Farzaneh Rezaeianaran
Reliable Student: Addressing Noise in Semi-Supervised 3D Object Detection
Apr 27, 2024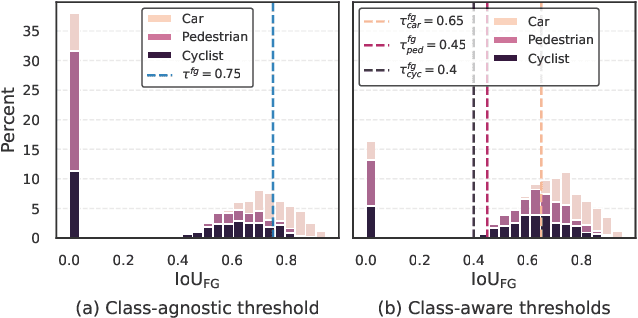
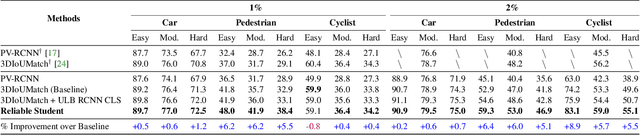
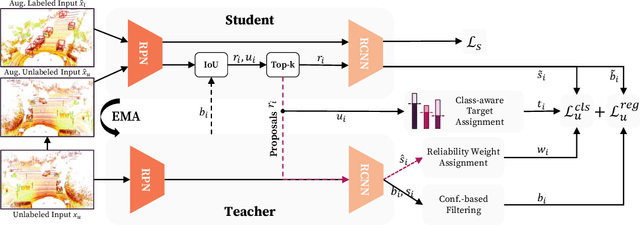
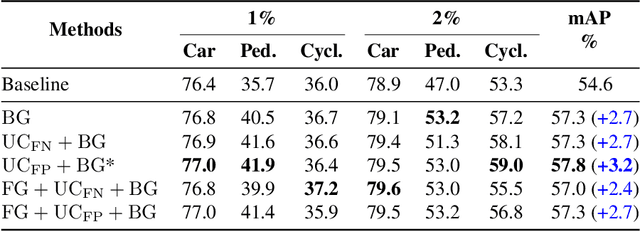
Abstract:Semi-supervised 3D object detection can benefit from the promising pseudo-labeling technique when labeled data is limited. However, recent approaches have overlooked the impact of noisy pseudo-labels during training, despite efforts to enhance pseudo-label quality through confidence-based filtering. In this paper, we examine the impact of noisy pseudo-labels on IoU-based target assignment and propose the Reliable Student framework, which incorporates two complementary approaches to mitigate errors. First, it involves a class-aware target assignment strategy that reduces false negative assignments in difficult classes. Second, it includes a reliability weighting strategy that suppresses false positive assignment errors while also addressing remaining false negatives from the first step. The reliability weights are determined by querying the teacher network for confidence scores of the student-generated proposals. Our work surpasses the previous state-of-the-art on KITTI 3D object detection benchmark on point clouds in the semi-supervised setting. On 1% labeled data, our approach achieves a 6.2% AP improvement for the pedestrian class, despite having only 37 labeled samples available. The improvements become significant for the 2% setting, achieving 6.0% AP and 5.7% AP improvements for the pedestrian and cyclist classes, respectively.
Seeking Similarities over Differences: Similarity-based Domain Alignment for Adaptive Object Detection
Oct 04, 2021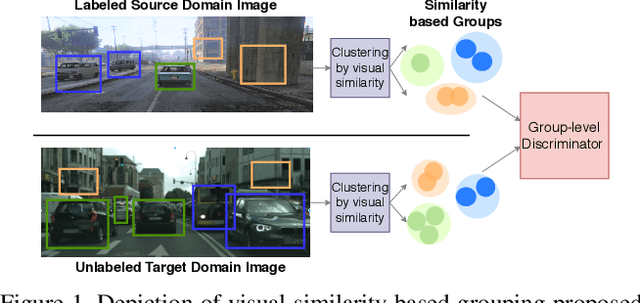
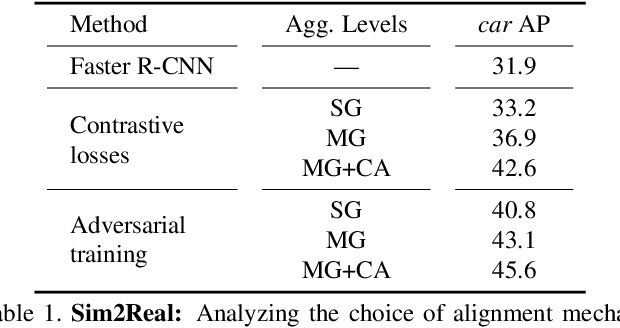
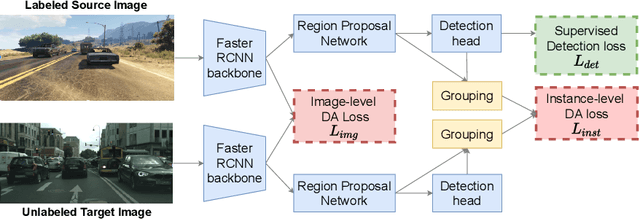
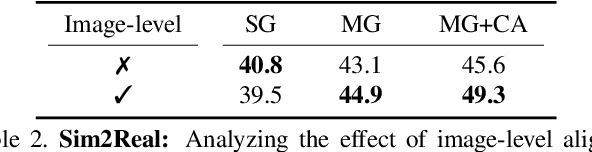
Abstract:In order to robustly deploy object detectors across a wide range of scenarios, they should be adaptable to shifts in the input distribution without the need to constantly annotate new data. This has motivated research in Unsupervised Domain Adaptation (UDA) algorithms for detection. UDA methods learn to adapt from labeled source domains to unlabeled target domains, by inducing alignment between detector features from source and target domains. Yet, there is no consensus on what features to align and how to do the alignment. In our work, we propose a framework that generalizes the different components commonly used by UDA methods laying the ground for an in-depth analysis of the UDA design space. Specifically, we propose a novel UDA algorithm, ViSGA, a direct implementation of our framework, that leverages the best design choices and introduces a simple but effective method to aggregate features at instance-level based on visual similarity before inducing group alignment via adversarial training. We show that both similarity-based grouping and adversarial training allows our model to focus on coarsely aligning feature groups, without being forced to match all instances across loosely aligned domains. Finally, we examine the applicability of ViSGA to the setting where labeled data are gathered from different sources. Experiments show that not only our method outperforms previous single-source approaches on Sim2Real and Adverse Weather, but also generalizes well to the multi-source setting.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge