Rob V. van Nieuwpoort
SuperCode: Sustainability PER AI-driven CO-DEsign
Dec 11, 2024Abstract:Currently, data-intensive scientific applications require vast amounts of compute resources to deliver world-leading science. The climate emergency has made it clear that unlimited use of resources (e.g., energy) for scientific discovery is no longer acceptable. Future computing hardware promises to be much more energy efficient, but without better optimized software this cannot reach its full potential. In this vision paper, we propose a generic AI-driven co-design methodology, using specialized Large Language Models (like ChatGPT), to effectively generate efficient code for emerging computing hardware. We describe how we will validate our methodology with two radio astronomy applications, with sustainability as the key performance indicator. This paper is a modified version of our accepted SuperCode project proposal. We present it here in this form to introduce the vision behind this project and to disseminate the work in the spirit of Open Science and transparency. An additional aim is to collect feedback, invite potential collaboration partners and use-cases to join the project.
Improving Novelty Detection using the Reconstructions of Nearest Neighbours
Nov 11, 2021

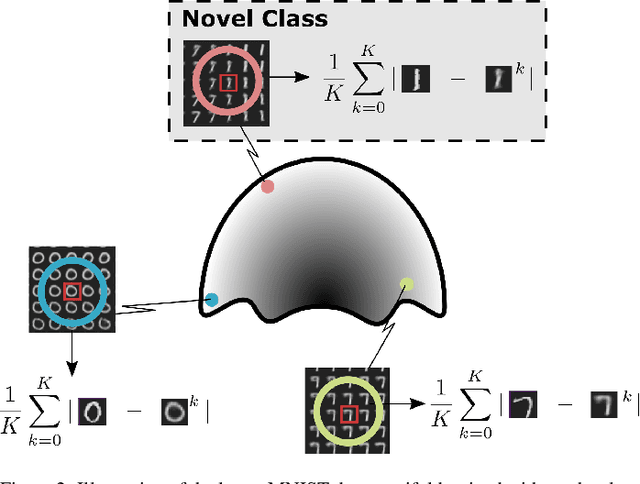

Abstract:We show that using nearest neighbours in the latent space of autoencoders (AE) significantly improves performance of semi-supervised novelty detection in both single and multi-class contexts. Autoencoding methods detect novelty by learning to differentiate between the non-novel training class(es) and all other unseen classes. Our method harnesses a combination of the reconstructions of the nearest neighbours and the latent-neighbour distances of a given input's latent representation. We demonstrate that our nearest-latent-neighbours (NLN) algorithm is memory and time efficient, does not require significant data augmentation, nor is reliant on pre-trained networks. Furthermore, we show that the NLN-algorithm is easily applicable to multiple datasets without modification. Additionally, the proposed algorithm is agnostic to autoencoder architecture and reconstruction error method. We validate our method across several standard datasets for a variety of different autoencoding architectures such as vanilla, adversarial and variational autoencoders using either reconstruction, residual or feature consistent losses. The results show that the NLN algorithm grants up to a 17% increase in Area Under the Receiver Operating Characteristics (AUROC) curve performance for the multi-class case and 8% for single-class novelty detection.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge