Dongsu Du
On-Device Constrained Self-Supervised Speech Representation Learning for Keyword Spotting via Knowledge Distillation
Jul 06, 2023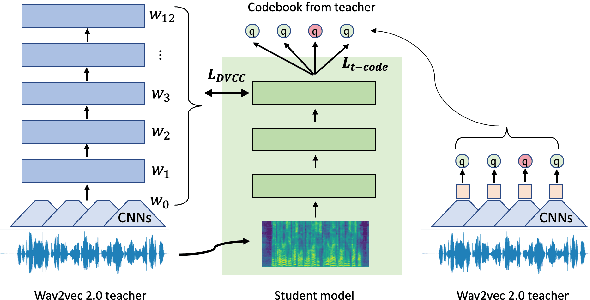

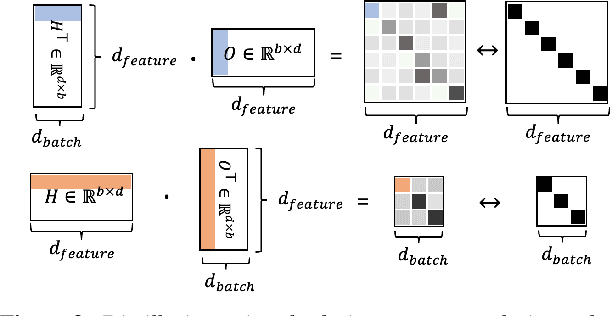
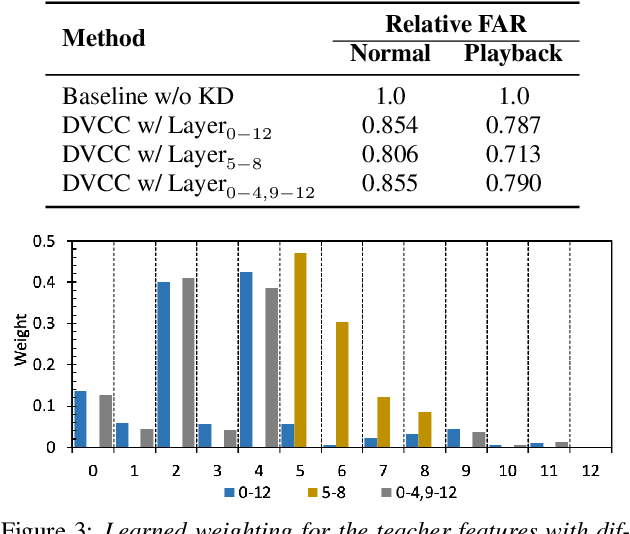
Abstract:Large self-supervised models are effective feature extractors, but their application is challenging under on-device budget constraints and biased dataset collection, especially in keyword spotting. To address this, we proposed a knowledge distillation-based self-supervised speech representation learning (S3RL) architecture for on-device keyword spotting. Our approach used a teacher-student framework to transfer knowledge from a larger, more complex model to a smaller, light-weight model using dual-view cross-correlation distillation and the teacher's codebook as learning objectives. We evaluated our model's performance on an Alexa keyword spotting detection task using a 16.6k-hour in-house dataset. Our technique showed exceptional performance in normal and noisy conditions, demonstrating the efficacy of knowledge distillation methods in constructing self-supervised models for keyword spotting tasks while working within on-device resource constraints.
Small-footprint slimmable networks for keyword spotting
Apr 21, 2023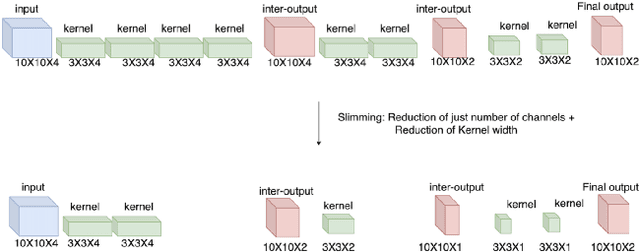
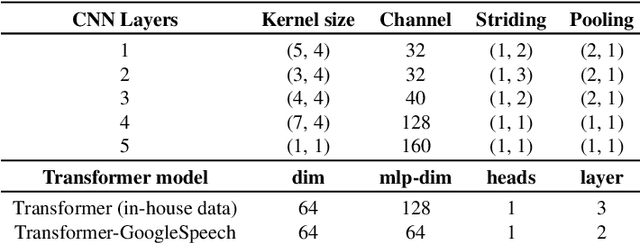
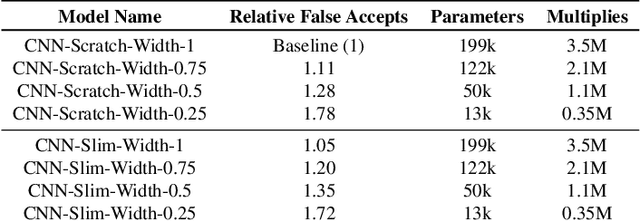
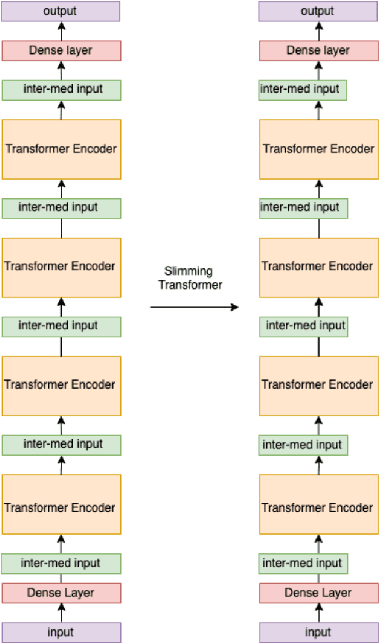
Abstract:In this work, we present Slimmable Neural Networks applied to the problem of small-footprint keyword spotting. We show that slimmable neural networks allow us to create super-nets from Convolutioanl Neural Networks and Transformers, from which sub-networks of different sizes can be extracted. We demonstrate the usefulness of these models on in-house Alexa data and Google Speech Commands, and focus our efforts on models for the on-device use case, limiting ourselves to less than 250k parameters. We show that slimmable models can match (and in some cases, outperform) models trained from scratch. Slimmable neural networks are therefore a class of models particularly useful when the same functionality is to be replicated at different memory and compute budgets, with different accuracy requirements.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge