Elena Ranguelova
Beyond the Veil of Similarity: Quantifying Semantic Continuity in Explainable AI
Jul 17, 2024Abstract:We introduce a novel metric for measuring semantic continuity in Explainable AI methods and machine learning models. We posit that for models to be truly interpretable and trustworthy, similar inputs should yield similar explanations, reflecting a consistent semantic understanding. By leveraging XAI techniques, we assess semantic continuity in the task of image recognition. We conduct experiments to observe how incremental changes in input affect the explanations provided by different XAI methods. Through this approach, we aim to evaluate the models' capability to generalize and abstract semantic concepts accurately and to evaluate different XAI methods in correctly capturing the model behaviour. This paper contributes to the broader discourse on AI interpretability by proposing a quantitative measure for semantic continuity for XAI methods, offering insights into the models' and explainers' internal reasoning processes, and promoting more reliable and transparent AI systems.
The ROAD to discovery: machine learning-driven anomaly detection in radio astronomy spectrograms
Jul 03, 2023Abstract:As radio telescopes increase in sensitivity and flexibility, so do their complexity and data-rates. For this reason automated system health management approaches are becoming increasingly critical to ensure nominal telescope operations. We propose a new machine learning anomaly detection framework for classifying both commonly occurring anomalies in radio telescopes as well as detecting unknown rare anomalies that the system has potentially not yet seen. To evaluate our method, we present a dataset consisting of 7050 autocorrelation-based spectrograms from the Low Frequency Array (LOFAR) telescope and assign 10 different labels relating to the system-wide anomalies from the perspective of telescope operators. This includes electronic failures, miscalibration, solar storms, network and compute hardware errors among many more. We demonstrate how a novel Self Supervised Learning (SSL) paradigm, that utilises both context prediction and reconstruction losses, is effective in learning normal behaviour of the LOFAR telescope. We present the Radio Observatory Anomaly Detector (ROAD), a framework that combines both SSL-based anomaly detection and a supervised classification, thereby enabling both classification of both commonly occurring anomalies and detection of unseen anomalies. We demonstrate that our system is real-time in the context of the LOFAR data processing pipeline, requiring <1ms to process a single spectrogram. Furthermore, ROAD obtains an anomaly detection F-2 score of 0.92 while maintaining a false positive rate of ~2\%, as well as a mean per-class classification F-2 score 0.89, outperforming other related works.
Improving Novelty Detection using the Reconstructions of Nearest Neighbours
Nov 11, 2021

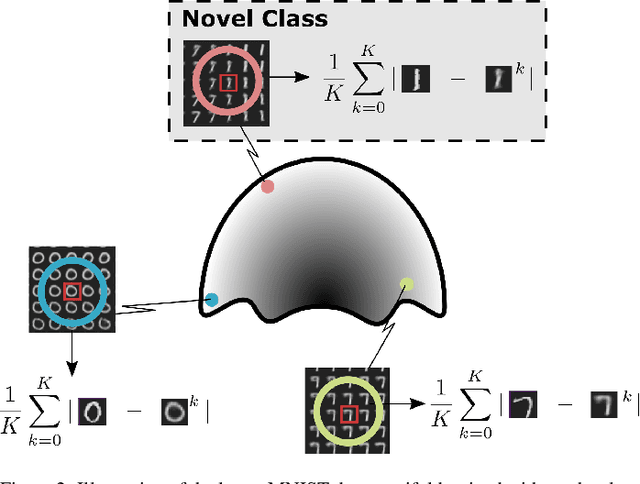

Abstract:We show that using nearest neighbours in the latent space of autoencoders (AE) significantly improves performance of semi-supervised novelty detection in both single and multi-class contexts. Autoencoding methods detect novelty by learning to differentiate between the non-novel training class(es) and all other unseen classes. Our method harnesses a combination of the reconstructions of the nearest neighbours and the latent-neighbour distances of a given input's latent representation. We demonstrate that our nearest-latent-neighbours (NLN) algorithm is memory and time efficient, does not require significant data augmentation, nor is reliant on pre-trained networks. Furthermore, we show that the NLN-algorithm is easily applicable to multiple datasets without modification. Additionally, the proposed algorithm is agnostic to autoencoder architecture and reconstruction error method. We validate our method across several standard datasets for a variety of different autoencoding architectures such as vanilla, adversarial and variational autoencoders using either reconstruction, residual or feature consistent losses. The results show that the NLN algorithm grants up to a 17% increase in Area Under the Receiver Operating Characteristics (AUROC) curve performance for the multi-class case and 8% for single-class novelty detection.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge