Evžen Wybitul
Representations of Text and Images Align From Layer One
Jan 12, 2026Abstract:We show that for a variety of concepts in adapter-based vision-language models, the representations of their images and their text descriptions are meaningfully aligned from the very first layer. This contradicts the established view that such image-text alignment only appears in late layers. We show this using a new synthesis-based method inspired by DeepDream: given a textual concept such as "Jupiter", we extract its concept vector at a given layer, and then use optimisation to synthesise an image whose representation aligns with that vector. We apply our approach to hundreds of concepts across seven layers in Gemma 3, and find that the synthesised images often depict salient visual features of the targeted textual concepts: for example, already at layer 1, more than 50 % of images depict recognisable features of animals, activities, or seasons. Our method thus provides direct, constructive evidence of image-text alignment on a concept-by-concept and layer-by-layer basis. Unlike previous methods for measuring multimodal alignment, our approach is simple, fast, and does not require auxiliary models or datasets. It also offers a new path towards model interpretability, by providing a way to visualise a model's representation space by backtracing through its image processing components.
Access Controls Will Solve the Dual-Use Dilemma
May 14, 2025Abstract:AI safety systems face a dual-use dilemma. Since the same request can be either harmless or harmful depending on who made it and why, if the system makes decisions based solely on the request's content, it will refuse some legitimate queries and let pass harmful ones. To address this, we propose a conceptual access control framework, based on verified user credentials (such as institutional affiliation) and classifiers that assign model outputs to risk categories (such as advanced virology). The system permits responses only when the user's verified credentials match the category's requirements. For implementation of the model output classifiers, we introduce a theoretical approach utilizing small, gated expert modules integrated into the generator model, trained with gradient routing, that enable efficient risk detection without the capability gap problems of external monitors. While open questions remain about the verification mechanisms, risk categories, and the technical implementation, our framework makes the first step toward enabling granular governance of AI capabilities: verified users gain access to specialized knowledge without arbitrary restrictions, while adversaries are blocked from it. This contextual approach reconciles model utility with robust safety, addressing the dual-use dilemma.
ViSTa Dataset: Do vision-language models understand sequential tasks?
Nov 21, 2024



Abstract:Using vision-language models (VLMs) as reward models in reinforcement learning holds promise for reducing costs and improving safety. So far, VLM reward models have only been used for goal-oriented tasks, where the agent must reach a particular final outcome. We explore VLMs' potential to supervise tasks that cannot be scored by the final state alone. To this end, we introduce ViSTa, a dataset for evaluating Vision-based understanding of Sequential Tasks. ViSTa comprises over 4,000 videos with step-by-step descriptions in virtual home, Minecraft, and real-world environments. Its novel hierarchical structure -- basic single-step tasks composed into more and more complex sequential tasks -- allows a fine-grained understanding of how well VLMs can judge tasks with varying complexity. To illustrate this, we use ViSTa to evaluate state-of-the-art VLMs, including CLIP, ViCLIP, and GPT-4o. We find that, while they are all good at object recognition, they fail to understand sequential tasks, with only GPT-4o achieving non-trivial performance.
Gradient Routing: Masking Gradients to Localize Computation in Neural Networks
Oct 06, 2024
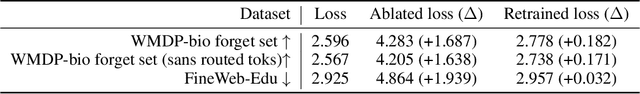
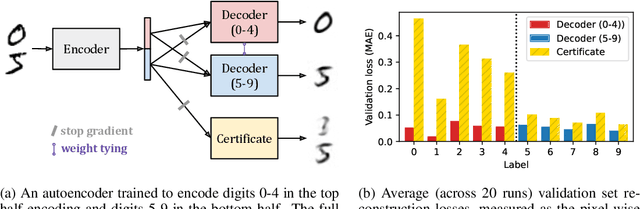

Abstract:Neural networks are trained primarily based on their inputs and outputs, without regard for their internal mechanisms. These neglected mechanisms determine properties that are critical for safety, like (i) transparency; (ii) the absence of sensitive information or harmful capabilities; and (iii) reliable generalization of goals beyond the training distribution. To address this shortcoming, we introduce gradient routing, a training method that isolates capabilities to specific subregions of a neural network. Gradient routing applies data-dependent, weighted masks to gradients during backpropagation. These masks are supplied by the user in order to configure which parameters are updated by which data points. We show that gradient routing can be used to (1) learn representations which are partitioned in an interpretable way; (2) enable robust unlearning via ablation of a pre-specified network subregion; and (3) achieve scalable oversight of a reinforcement learner by localizing modules responsible for different behaviors. Throughout, we find that gradient routing localizes capabilities even when applied to a limited, ad-hoc subset of the data. We conclude that the approach holds promise for challenging, real-world applications where quality data are scarce.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge