Diogo Pernes
Multi-Target Cross-Lingual Summarization: a novel task and a language-neutral approach
Oct 01, 2024



Abstract:Cross-lingual summarization aims to bridge language barriers by summarizing documents in different languages. However, ensuring semantic coherence across languages is an overlooked challenge and can be critical in several contexts. To fill this gap, we introduce multi-target cross-lingual summarization as the task of summarizing a document into multiple target languages while ensuring that the produced summaries are semantically similar. We propose a principled re-ranking approach to this problem and a multi-criteria evaluation protocol to assess semantic coherence across target languages, marking a first step that will hopefully stimulate further research on this problem.
Supervising the Centroid Baseline for Extractive Multi-Document Summarization
Nov 29, 2023



Abstract:The centroid method is a simple approach for extractive multi-document summarization and many improvements to its pipeline have been proposed. We further refine it by adding a beam search process to the sentence selection and also a centroid estimation attention model that leads to improved results. We demonstrate this in several multi-document summarization datasets, including in a multilingual scenario.
Towards End-to-end Speech-to-text Summarization
Jun 06, 2023



Abstract:Speech-to-text (S2T) summarization is a time-saving technique for filtering and keeping up with the broadcast news uploaded online on a daily basis. The rise of large language models from deep learning with impressive text generation capabilities has placed the research focus on summarization systems that produce paraphrased compact versions of the document content, also known as abstractive summaries. End-to-end (E2E) modelling of S2T abstractive summarization is a promising approach that offers the possibility of generating rich latent representations that leverage non-verbal and acoustic information, as opposed to the use of only linguistic information from automatically generated transcripts in cascade systems. However, the few literature on E2E modelling of this task fails on exploring different domains, namely broadcast news, which is challenging domain where large and diversified volumes of data are presented to the user every day. We model S2T summarization both with a cascade and an E2E system for a corpus of broadcast news in French. Our novel E2E model leverages external data by resorting to transfer learning from a pre-trained T2T summarizer. Experiments show that both our cascade and E2E abstractive summarizers are stronger than an extractive baseline. However, the performance of the E2E model still lies behind the cascade one, which is object of an extensive analysis that includes future directions to close that gap.
Improving abstractive summarization with energy-based re-ranking
Nov 07, 2022



Abstract:Current abstractive summarization systems present important weaknesses which prevent their deployment in real-world applications, such as the omission of relevant information and the generation of factual inconsistencies (also known as hallucinations). At the same time, automatic evaluation metrics such as CTC scores have been recently proposed that exhibit a higher correlation with human judgments than traditional lexical-overlap metrics such as ROUGE. In this work, we intend to close the loop by leveraging the recent advances in summarization metrics to create quality-aware abstractive summarizers. Namely, we propose an energy-based model that learns to re-rank summaries according to one or a combination of these metrics. We experiment using several metrics to train our energy-based re-ranker and show that it consistently improves the scores achieved by the predicted summaries. Nonetheless, human evaluation results show that the re-ranking approach should be used with care for highly abstractive summaries, as the available metrics are not yet sufficiently reliable for this purpose.
Tackling unsupervised multi-source domain adaptation with optimism and consistency
Sep 29, 2020



Abstract:It has been known for a while that the problem of multi-source domain adaptation can be regarded as a single source domain adaptation task where the source domain corresponds to a mixture of the original source domains. Nonetheless, how to adjust the mixture distribution weights remains an open question. Moreover, most existing work on this topic focuses only on minimizing the error on the source domains and achieving domain-invariant representations, which is insufficient to ensure low error on the target domain. In this work, we present a novel framework that addresses both problems and beats the current state of the art by using a mildly optimistic objective function and consistency regularization on the target samples.
SpaMHMM: Sparse Mixture of Hidden Markov Models for Graph Connected Entities
Mar 31, 2019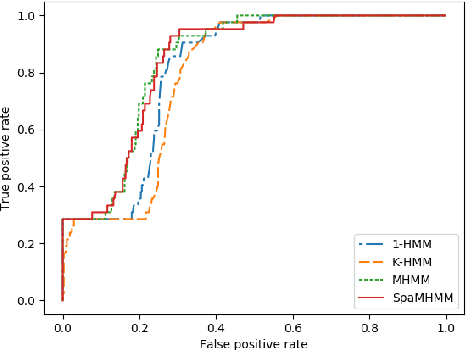
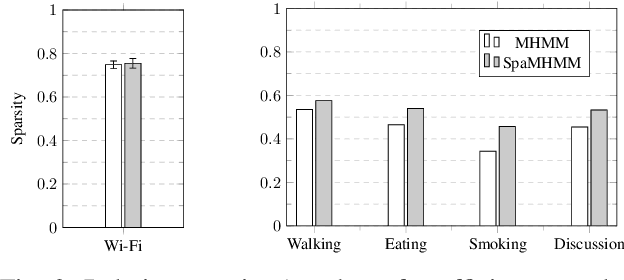
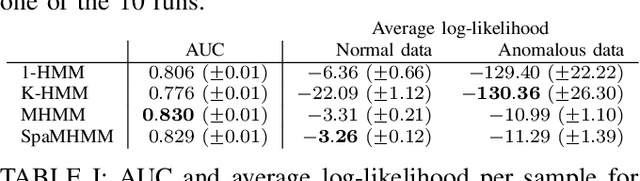
Abstract:We propose a framework to model the distribution of sequential data coming from a set of entities connected in a graph with a known topology. The method is based on a mixture of shared hidden Markov models (HMMs), which are jointly trained in order to exploit the knowledge of the graph structure and in such a way that the obtained mixtures tend to be sparse. Experiments in different application domains demonstrate the effectiveness and versatility of the method.
Dimensional emotion recognition using visual and textual cues
May 03, 2018


Abstract:This paper addresses the problem of automatic emotion recognition in the scope of the One-Minute Gradual-Emotional Behavior challenge (OMG-Emotion challenge). The underlying objective of the challenge is the automatic estimation of emotion expressions in the two-dimensional emotion representation space (i.e., arousal and valence). The adopted methodology is a weighted ensemble of several models from both video and text modalities. For video-based recognition, two different types of visual cues (i.e., face and facial landmarks) were considered to feed a multi-input deep neural network. Regarding the text modality, a sequential model based on a simple recurrent architecture was implemented. In addition, we also introduce a model based on high-level features in order to embed domain knowledge in the learning process. Experimental results on the OMG-Emotion validation set demonstrate the effectiveness of the implemented ensemble model as it clearly outperforms the current baseline methods.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge