Feihu Jin
Prior-Informed Zeroth-Order Optimization with Adaptive Direction Alignment for Memory-Efficient LLM Fine-Tuning
Jan 08, 2026Abstract:Fine-tuning large language models (LLMs) has achieved remarkable success across various NLP tasks, but the substantial memory overhead during backpropagation remains a critical bottleneck, especially as model scales grow. Zeroth-order (ZO) optimization alleviates this issue by estimating gradients through forward passes and Gaussian sampling, avoiding the need for backpropagation. However, conventional ZO methods suffer from high variance in gradient estimation due to their reliance on random perturbations, leading to slow convergence and suboptimal performance. We propose a simple plug-and-play method that incorporates prior-informed perturbations to refine gradient estimation. Our method dynamically computes a guiding vector from Gaussian samples, which directs perturbations toward more informative directions, significantly accelerating convergence compared to standard ZO approaches. We further investigate a greedy perturbation strategy to explore the impact of prior knowledge on gradient estimation. Theoretically, we prove that our gradient estimator achieves stronger alignment with the true gradient direction, enhancing optimization efficiency. Extensive experiments across LLMs of varying scales and architectures demonstrate that our proposed method could seamlessly integrate into existing optimization methods, delivering faster convergence and superior performance. Notably, on the OPT-13B model, our method outperforms traditional ZO optimization across all 11 benchmark tasks and surpasses gradient-based baselines on 9 out of 11 tasks, establishing a robust balance between efficiency and accuracy.
Derivative-Free Optimization for Low-Rank Adaptation in Large Language Models
Mar 04, 2024
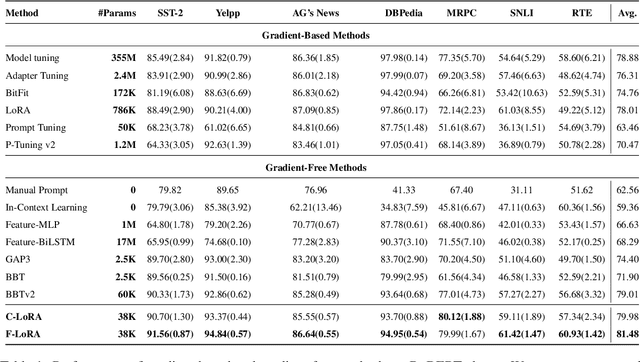

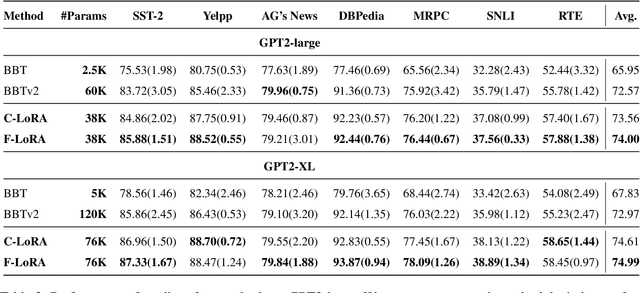
Abstract:Parameter-efficient tuning methods such as LoRA could achieve comparable performance to model tuning by tuning a small portion of the parameters. However, substantial computational resources are still required, as this process involves calculating gradients and performing back-propagation throughout the model. Much effort has recently been devoted to utilizing the derivative-free optimization method to eschew the computation of gradients and showcase an augmented level of robustness in few-shot settings. In this paper, we prepend the low-rank modules into each self-attention layer of the model and employ two derivative-free optimization methods to optimize these low-rank modules at each layer alternately. Extensive results on various tasks and language models demonstrate that our proposed method achieves substantial improvement and exhibits clear advantages in memory usage and convergence speed compared to existing gradient-based parameter-efficient tuning and derivative-free optimization methods in few-shot settings.
Zero-Shot Chain-of-Thought Reasoning Guided by Evolutionary Algorithms in Large Language Models
Feb 08, 2024Abstract:Large Language Models (LLMs) have demonstrated remarkable performance across diverse tasks and exhibited impressive reasoning abilities by applying zero-shot Chain-of-Thought (CoT) prompting. However, due to the evolving nature of sentence prefixes during the pre-training phase, existing zero-shot CoT prompting methods that employ identical CoT prompting across all task instances may not be optimal. In this paper, we introduce a novel zero-shot prompting method that leverages evolutionary algorithms to generate diverse promptings for LLMs dynamically. Our approach involves initializing two CoT promptings, performing evolutionary operations based on LLMs to create a varied set, and utilizing the LLMs to select a suitable CoT prompting for a given problem. Additionally, a rewriting operation, guided by the selected CoT prompting, enhances the understanding of the LLMs about the problem. Extensive experiments conducted across ten reasoning datasets demonstrate the superior performance of our proposed method compared to current zero-shot CoT prompting methods on GPT-3.5-turbo and GPT-4. Moreover, in-depth analytical experiments underscore the adaptability and effectiveness of our method in various reasoning tasks.
Instance-aware Prompt Learning for Language Understanding and Generation
Jan 18, 2022



Abstract:Recently, prompt learning has become a new paradigm to utilize pre-trained language models (PLMs) and achieves promising results in downstream tasks with a negligible increase of parameters. The current usage of discrete and continuous prompts assumes that the prompt is fixed for a specific task and all samples in the task share the same prompt. However, a task may contain quite diverse samples in which some are easy and others are difficult, and diverse prompts are desirable. In this paper, we propose an instance-aware prompt learning method that learns a different prompt for each instance. Specifically, we suppose that each learnable prompt token has a different contribution to different instances, and we learn the contribution by calculating the relevance score between an instance and each prompt token. The contribution weighted prompt would be instance aware. We apply our method to both unidirectional and bidirectional PLMs on both language understanding and generation tasks. Extensive experiments demonstrate that our method obtains considerable improvements compared to strong baselines. Especially, our method achieves the state-of-the-art on the SuperGLUE few-shot learning benchmark.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge