Francesco Luzi
Are Deep Learning Models Robust to Partial Object Occlusion in Visual Recognition Tasks?
Sep 16, 2024
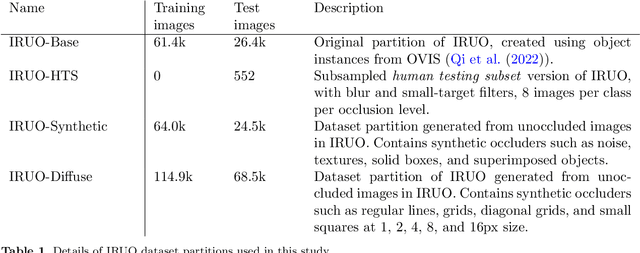

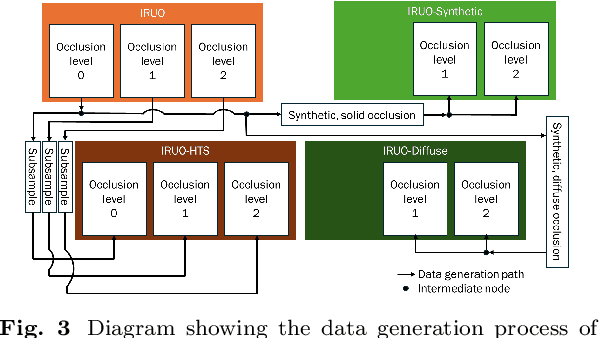
Abstract:Image classification models, including convolutional neural networks (CNNs), perform well on a variety of classification tasks but struggle under conditions of partial occlusion, i.e., conditions in which objects are partially covered from the view of a camera. Methods to improve performance under occlusion, including data augmentation, part-based clustering, and more inherently robust architectures, including Vision Transformer (ViT) models, have, to some extent, been evaluated on their ability to classify objects under partial occlusion. However, evaluations of these methods have largely relied on images containing artificial occlusion, which are typically computer-generated and therefore inexpensive to label. Additionally, methods are rarely compared against each other, and many methods are compared against early, now outdated, deep learning models. We contribute the Image Recognition Under Occlusion (IRUO) dataset, based on the recently developed Occluded Video Instance Segmentation (OVIS) dataset (arXiv:2102.01558). IRUO utilizes real-world and artificially occluded images to test and benchmark leading methods' robustness to partial occlusion in visual recognition tasks. In addition, we contribute the design and results of a human study using images from IRUO that evaluates human classification performance at multiple levels and types of occlusion. We find that modern CNN-based models show improved recognition accuracy on occluded images compared to earlier CNN-based models, and ViT-based models are more accurate than CNN-based models on occluded images, performing only modestly worse than human accuracy. We also find that certain types of occlusion, including diffuse occlusion, where relevant objects are seen through "holes" in occluders such as fences and leaves, can greatly reduce the accuracy of deep recognition models as compared to humans, especially those with CNN backbones.
Segment anything, from space?
May 15, 2023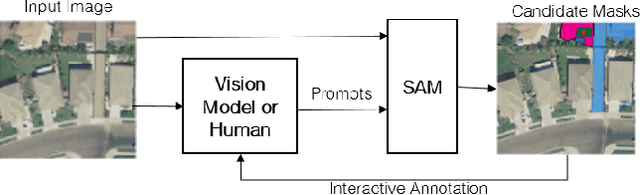
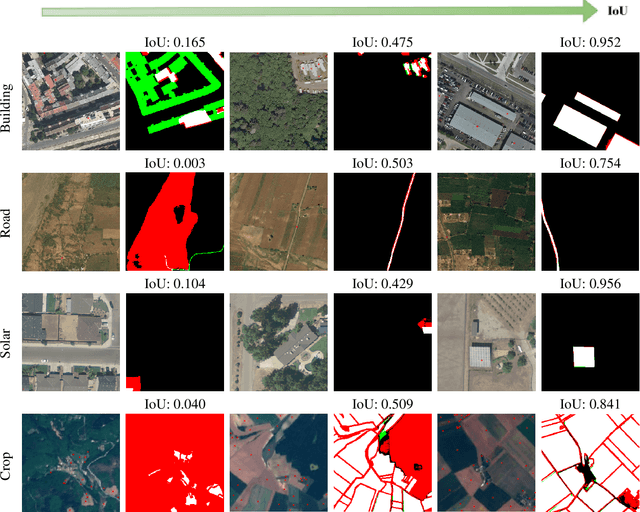
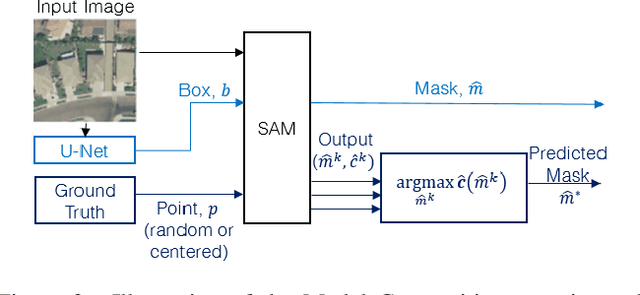
Abstract:Recently, the first foundation model developed specifically for vision tasks was developed, termed the "Segment Anything Model" (SAM). SAM can segment objects in input imagery based upon cheap input prompts, such as one (or more) points, a bounding box, or a mask. The authors examined the zero-shot image segmentation accuracy of SAM on a large number of vision benchmark tasks and found that SAM usually achieved recognition accuracy similar to, or sometimes exceeding, vision models that had been trained on the target tasks. The impressive generalization of SAM for segmentation has major implications for vision researchers working on natural imagery. In this work, we examine whether SAM's impressive performance extends to overhead imagery problems, and help guide the community's response to its development. We examine SAM's performance on a set of diverse and widely-studied benchmark tasks. We find that SAM does often generalize well to overhead imagery, although it fails in some cases due to the unique characteristics of overhead imagery and the target objects. We report on these unique systematic failure cases for remote sensing imagery that may comprise useful future research for the community. Note that this is a working paper, and it will be updated as additional analysis and results are completed.
Meta-Learning for Color-to-Infrared Cross-Modal Style Transfer
Dec 24, 2022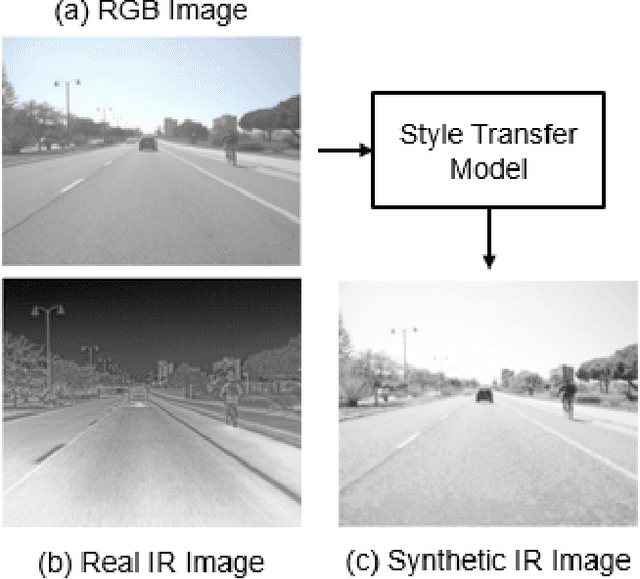


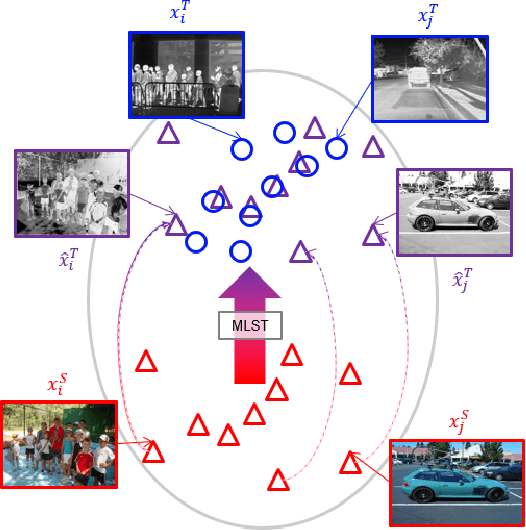
Abstract:Recent object detection models for infrared (IR) imagery are based upon deep neural networks (DNNs) and require large amounts of labeled training imagery. However, publicly-available datasets that can be used for such training are limited in their size and diversity. To address this problem, we explore cross-modal style transfer (CMST) to leverage large and diverse color imagery datasets so that they can be used to train DNN-based IR image based object detectors. We evaluate six contemporary stylization methods on four publicly-available IR datasets - the first comparison of its kind - and find that CMST is highly effective for DNN-based detectors. Surprisingly, we find that existing data-driven methods are outperformed by a simple grayscale stylization (an average of the color channels). Our analysis reveals that existing data-driven methods are either too simplistic or introduce significant artifacts into the imagery. To overcome these limitations, we propose meta-learning style transfer (MLST), which learns a stylization by composing and tuning well-behaved analytic functions. We find that MLST leads to more complex stylizations without introducing significant image artifacts and achieves the best overall detector performance on our benchmark datasets.
Transformers For Recognition In Overhead Imagery: A Reality Check
Oct 31, 2022



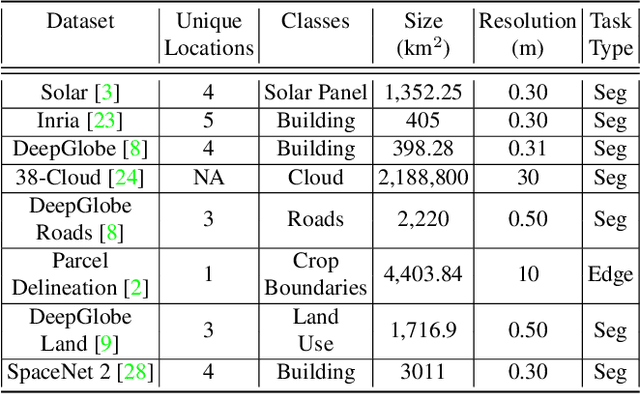
Abstract:There is evidence that transformers offer state-of-the-art recognition performance on tasks involving overhead imagery (e.g., satellite imagery). However, it is difficult to make unbiased empirical comparisons between competing deep learning models, making it unclear whether, and to what extent, transformer-based models are beneficial. In this paper we systematically compare the impact of adding transformer structures into state-of-the-art segmentation models for overhead imagery. Each model is given a similar budget of free parameters, and their hyperparameters are optimized using Bayesian Optimization with a fixed quantity of data and computation time. We conduct our experiments with a large and diverse dataset comprising two large public benchmarks: Inria and DeepGlobe. We perform additional ablation studies to explore the impact of specific transformer-based modeling choices. Our results suggest that transformers provide consistent, but modest, performance improvements. We only observe this advantage however in hybrid models that combine convolutional and transformer-based structures, while fully transformer-based models achieve relatively poor performance.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge