Dylan Steinecke
Explainable Biomedical Hypothesis Generation via Retrieval Augmented Generation enabled Large Language Models
Jul 17, 2024Abstract:The vast amount of biomedical information available today presents a significant challenge for investigators seeking to digest, process, and understand these findings effectively. Large Language Models (LLMs) have emerged as powerful tools to navigate this complex and challenging data landscape. However, LLMs may lead to hallucinatory responses, making Retrieval Augmented Generation (RAG) crucial for achieving accurate information. In this protocol, we present RUGGED (Retrieval Under Graph-Guided Explainable disease Distinction), a comprehensive workflow designed to support investigators with knowledge integration and hypothesis generation, identifying validated paths forward. Relevant biomedical information from publications and knowledge bases are reviewed, integrated, and extracted via text-mining association analysis and explainable graph prediction models on disease nodes, forecasting potential links among drugs and diseases. These analyses, along with biomedical texts, are integrated into a framework that facilitates user-directed mechanism elucidation as well as hypothesis exploration through RAG-enabled LLMs. A clinical use-case demonstrates RUGGED's ability to evaluate and recommend therapeutics for Arrhythmogenic Cardiomyopathy (ACM) and Dilated Cardiomyopathy (DCM), analyzing prescribed drugs for molecular interactions and unexplored uses. The platform minimizes LLM hallucinations, offers actionable insights, and improves the investigation of novel therapeutics.
Know2BIO: A Comprehensive Dual-View Benchmark for Evolving Biomedical Knowledge Graphs
Oct 05, 2023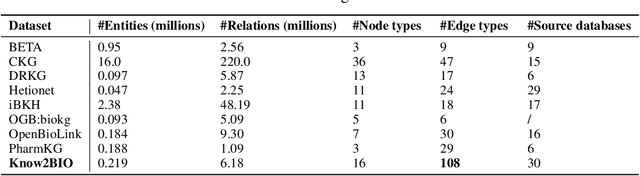
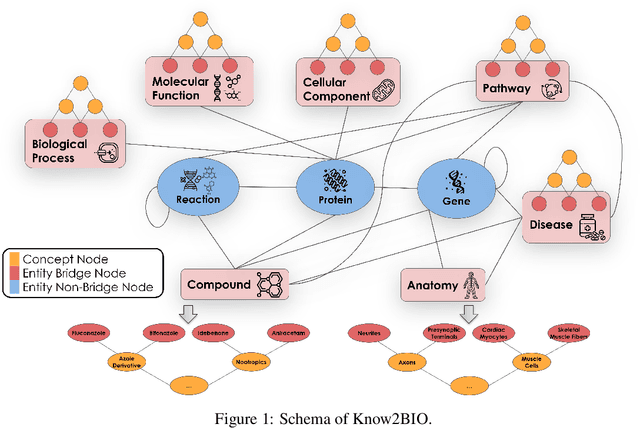
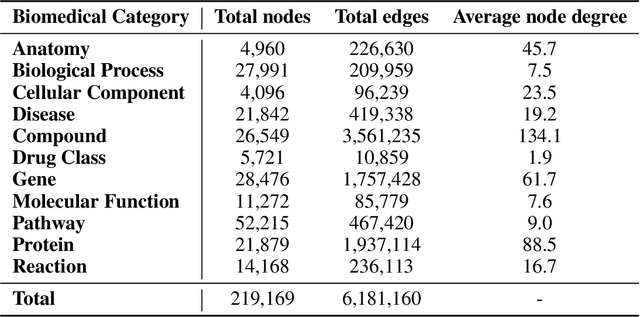
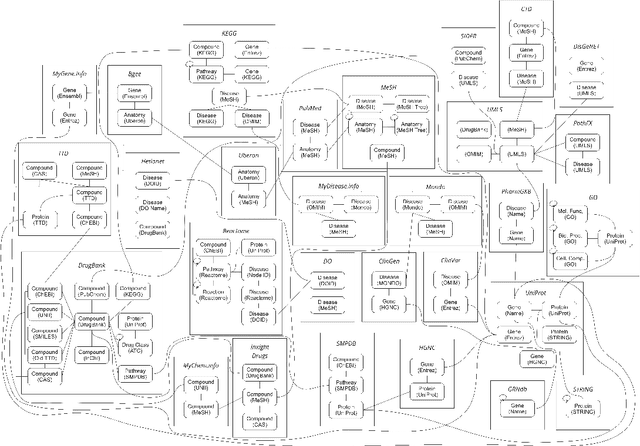
Abstract:Knowledge graphs (KGs) have emerged as a powerful framework for representing and integrating complex biomedical information. However, assembling KGs from diverse sources remains a significant challenge in several aspects, including entity alignment, scalability, and the need for continuous updates to keep pace with scientific advancements. Moreover, the representative power of KGs is often limited by the scarcity of multi-modal data integration. To overcome these challenges, we propose Know2BIO, a general-purpose heterogeneous KG benchmark for the biomedical domain. Know2BIO integrates data from 30 diverse sources, capturing intricate relationships across 11 biomedical categories. It currently consists of ~219,000 nodes and ~6,200,000 edges. Know2BIO is capable of user-directed automated updating to reflect the latest knowledge in biomedical science. Furthermore, Know2BIO is accompanied by multi-modal data: node features including text descriptions, protein and compound sequences and structures, enabling the utilization of emerging natural language processing methods and multi-modal data integration strategies. We evaluate KG representation models on Know2BIO, demonstrating its effectiveness as a benchmark for KG representation learning in the biomedical field. Data and source code of Know2BIO are available at https://github.com/Yijia-Xiao/Know2BIO/.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge