Drew Edwards
GAPS: A Large and Diverse Classical Guitar Dataset and Benchmark Transcription Model
Aug 16, 2024Abstract:We introduce GAPS (Guitar-Aligned Performance Scores), a new dataset of classical guitar performances, and a benchmark guitar transcription model that achieves state-of-the-art performance on GuitarSet in both supervised and zero-shot settings. GAPS is the largest dataset of real guitar audio, containing 14 hours of freely available audio-score aligned pairs, recorded in diverse conditions by over 200 performers, together with high-resolution note-level MIDI alignments and performance videos. These enable us to train a state-of-the-art model for automatic transcription of solo guitar recordings which can generalise well to real world audio that is unseen during training.
MIDI-to-Tab: Guitar Tablature Inference via Masked Language Modeling
Aug 09, 2024
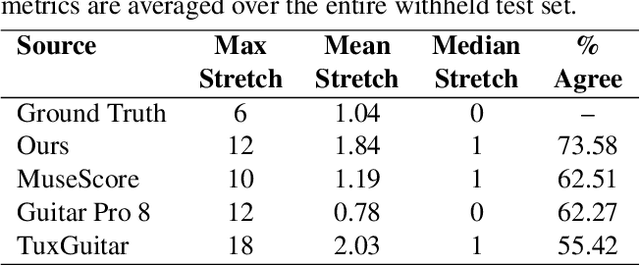
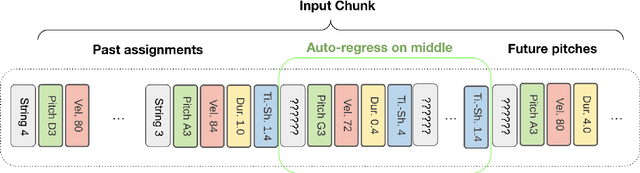
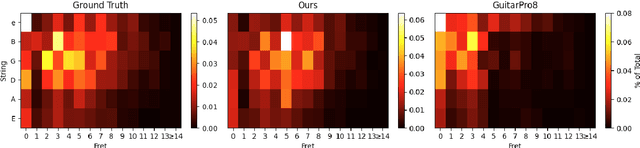
Abstract:Guitar tablatures enrich the structure of traditional music notation by assigning each note to a string and fret of a guitar in a particular tuning, indicating precisely where to play the note on the instrument. The problem of generating tablature from a symbolic music representation involves inferring this string and fret assignment per note across an entire composition or performance. On the guitar, multiple string-fret assignments are possible for most pitches, which leads to a large combinatorial space that prevents exhaustive search approaches. Most modern methods use constraint-based dynamic programming to minimize some cost function (e.g.\ hand position movement). In this work, we introduce a novel deep learning solution to symbolic guitar tablature estimation. We train an encoder-decoder Transformer model in a masked language modeling paradigm to assign notes to strings. The model is first pre-trained on DadaGP, a dataset of over 25K tablatures, and then fine-tuned on a curated set of professionally transcribed guitar performances. Given the subjective nature of assessing tablature quality, we conduct a user study amongst guitarists, wherein we ask participants to rate the playability of multiple versions of tablature for the same four-bar excerpt. The results indicate our system significantly outperforms competing algorithms.
High Resolution Guitar Transcription via Domain Adaptation
Feb 23, 2024



Abstract:Automatic music transcription (AMT) has achieved high accuracy for piano due to the availability of large, high-quality datasets such as MAESTRO and MAPS, but comparable datasets are not yet available for other instruments. In recent work, however, it has been demonstrated that aligning scores to transcription model activations can produce high quality AMT training data for instruments other than piano. Focusing on the guitar, we refine this approach to training on score data using a dataset of commercially available score-audio pairs. We propose the use of a high-resolution piano transcription model to train a new guitar transcription model. The resulting model obtains state-of-the-art transcription results on GuitarSet in a zero-shot context, improving on previously published methods.
A Data-Driven Analysis of Robust Automatic Piano Transcription
Feb 02, 2024Abstract:Algorithms for automatic piano transcription have improved dramatically in recent years due to new datasets and modeling techniques. Recent developments have focused primarily on adapting new neural network architectures, such as the Transformer and Perceiver, in order to yield more accurate systems. In this work, we study transcription systems from the perspective of their training data. By measuring their performance on out-of-distribution annotated piano data, we show how these models can severely overfit to acoustic properties of the training data. We create a new set of audio for the MAESTRO dataset, captured automatically in a professional studio recording environment via Yamaha Disklavier playback. Using various data augmentation techniques when training with the original and re-performed versions of the MAESTRO dataset, we achieve state-of-the-art note-onset accuracy of 88.4 F1-score on the MAPS dataset, without seeing any of its training data. We subsequently analyze these data augmentation techniques in a series of ablation studies to better understand their influence on the resulting models.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge