Erik Buchholz
What is the Cost of Differential Privacy for Deep Learning-Based Trajectory Generation?
Jun 11, 2025Abstract:While location trajectories offer valuable insights, they also reveal sensitive personal information. Differential Privacy (DP) offers formal protection, but achieving a favourable utility-privacy trade-off remains challenging. Recent works explore deep learning-based generative models to produce synthetic trajectories. However, current models lack formal privacy guarantees and rely on conditional information derived from real data during generation. This work investigates the utility cost of enforcing DP in such models, addressing three research questions across two datasets and eleven utility metrics. (1) We evaluate how DP-SGD, the standard DP training method for deep learning, affects the utility of state-of-the-art generative models. (2) Since DP-SGD is limited to unconditional models, we propose a novel DP mechanism for conditional generation that provides formal guarantees and assess its impact on utility. (3) We analyse how model types - Diffusion, VAE, and GAN - affect the utility-privacy trade-off. Our results show that DP-SGD significantly impacts performance, although some utility remains if the datasets is sufficiently large. The proposed DP mechanism improves training stability, particularly when combined with DP-SGD, for unstable models such as GANs and on smaller datasets. Diffusion models yield the best utility without guarantees, but with DP-SGD, GANs perform best, indicating that the best non-private model is not necessarily optimal when targeting formal guarantees. In conclusion, DP trajectory generation remains a challenging task, and formal guarantees are currently only feasible with large datasets and in constrained use cases.
Demystifying Trajectory Recovery From Ash: An Open-Source Evaluation and Enhancement
Sep 23, 2024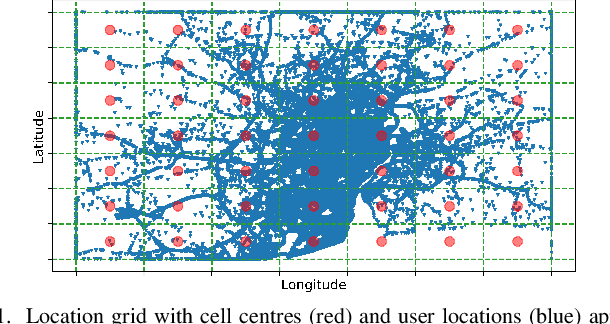
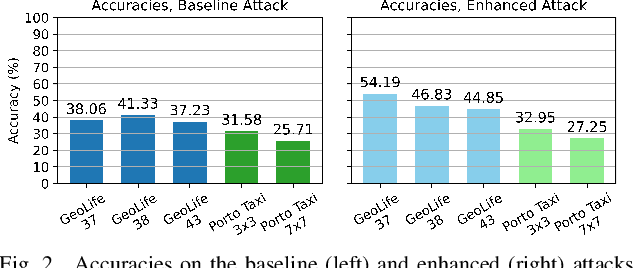
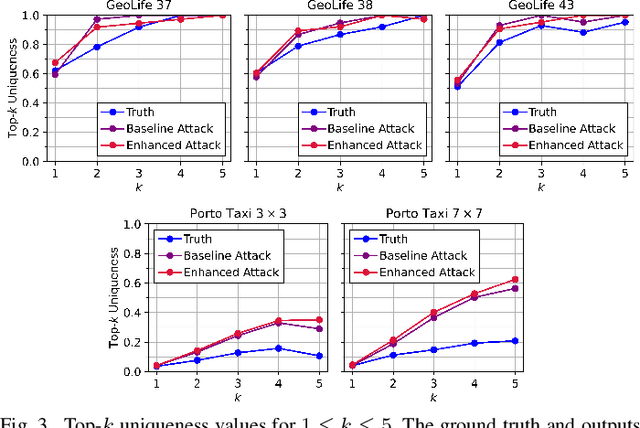
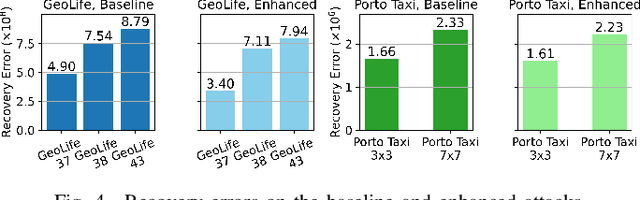
Abstract:Once analysed, location trajectories can provide valuable insights beneficial to various applications. However, such data is also highly sensitive, rendering them susceptible to privacy risks in the event of mismanagement, for example, revealing an individual's identity, home address, or political affiliations. Hence, ensuring that privacy is preserved for this data is a priority. One commonly taken measure to mitigate this concern is aggregation. Previous work by Xu et al. shows that trajectories are still recoverable from anonymised and aggregated datasets. However, the study lacks implementation details, obfuscating the mechanisms of the attack. Additionally, the attack was evaluated on commercial non-public datasets, rendering the results and subsequent claims unverifiable. This study reimplements the trajectory recovery attack from scratch and evaluates it on two open-source datasets, detailing the preprocessing steps and implementation. Results confirm that privacy leakage still exists despite common anonymisation and aggregation methods but also indicate that the initial accuracy claims may have been overly ambitious. We release all code as open-source to ensure the results are entirely reproducible and, therefore, verifiable. Moreover, we propose a stronger attack by designing a series of enhancements to the baseline attack. These enhancements yield higher accuracies by up to 16%, providing an improved benchmark for future research in trajectory recovery methods. Our improvements also enable online execution of the attack, allowing partial attacks on larger datasets previously considered unprocessable, thereby furthering the extent of privacy leakage. The findings emphasise the importance of using strong privacy-preserving mechanisms when releasing aggregated mobility data and not solely relying on aggregation as a means of anonymisation.
Synthetic Trajectory Generation Through Convolutional Neural Networks
Jul 24, 2024


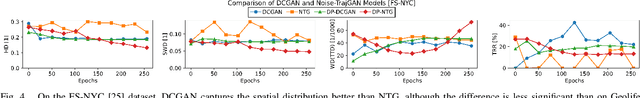
Abstract:Location trajectories provide valuable insights for applications from urban planning to pandemic control. However, mobility data can also reveal sensitive information about individuals, such as political opinions, religious beliefs, or sexual orientations. Existing privacy-preserving approaches for publishing this data face a significant utility-privacy trade-off. Releasing synthetic trajectory data generated through deep learning offers a promising solution. Due to the trajectories' sequential nature, most existing models are based on recurrent neural networks (RNNs). However, research in generative adversarial networks (GANs) largely employs convolutional neural networks (CNNs) for image generation. This discrepancy raises the question of whether advances in computer vision can be applied to trajectory generation. In this work, we introduce a Reversible Trajectory-to-CNN Transformation (RTCT) that adapts trajectories into a format suitable for CNN-based models. We integrated this transformation with the well-known DCGAN in a proof-of-concept (PoC) and evaluated its performance against an RNN-based trajectory GAN using four metrics across two datasets. The PoC was superior in capturing spatial distributions compared to the RNN model but had difficulty replicating sequential and temporal properties. Although the PoC's utility is not sufficient for practical applications, the results demonstrate the transformation's potential to facilitate the use of CNNs for trajectory generation, opening up avenues for future research. To support continued research, all source code has been made available under an open-source license.
SoK: Can Trajectory Generation Combine Privacy and Utility?
Mar 12, 2024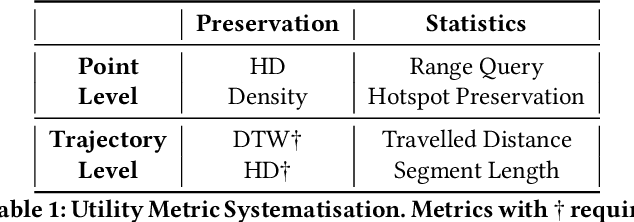
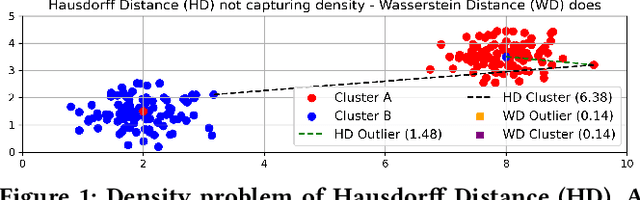
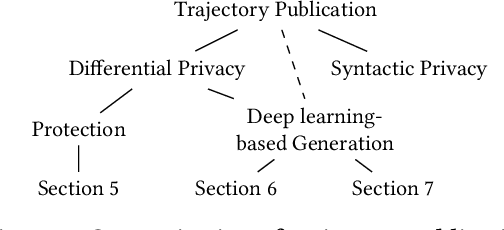
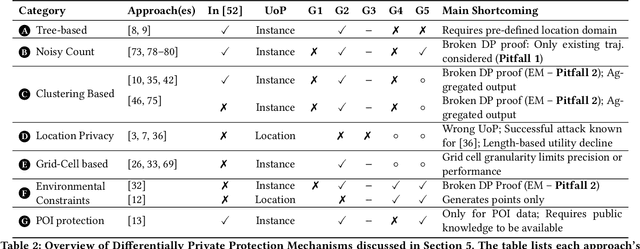
Abstract:While location trajectories represent a valuable data source for analyses and location-based services, they can reveal sensitive information, such as political and religious preferences. Differentially private publication mechanisms have been proposed to allow for analyses under rigorous privacy guarantees. However, the traditional protection schemes suffer from a limiting privacy-utility trade-off and are vulnerable to correlation and reconstruction attacks. Synthetic trajectory data generation and release represent a promising alternative to protection algorithms. While initial proposals achieve remarkable utility, they fail to provide rigorous privacy guarantees. This paper proposes a framework for designing a privacy-preserving trajectory publication approach by defining five design goals, particularly stressing the importance of choosing an appropriate Unit of Privacy. Based on this framework, we briefly discuss the existing trajectory protection approaches, emphasising their shortcomings. This work focuses on the systematisation of the state-of-the-art generative models for trajectories in the context of the proposed framework. We find that no existing solution satisfies all requirements. Thus, we perform an experimental study evaluating the applicability of six sequential generative models to the trajectory domain. Finally, we conclude that a generative trajectory model providing semantic guarantees remains an open research question and propose concrete next steps for future research.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge