Jingcong Li
A Novel Semi-supervised Meta Learning Method for Subject-transfer Brain-computer Interface
Sep 07, 2022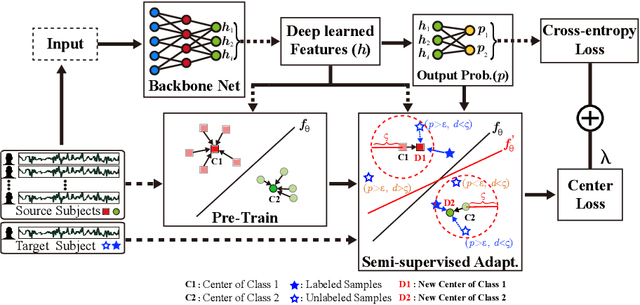
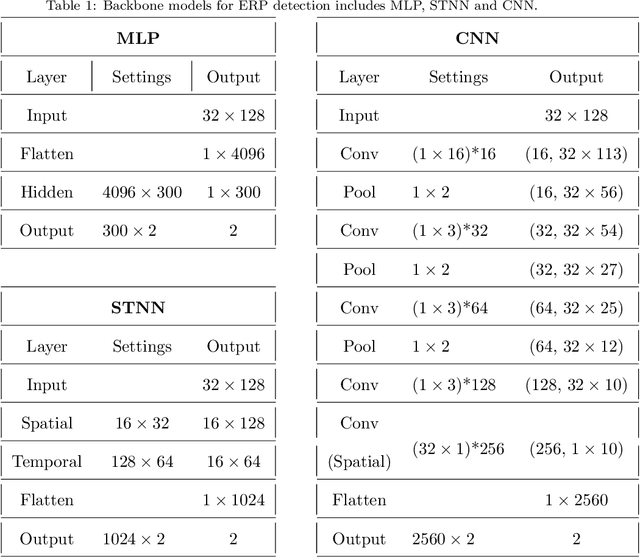
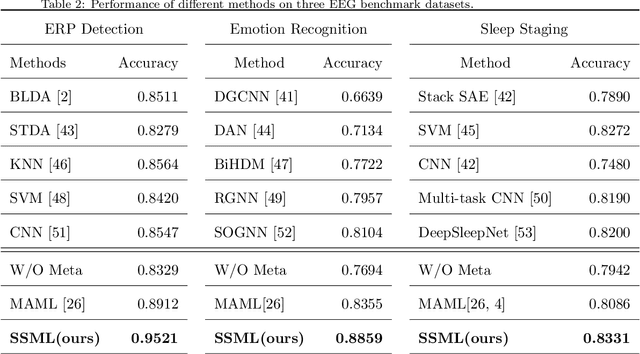
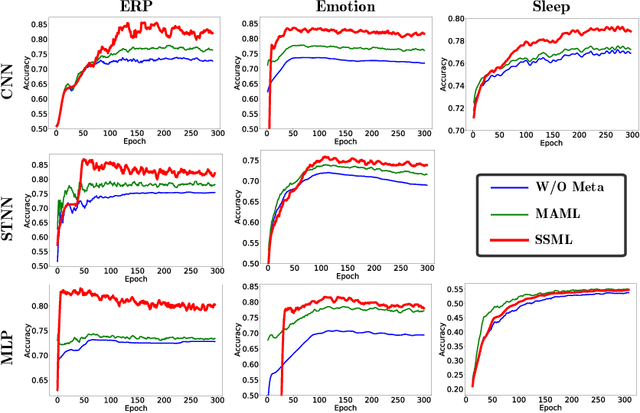
Abstract:Brain-computer interface (BCI) provides a direct communication pathway between human brain and external devices. Before a new subject could use BCI, a calibration procedure is usually required. Because the inter- and intra-subject variances are so large that the models trained by the existing subjects perform poorly on new subjects. Therefore, effective subject-transfer and calibration method is essential. In this paper, we propose a semi-supervised meta learning (SSML) method for subject-transfer learning in BCIs. The proposed SSML learns a meta model with the existing subjects first, then fine-tunes the model in a semi-supervised learning manner, i.e. using few labeled and many unlabeled samples of target subject for calibration. It is significant for BCI applications where the labeled data are scarce or expensive while unlabeled data are readily available. To verify the SSML method, three different BCI paradigms are tested: 1) event-related potential detection; 2) emotion recognition; and 3) sleep staging. The SSML achieved significant improvements of over 15% on the first two paradigms and 4.9% on the third. The experimental results demonstrated the effectiveness and potential of the SSML method in BCI applications.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge