Donna Xu
Multi-view Alignment and Generation in CCA via Consistent Latent Encoding
May 24, 2020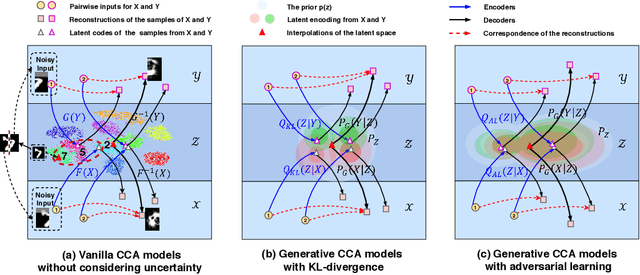
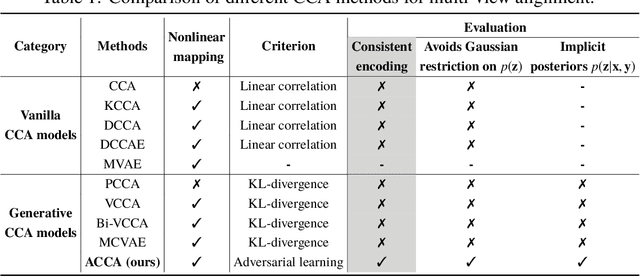
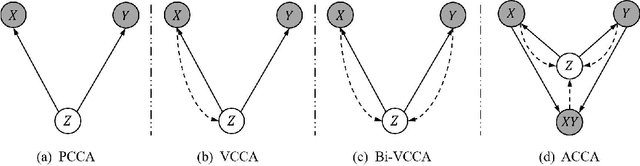
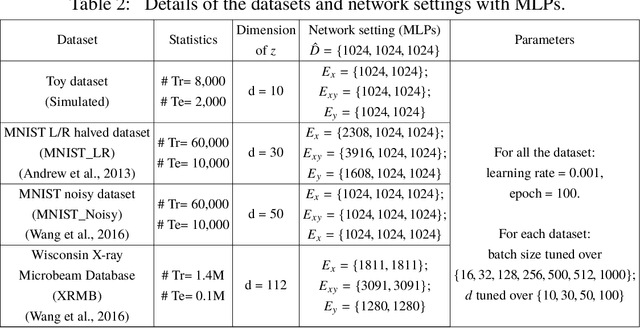
Abstract:Multi-view alignment, achieving one-to-one correspondence of multi-view inputs, is critical in many real-world multi-view applications, especially for cross-view data analysis problems. Recently, an increasing number of works study this alignment problem with Canonical Correlation Analysis (CCA). However, existing CCA models are prone to misalign the multiple views due to either the neglect of uncertainty or the inconsistent encoding of the multiple views. To tackle these two issues, this paper studies multi-view alignment from the Bayesian perspective. Delving into the impairments of inconsistent encodings, we propose to recover correspondence of the multi-view inputs by matching the marginalization of the joint distribution of multi-view random variables under different forms of factorization. To realize our design, we present Adversarial CCA (ACCA) which achieves consistent latent encodings by matching the marginalized latent encodings through the adversarial training paradigm. Our analysis based on conditional mutual information reveals that ACCA is flexible for handling implicit distributions. Extensive experiments on correlation analysis and cross-view generation under noisy input settings demonstrate the superiority of our model.
Probabilistic CCA with Implicit Distributions
Jul 04, 2019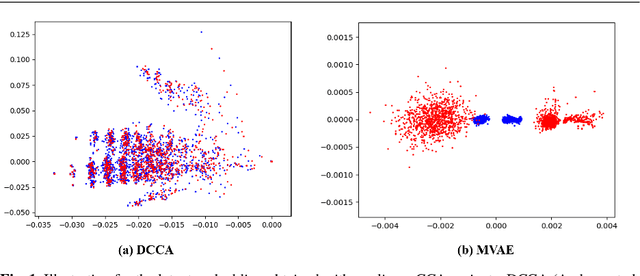
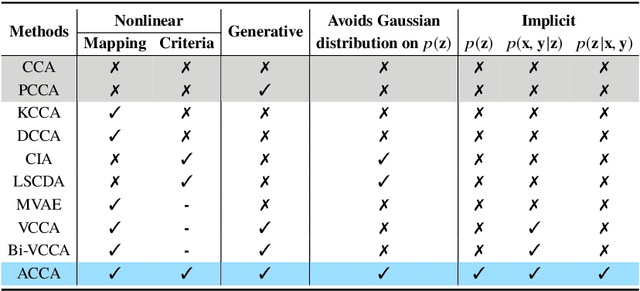
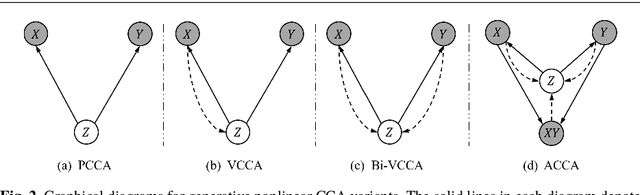
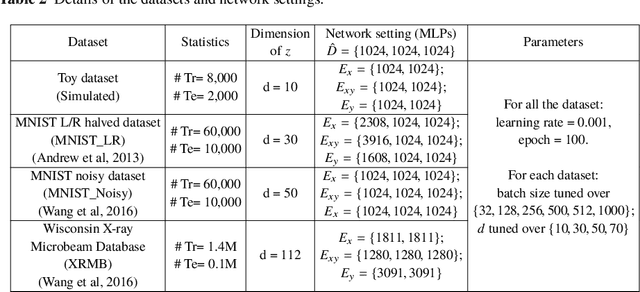
Abstract:Canonical Correlation Analysis (CCA) is a classic technique for multi-view data analysis. To overcome the deficiency of linear correlation in practical multi-view learning tasks, various CCA variants were proposed to capture nonlinear dependency. However, it is non-trivial to have an in-principle understanding of these variants due to their inherent restrictive assumption on the data and latent code distributions. Although some works have studied probabilistic interpretation for CCA, these models still require the explicit form of the distributions to achieve a tractable solution for the inference. In this work, we study probabilistic interpretation for CCA based on implicit distributions. We present Conditional Mutual Information (CMI) as a new criterion for CCA to consider both linear and nonlinear dependency for arbitrarily distributed data. To eliminate direct estimation for CMI, in which explicit form of the distributions is still required, we derive an objective which can provide an estimation for CMI with efficient inference methods. To facilitate Bayesian inference of multi-view analysis, we propose Adversarial CCA (ACCA), which achieves consistent encoding for multi-view data with the consistent constraint imposed on the marginalization of the implicit posteriors. Such a model would achieve superiority in the alignment of the multi-view data with implicit distributions. It is interesting to note that most of the existing CCA variants can be connected with our proposed CCA model by assigning specific form for the posterior and likelihood distributions. Extensive experiments on nonlinear correlation analysis and cross-view generation on benchmark and real-world datasets demonstrate the superiority of our model.
A Survey on Multi-output Learning
Jan 02, 2019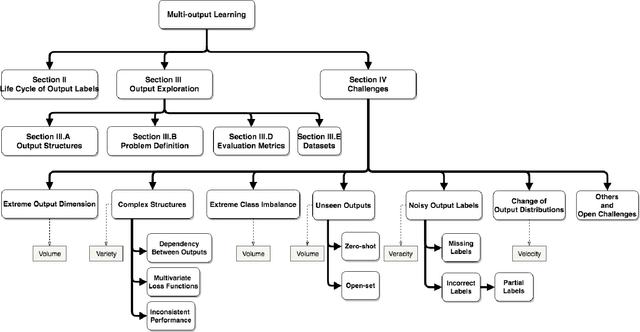
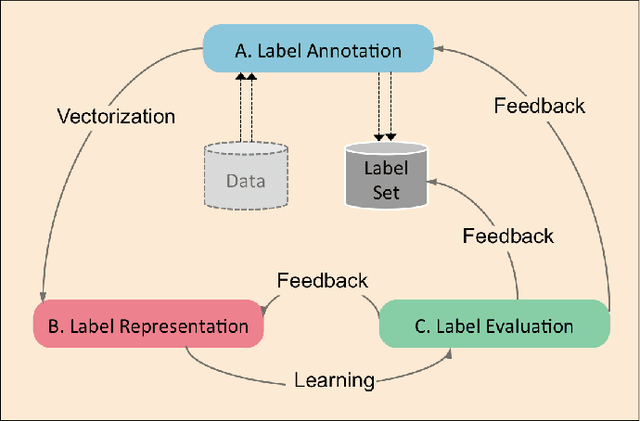
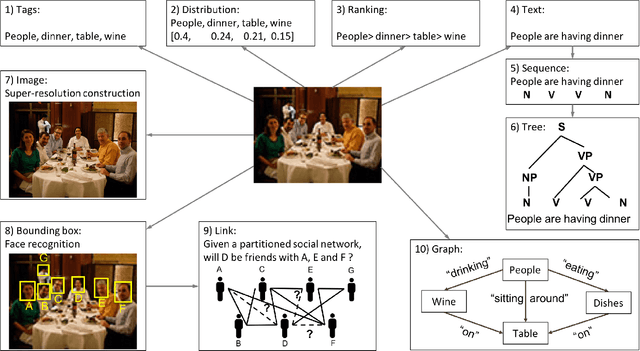
Abstract:Multi-output learning aims to simultaneously predict multiple outputs given an input. It is an important learning problem due to the pressing need for sophisticated decision making in real-world applications. Inspired by big data, the 4Vs characteristics of multi-output imposes a set of challenges to multi-output learning, in terms of the volume, velocity, variety and veracity of the outputs. Increasing number of works in the literature have been devoted to the study of multi-output learning and the development of novel approaches for addressing the challenges encountered. However, it lacks a comprehensive overview on different types of challenges of multi-output learning brought by the characteristics of the multiple outputs and the techniques proposed to overcome the challenges. This paper thus attempts to fill in this gap to provide a comprehensive review on this area. We first introduce different stages of the life cycle of the output labels. Then we present the paradigm on multi-output learning, including its myriads of output structures, definitions of its different sub-problems, model evaluation metrics and popular data repositories used in the study. Subsequently, we review a number of state-of-the-art multi-output learning methods, which are categorized based on the challenges.
Multi-Context Label Embedding
May 03, 2018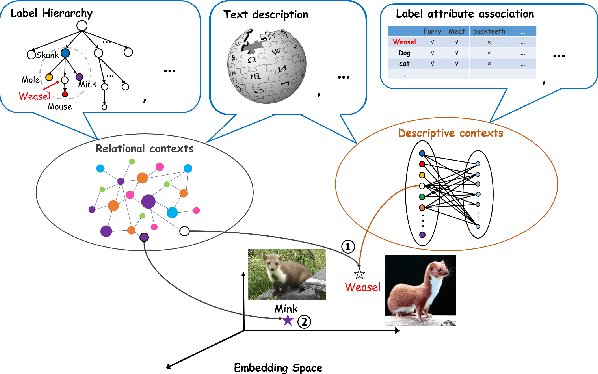
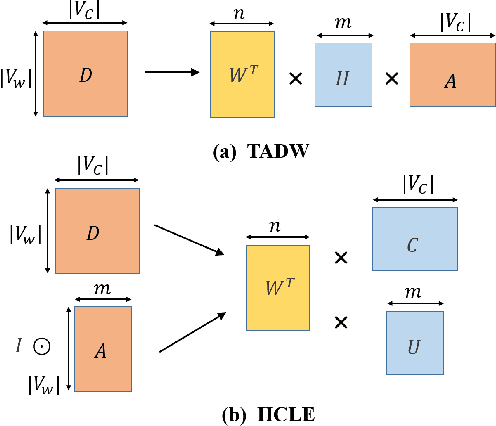
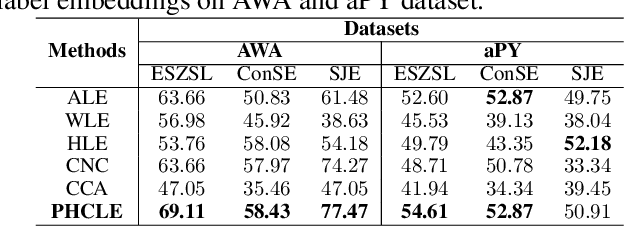
Abstract:Label embedding plays an important role in zero-shot learning. Side information such as attributes, semantic text representations, and label hierarchy are commonly used as the label embedding in zero-shot classification tasks. However, the label embedding used in former works considers either only one single context of the label, or multiple contexts without dependency. Therefore, different contexts of the label may not be well aligned in the embedding space to preserve the relatedness between labels, which will result in poor interpretability of the label embedding. In this paper, we propose a Multi-Context Label Embedding (MCLE) approach to incorporate multiple label contexts, e.g., label hierarchy and attributes, within a unified matrix factorization framework. To be specific, we model each single context by a matrix factorization formula and introduce a shared variable to capture the dependency among different contexts. Furthermore, we enforce sparsity constraint on our multi-context framework to strengthen the interpretability of the learned label embedding. Extensive experiments on two real-world datasets demonstrate the superiority of our MCLE in label description and zero-shot image classification.
Online Product Quantization
Mar 24, 2018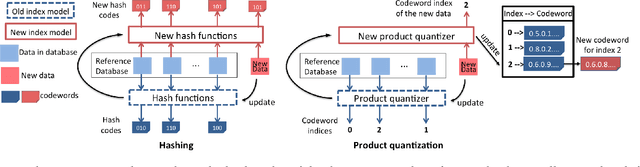
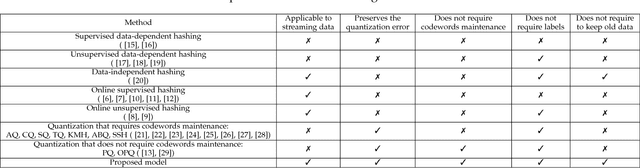
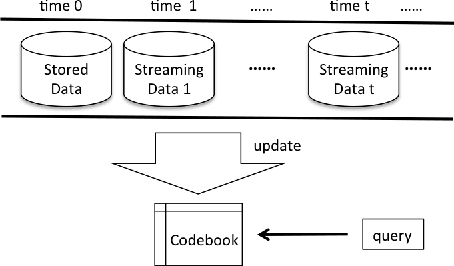
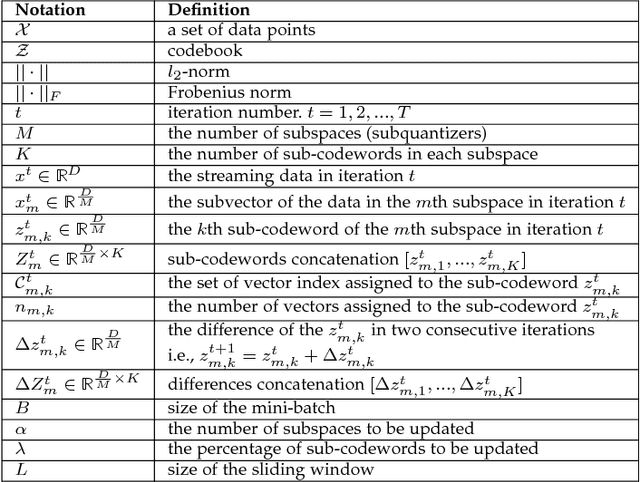
Abstract:Approximate nearest neighbor (ANN) search has achieved great success in many tasks. However, existing popular methods for ANN search, such as hashing and quantization methods, are designed for static databases only. They cannot handle well the database with data distribution evolving dynamically, due to the high computational effort for retraining the model based on the new database. In this paper, we address the problem by developing an online product quantization (online PQ) model and incrementally updating the quantization codebook that accommodates to the incoming streaming data. Moreover, to further alleviate the issue of large scale computation for the online PQ update, we design two budget constraints for the model to update partial PQ codebook instead of all. We derive a loss bound which guarantees the performance of our online PQ model. Furthermore, we develop an online PQ model over a sliding window with both data insertion and deletion supported, to reflect the real-time behaviour of the data. The experiments demonstrate that our online PQ model is both time-efficient and effective for ANN search in dynamic large scale databases compared with baseline methods and the idea of partial PQ codebook update further reduces the update cost.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge