Eirini Troullinou
Artificial neural networks in action for an automated cell-type classification of biological neural networks
Nov 22, 2019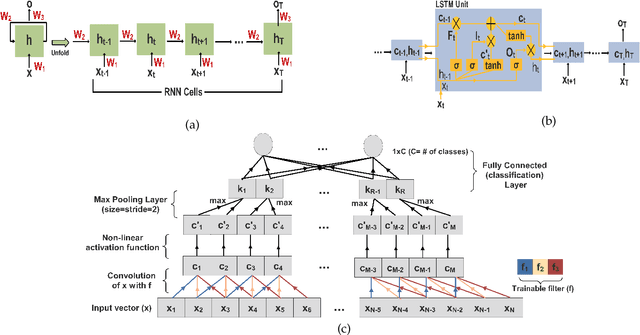
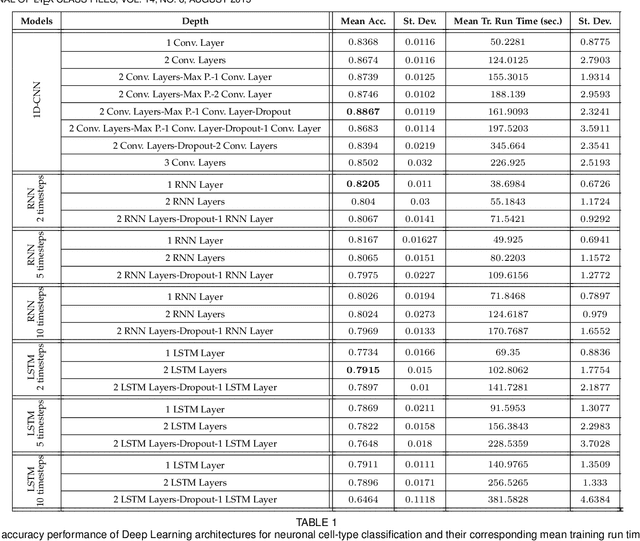
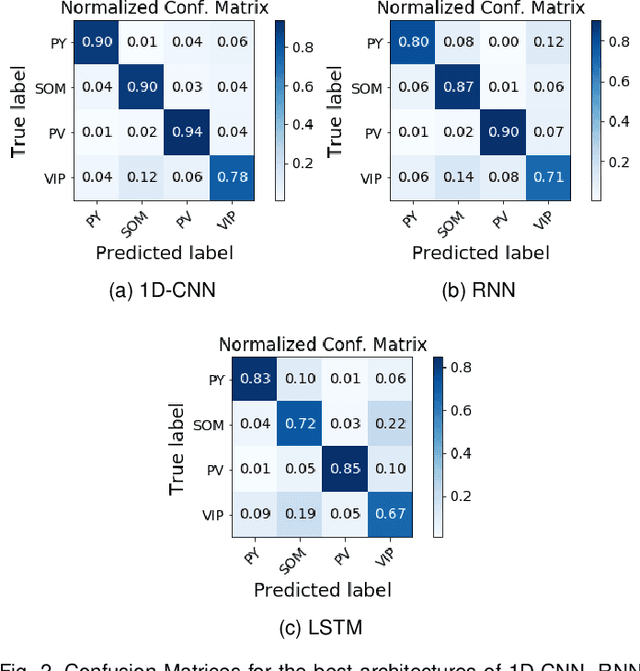
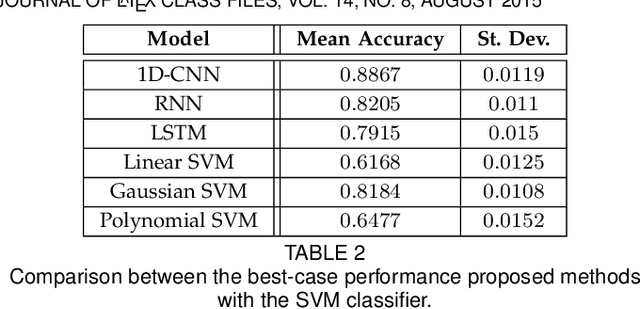
Abstract:In this work we address the problem of neuronal cell-type classification, and we employ a real-world dataset of raw neuronal activity measurements obtained with calcium imaging techniques. While neuronal cell-type classification is a crucial step in understanding the function of neuronal circuits, and thus a systematic classification of neurons is much needed, it still remains a challenge. In recent years, several approaches have been employed for a reliable neuronal cell-type recognition, such as immunohistochemical (IHC) analysis and feature extraction algorithms based on several characteristics of neuronal cells. These methods, however, demand a lot of human intervention and observation, they are time-consuming and regarding the feature extraction algorithms it is not clear or obvious what are the best features that define a neuronal cell class. In this work we examine three different deep learning models aiming at an automated neuronal cell-type classification and compare their performance. Experimental analysis demonstrates the efficacy and potent capabilities for each one of the proposed schemes.
Adversarial dictionary learning for a robust analysis and modelling of spontaneous neuronal activity
Nov 05, 2019



Abstract:The field of neuroscience is experiencing rapid growth in the complexity and quantity of the recorded neural activity allowing us unprecedented access to its dynamics in different brain areas. One of the major goals of neuroscience is to find interpretable descriptions of what the brain represents and computes by trying to explain complex phenomena in simple terms. Considering this task from the perspective of dimensionality reduction provides an entry point into principled mathematical techniques allowing us to discover these representations directly from experimental data, a key step to developing rich yet comprehensible models for brain function. In this work, we employ two real-world binary datasets describing the spontaneous neuronal activity of two laboratory mice over time, and we aim to their efficient low-dimensional representation. We develop an innovative, robust to noise, dictionary learning algorithm for the identification of patterns with synchronous activity and we also extend it to identify patterns within larger time windows. The results on the classification accuracy for the discrimination between the clean and the adversarial-noisy activation patterns obtained by an SVM classifier highlight the efficacy of the proposed scheme, and the visualization of the dictionary's distribution demonstrates the multifarious information that we obtain from it.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge