Diana Davletshina
Unsupervised Anomaly Detection for X-Ray Images
Jan 29, 2020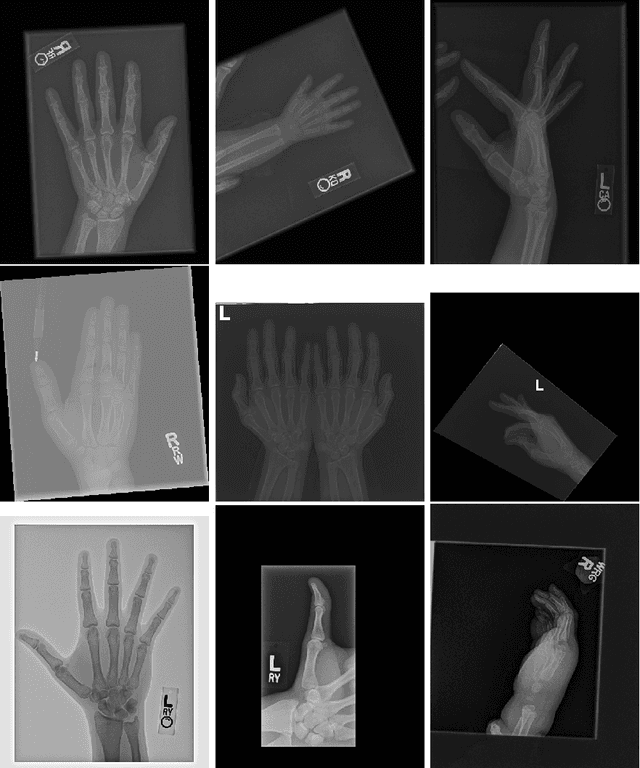
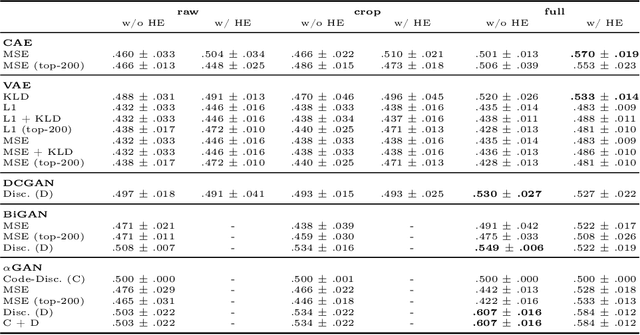
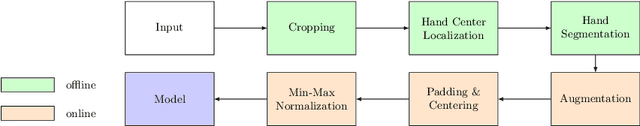
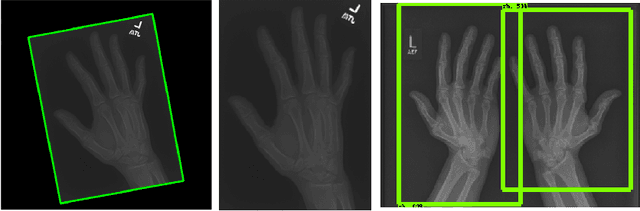
Abstract:Obtaining labels for medical (image) data requires scarce and expensive experts. Moreover, due to ambiguous symptoms, single images rarely suffice to correctly diagnose a medical condition. Instead, it often requires to take additional background information such as the patient's medical history or test results into account. Hence, instead of focusing on uninterpretable black-box systems delivering an uncertain final diagnosis in an end-to-end-fashion, we investigate how unsupervised methods trained on images without anomalies can be used to assist doctors in evaluating X-ray images of hands. Our method increases the efficiency of making a diagnosis and reduces the risk of missing important regions. Therefore, we adopt state-of-the-art approaches for unsupervised learning to detect anomalies and show how the outputs of these methods can be explained. To reduce the effect of noise, which often can be mistaken for an anomaly, we introduce a powerful preprocessing pipeline. We provide an extensive evaluation of different approaches and demonstrate empirically that even without labels it is possible to achieve satisfying results on a real-world dataset of X-ray images of hands. We also evaluate the importance of preprocessing and one of our main findings is that without it, most of our approaches perform not better than random. To foster reproducibility and accelerate research we make our code publicly available at https://github.com/Valentyn1997/xray
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge