Feifei Qi
A Novel Semi-supervised Meta Learning Method for Subject-transfer Brain-computer Interface
Sep 07, 2022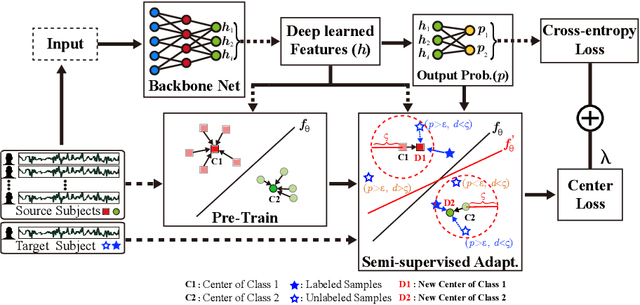
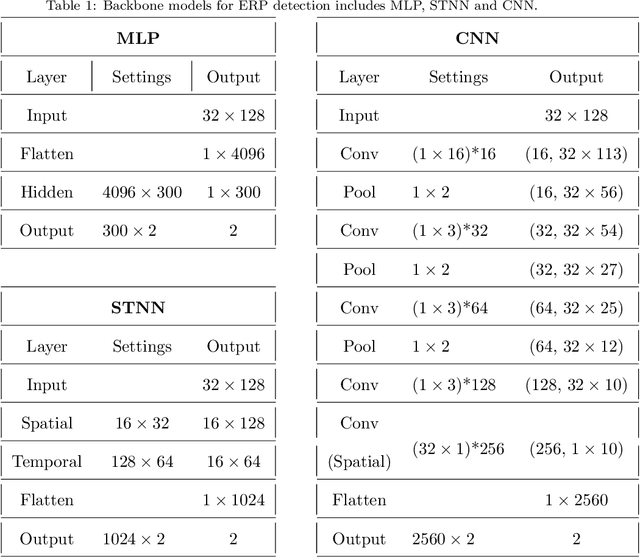
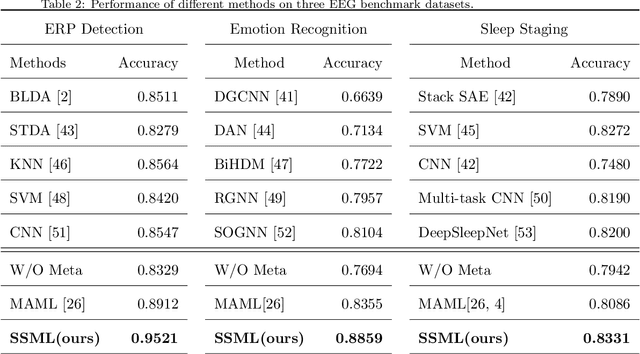
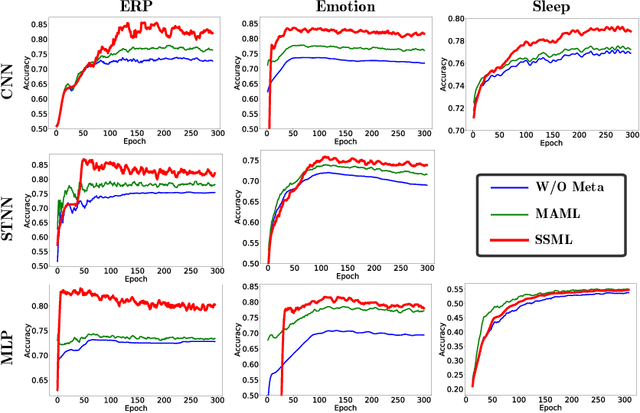
Abstract:Brain-computer interface (BCI) provides a direct communication pathway between human brain and external devices. Before a new subject could use BCI, a calibration procedure is usually required. Because the inter- and intra-subject variances are so large that the models trained by the existing subjects perform poorly on new subjects. Therefore, effective subject-transfer and calibration method is essential. In this paper, we propose a semi-supervised meta learning (SSML) method for subject-transfer learning in BCIs. The proposed SSML learns a meta model with the existing subjects first, then fine-tunes the model in a semi-supervised learning manner, i.e. using few labeled and many unlabeled samples of target subject for calibration. It is significant for BCI applications where the labeled data are scarce or expensive while unlabeled data are readily available. To verify the SSML method, three different BCI paradigms are tested: 1) event-related potential detection; 2) emotion recognition; and 3) sleep staging. The SSML achieved significant improvements of over 15% on the first two paradigms and 4.9% on the third. The experimental results demonstrated the effectiveness and potential of the SSML method in BCI applications.
Electromagnetic Source Imaging via a Data-Synthesis-Based Denoising Autoencoder
Oct 31, 2020



Abstract:Electromagnetic source imaging (ESI) is a highly ill-posed inverse problem. To find a unique solution, traditional ESI methods impose a variety of priors that may not reflect the actual source properties. Such limitations of traditional ESI methods hinder their further applications. Inspired by deep learning approaches, a novel data-synthesized spatio-temporal denoising autoencoder method (DST-DAE) method was proposed to solve the ESI inverse problem. Unlike the traditional methods, we utilize a neural network to directly seek generalized mapping from the measured E/MEG signals to the cortical sources. A novel data synthesis strategy is employed by introducing the prior information of sources to the generated large-scale samples using the forward model of ESI. All the generated data are used to drive the neural network to automatically learn inverse mapping. To achieve better estimation performance, a denoising autoencoder (DAE) architecture with spatio-temporal feature extraction blocks is designed. Compared with the traditional methods, we show (1) that the novel deep learning approach provides an effective and easy-to-apply way to solve the ESI problem, that (2) compared to traditional methods, DST-DAE with the data synthesis strategy can better consider the characteristics of real sources than the mathematical formulation of prior assumptions, and that (3) the specifically designed architecture of DAE can not only provide a better estimation of source signals but also be robust to noise pollution. Extensive numerical experiments show that the proposed method is superior to the traditional knowledge-driven ESI methods.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge