Ellen Yi-Ge
DRUM: Learning Demonstration Retriever for Large MUlti-modal Models
Dec 10, 2024



Abstract:Recently, large language models (LLMs) have demonstrated impressive capabilities in dealing with new tasks with the help of in-context learning (ICL). In the study of Large Vision-Language Models (LVLMs), when implementing ICL, researchers usually adopts the naive strategies like fixed demonstrations across different samples, or selecting demonstrations directly via a visual-language embedding model. These methods does not guarantee the configured demonstrations fit the need of the LVLMs. To address this issue, we now propose a novel framework, \underline{d}emonstration \underline{r}etriever for large m\underline{u}lti-modal \underline{m}odel (DRUM), which fine-tunes the visual-language embedding model to better meet the LVLM's needs. First, we discuss the retrieval strategies for a visual-language task, assuming an embedding model is given. And we propose to concate the image and text embeddings to enhance the retrieval performance. Second, we propose to re-rank the demonstrations retrieved by the embedding model via the LVLM's feedbacks, and calculate a list-wise ranking loss for training the embedding model. Third, we propose an iterative demonstration mining strategy to improve the training of the embedding model. Through extensive experiments on 3 types of visual-language tasks, 7 benchmark datasets, our DRUM framework is proven to be effective in boosting the LVLM's in-context learning performance via retrieving more proper demonstrations.
Conditional Link Prediction of Category-Implicit Keypoint Detection
Nov 29, 2020
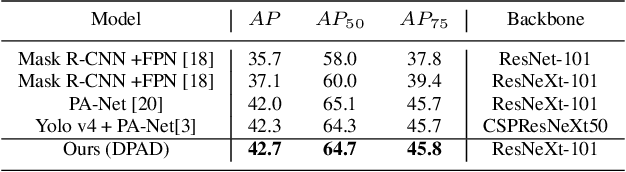

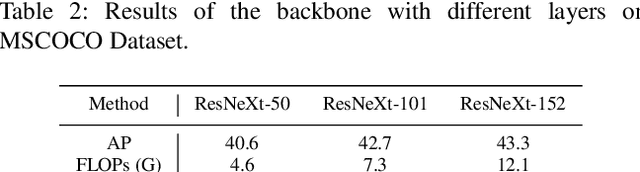
Abstract:Keypoints of objects reflect their concise abstractions, while the corresponding connection links (CL) build the skeleton by detecting the intrinsic relations between keypoints. Existing approaches are typically computationally-intensive, inapplicable for instances belonging to multiple classes, and/or infeasible to simultaneously encode connection information. To address the aforementioned issues, we propose an end-to-end category-implicit Keypoint and Link Prediction Network (KLPNet), which is the first approach for simultaneous semantic keypoint detection (for multi-class instances) and CL rejuvenation. In our KLPNet, a novel Conditional Link Prediction Graph is proposed for link prediction among keypoints that are contingent on a predefined category. Furthermore, a Cross-stage Keypoint Localization Module (CKLM) is introduced to explore feature aggregation for coarse-to-fine keypoint localization. Comprehensive experiments conducted on three publicly available benchmarks demonstrate that our KLPNet consistently outperforms all other state-of-the-art approaches. Furthermore, the experimental results of CL prediction also show the effectiveness of our KLPNet with respect to occlusion problems.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge