versus 0.61 [0.49-0.73], respectively. Additionally, the AI test added independent information to Oncotype DX in a multivariate analysis (HR: 3.11 [1.91-5.09, p<0.01)]). The test demonstrated robust accuracy across all major breast cancer subtypes, including TNBC (C-index: 0.71 [0.62-0.81], HR: 3.81 [2.35-6.17, p=0.02]), where no diagnostic tools are currently recommended by clinical guidelines. These results suggest that our AI test can improve accuracy, extend applicability to a wider range of patients, and enhance access to treatment selection tools.
Leveraging Transformers to Improve Breast Cancer Classification and Risk Assessment with Multi-modal and Longitudinal Data
Nov 15, 2023
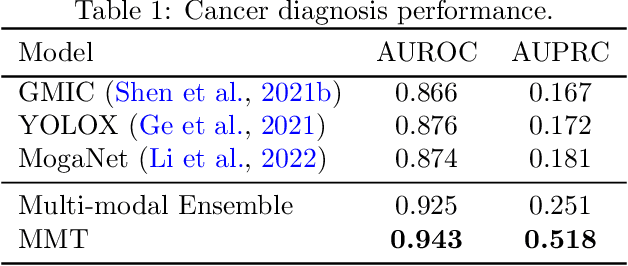
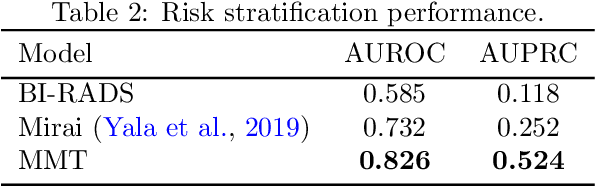
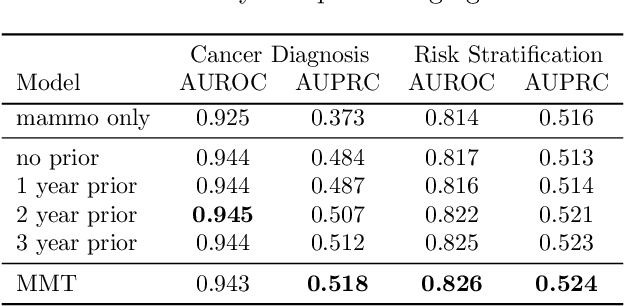
Abstract:Breast cancer screening, primarily conducted through mammography, is often supplemented with ultrasound for women with dense breast tissue. However, existing deep learning models analyze each modality independently, missing opportunities to integrate information across imaging modalities and time. In this study, we present Multi-modal Transformer (MMT), a neural network that utilizes mammography and ultrasound synergistically, to identify patients who currently have cancer and estimate the risk of future cancer for patients who are currently cancer-free. MMT aggregates multi-modal data through self-attention and tracks temporal tissue changes by comparing current exams to prior imaging. Trained on 1.3 million exams, MMT achieves an AUROC of 0.943 in detecting existing cancers, surpassing strong uni-modal baselines. For 5-year risk prediction, MMT attains an AUROC of 0.826, outperforming prior mammography-based risk models. Our research highlights the value of multi-modal and longitudinal imaging in cancer diagnosis and risk stratification.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge