Erfan Soltanmohammadi
Speech Retrieval-Augmented Generation without Automatic Speech Recognition
Dec 21, 2024



Abstract:One common approach for question answering over speech data is to first transcribe speech using automatic speech recognition (ASR) and then employ text-based retrieval-augmented generation (RAG) on the transcriptions. While this cascaded pipeline has proven effective in many practical settings, ASR errors can propagate to the retrieval and generation steps. To overcome this limitation, we introduce SpeechRAG, a novel framework designed for open-question answering over spoken data. Our proposed approach fine-tunes a pre-trained speech encoder into a speech adapter fed into a frozen large language model (LLM)--based retrieval model. By aligning the embedding spaces of text and speech, our speech retriever directly retrieves audio passages from text-based queries, leveraging the retrieval capacity of the frozen text retriever. Our retrieval experiments on spoken question answering datasets show that direct speech retrieval does not degrade over the text-based baseline, and outperforms the cascaded systems using ASR. For generation, we use a speech language model (SLM) as a generator, conditioned on audio passages rather than transcripts. Without fine-tuning of the SLM, this approach outperforms cascaded text-based models when there is high WER in the transcripts.
Neural Harmonium: An Interpretable Deep Structure for Nonlinear Dynamic System Identification with Application to Audio Processing
Oct 10, 2023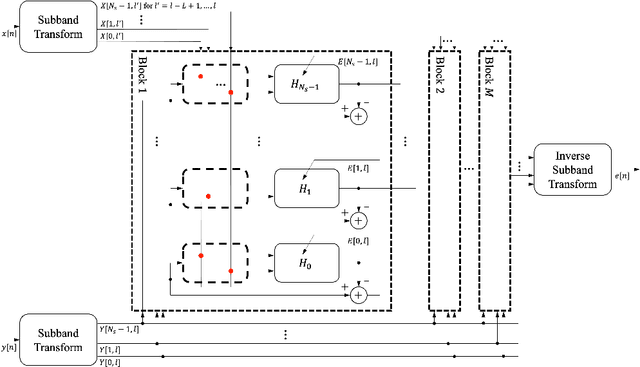
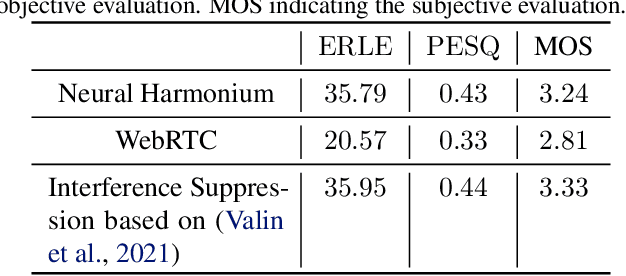
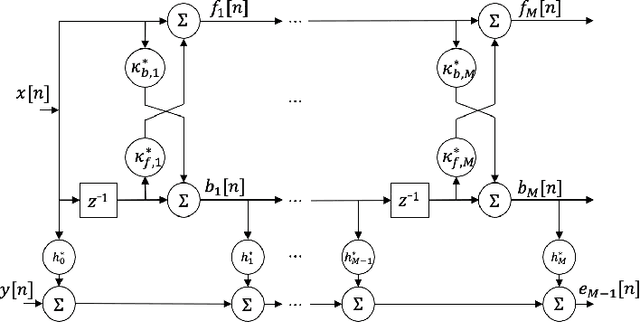
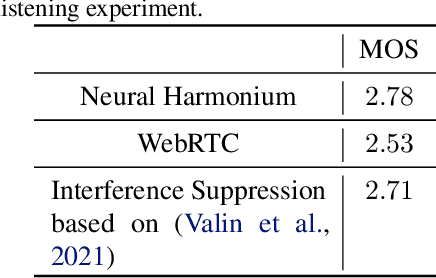
Abstract:Improving the interpretability of deep neural networks has recently gained increased attention, especially when the power of deep learning is leveraged to solve problems in physics. Interpretability helps us understand a model's ability to generalize and reveal its limitations. In this paper, we introduce a causal interpretable deep structure for modeling dynamic systems. Our proposed model makes use of the harmonic analysis by modeling the system in a time-frequency domain while maintaining high temporal and spectral resolution. Moreover, the model is built in an order recursive manner which allows for fast, robust, and exact second order optimization without the need for an explicit Hessian calculation. To circumvent the resulting high dimensionality of the building blocks of our system, a neural network is designed to identify the frequency interdependencies. The proposed model is illustrated and validated on nonlinear system identification problems as required for audio signal processing tasks. Crowd-sourced experimentation contrasting the performance of the proposed approach to other state-of-the-art solutions on an acoustic echo cancellation scenario confirms the effectiveness of our method for real-life applications.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge