Elham Seifossadat
SINA-BERT: A pre-trained Language Model for Analysis of Medical Texts in Persian
Apr 15, 2021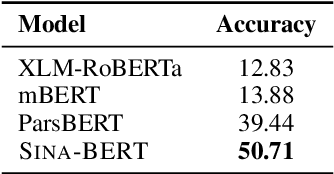
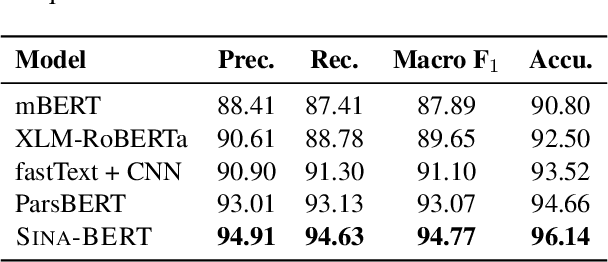
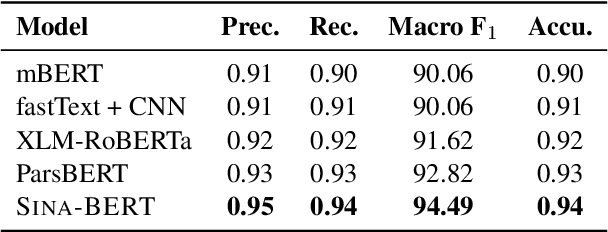
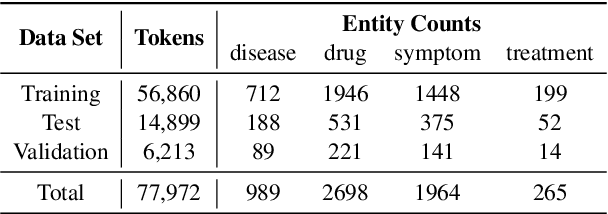
Abstract:We have released Sina-BERT, a language model pre-trained on BERT (Devlin et al., 2018) to address the lack of a high-quality Persian language model in the medical domain. SINA-BERT utilizes pre-training on a large-scale corpus of medical contents including formal and informal texts collected from a variety of online resources in order to improve the performance on health-care related tasks. We employ SINA-BERT to complete following representative tasks: categorization of medical questions, medical sentiment analysis, and medical question retrieval. For each task, we have developed Persian annotated data sets for training and evaluation and learnt a representation for the data of each task especially complex and long medical questions. With the same architecture being used across tasks, SINA-BERT outperforms BERT-based models that were previously made available in the Persian language.
Stochastic Natural Language Generation Using Dependency Information
Jan 12, 2020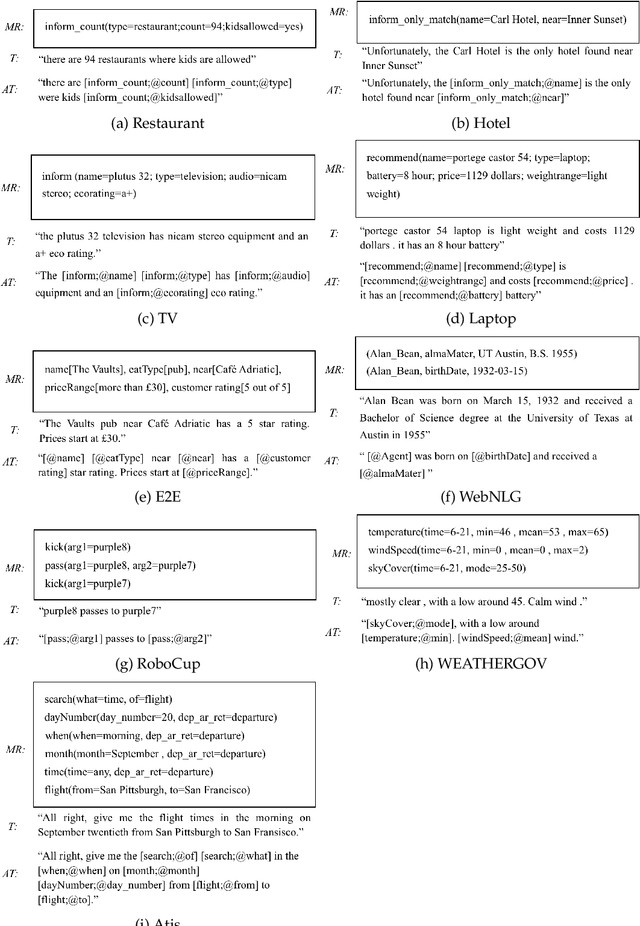
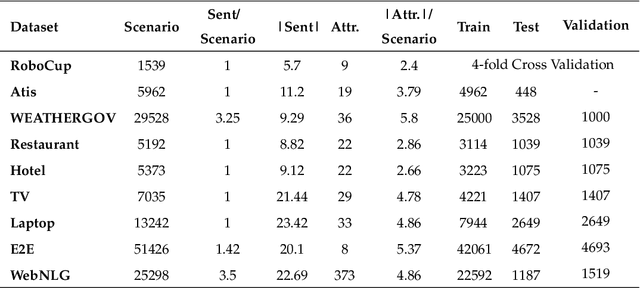
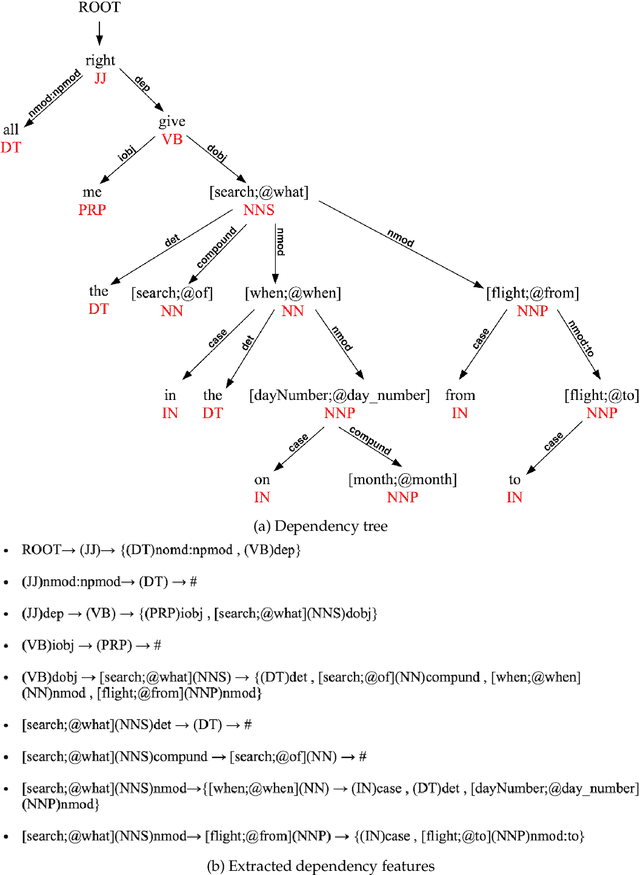
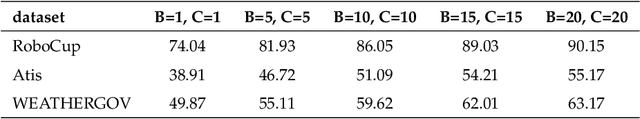
Abstract:This article presents a stochastic corpus-based model for generating natural language text. Our model first encodes dependency relations from training data through a feature set, then concatenates these features to produce a new dependency tree for a given meaning representation, and finally generates a natural language utterance from the produced dependency tree. We test our model on nine domains from tabular, dialogue act and RDF format. Our model outperforms the corpus-based state-of-the-art methods trained on tabular datasets and also achieves comparable results with neural network-based approaches trained on dialogue act, E2E and WebNLG datasets for BLEU and ERR evaluation metrics. Also, by reporting Human Evaluation results, we show that our model produces high-quality utterances in aspects of informativeness and naturalness as well as quality.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge