Flavio A. P. Alvarenga
Animal Behavior Classification via Accelerometry Data and Recurrent Neural Networks
Nov 24, 2021
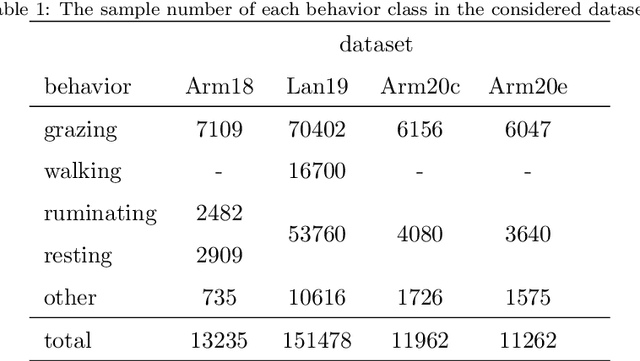
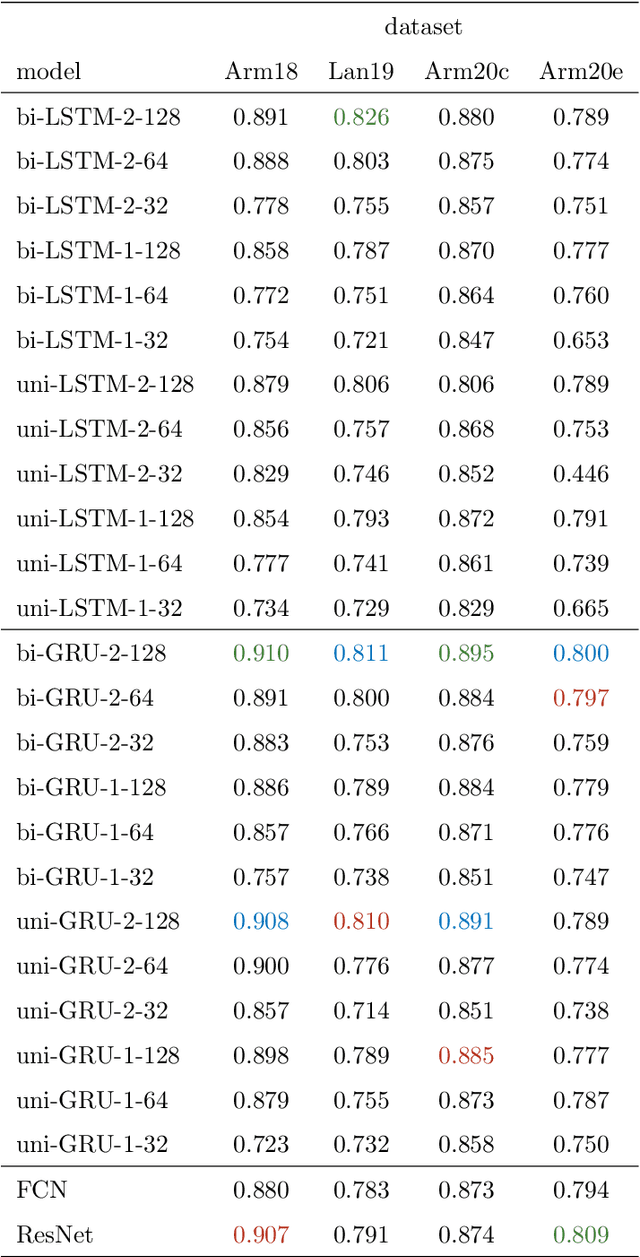
Abstract:We study the classification of animal behavior using accelerometry data through various recurrent neural network (RNN) models. We evaluate the classification performance and complexity of the considered models, which feature long short-time memory (LSTM) or gated recurrent unit (GRU) architectures with varying depths and widths, using four datasets acquired from cattle via collar or ear tags. We also include two state-of-the-art convolutional neural network (CNN)-based time-series classification models in the evaluations. The results show that the RNN-based models can achieve similar or higher classification accuracy compared with the CNN-based models while having less computational and memory requirements. We also observe that the models with GRU architecture generally outperform the ones with LSTM architecture in terms of classification accuracy despite being less complex. A single-layer uni-directional GRU model with 64 hidden units appears to offer a good balance between accuracy and complexity making it suitable for implementation on edge/embedded devices.
Animal Behavior Classification via Deep Learning on Embedded Systems
Nov 24, 2021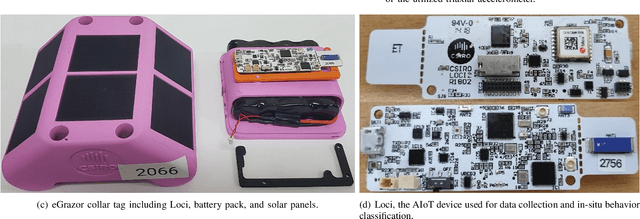
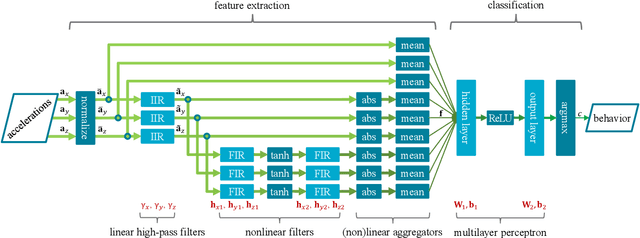
Abstract:We develop an end-to-end deep-neural-network-based algorithm for classifying animal behavior using accelerometry data on the embedded system of an artificial intelligence of things (AIoT) device installed in a wearable collar tag. The proposed algorithm jointly performs feature extraction and classification utilizing a set of infinite-impulse-response (IIR) and finite-impulse-response (FIR) filters together with a multilayer perceptron. The utilized IIR and FIR filters can be viewed as specific types of recurrent and convolutional neural network layers, respectively. We evaluate the performance of the proposed algorithm via two real-world datasets collected from grazing cattle. The results show that the proposed algorithm offers good intra- and inter-dataset classification accuracy and outperforms its closest contenders including two state-of-the-art convolutional-neural-network-based time-series classification algorithms, which are significantly more complex. We implement the proposed algorithm on the embedded system of the collar tag's AIoT device to perform in-situ classification of animal behavior. We achieve real-time in-situ behavior inference from accelerometry data without imposing any strain on the available computational, memory, or energy resources of the embedded system.
Video-based cattle identification and action recognition
Oct 14, 2021

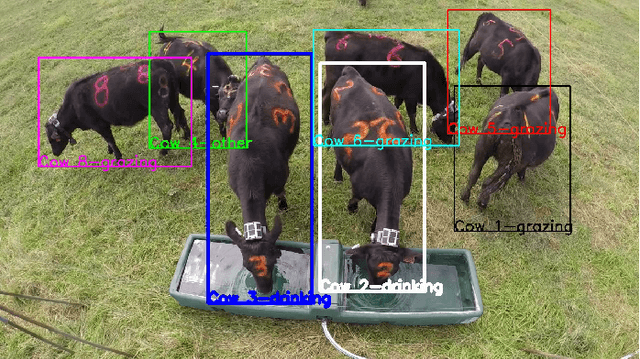
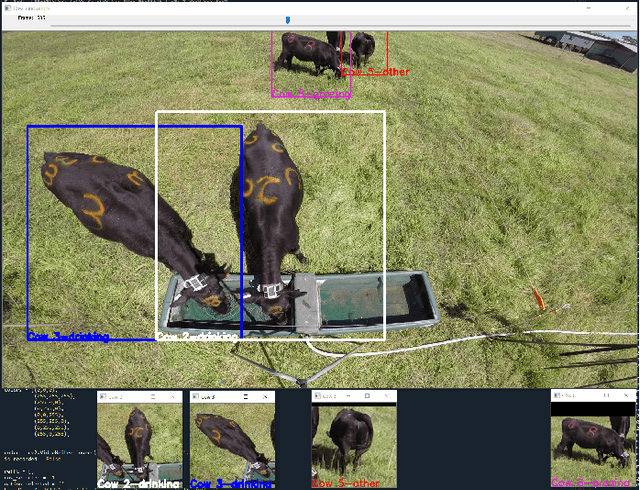
Abstract:We demonstrate a working prototype for the monitoring of cow welfare by automatically analysing the animal behaviours. Deep learning models have been developed and tested with videos acquired in a farm, and a precision of 81.2\% has been achieved for cow identification. An accuracy of 84.4\% has been achieved for the detection of drinking events, and 94.4\% for the detection of grazing events. Experimental results show that the proposed deep learning method can be used to identify the behaviours of individual animals to enable automated farm provenance. Our raw and ground-truth dataset will be released as the first public video dataset for cow identification and action recognition. Recommendations for further development are also provided.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge