Ella Neeman
DisentQA: Disentangling Parametric and Contextual Knowledge with Counterfactual Question Answering
Nov 10, 2022Abstract:Question answering models commonly have access to two sources of "knowledge" during inference time: (1) parametric knowledge - the factual knowledge encoded in the model weights, and (2) contextual knowledge - external knowledge (e.g., a Wikipedia passage) given to the model to generate a grounded answer. Having these two sources of knowledge entangled together is a core issue for generative QA models as it is unclear whether the answer stems from the given non-parametric knowledge or not. This unclarity has implications on issues of trust, interpretability and factuality. In this work, we propose a new paradigm in which QA models are trained to disentangle the two sources of knowledge. Using counterfactual data augmentation, we introduce a model that predicts two answers for a given question: one based on given contextual knowledge and one based on parametric knowledge. Our experiments on the Natural Questions dataset show that this approach improves the performance of QA models by making them more robust to knowledge conflicts between the two knowledge sources, while generating useful disentangled answers.
$Q^{2}$: Evaluating Factual Consistency in Knowledge-Grounded Dialogues via Question Generation and Question Answering
Apr 16, 2021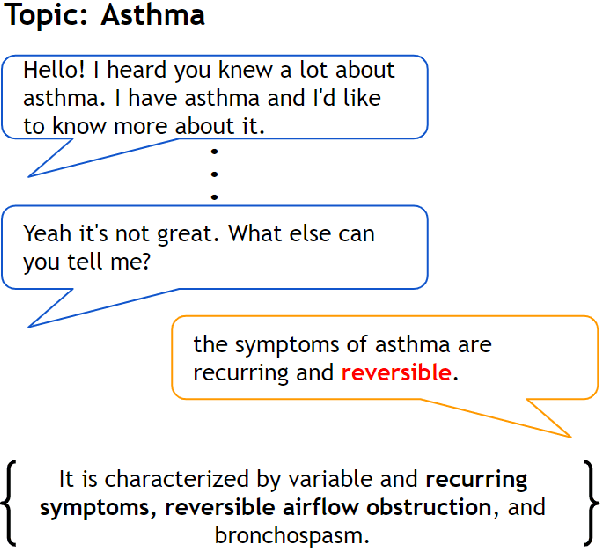
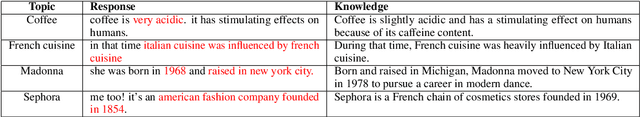
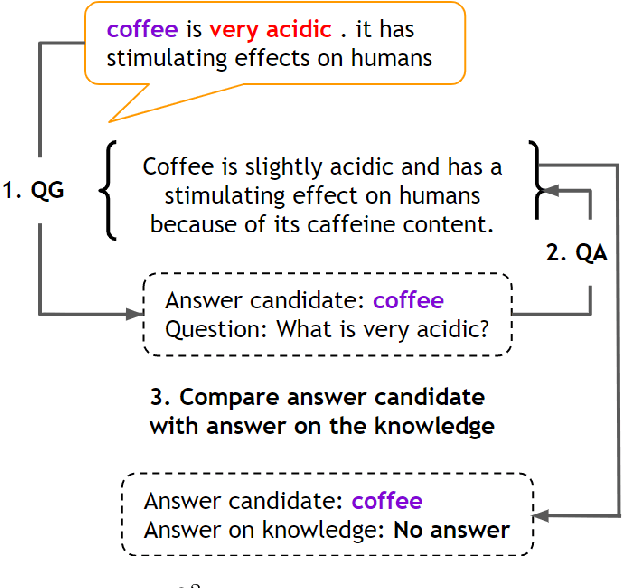
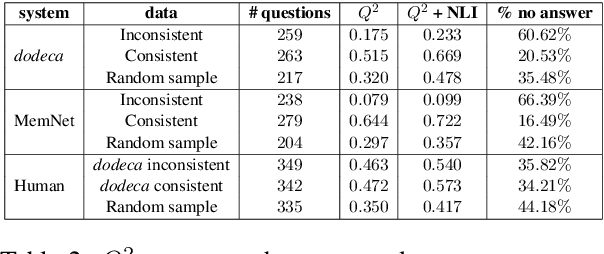
Abstract:Neural knowledge-grounded generative models for dialogue often produce content that is factually inconsistent with the source text they rely on. As a consequence, such models are unreliable, limiting their real-world applicability. Inspired by recent work on evaluating factual consistency in abstractive summarization (Durmus et al., 2020; Wang et al., 2020), we propose an automatic evaluation metric for factual consistency in knowledge-grounded dialogue models using automatic question generation and question answering. Unlike previous works which use naive token-based comparison of answer spans, our metric makes use of co-reference resolution and natural language inference capabilities which greatly improve its performance. To foster proper evaluation, we curate a novel dataset of state-of-the-art dialogue system outputs for the Wizard-of-Wikipedia dataset (Dinan et al., 2019), which we manually annotate for factual consistency. We perform a thorough meta-evaluation of our metric against other metrics using the new dataset and two others, where it greatly outperforms the baselines.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge