Dhyey Manish Rajani
Quantile Transfer for Reliable Operating Point Selection in Visual Place Recognition
Feb 04, 2026Abstract:Visual Place Recognition (VPR) is a key component for localisation in GNSS-denied environments, but its performance critically depends on selecting an image matching threshold (operating point) that balances precision and recall. Thresholds are typically hand-tuned offline for a specific environment and fixed during deployment, leading to degraded performance under environmental change. We propose a method that, given a user-defined precision requirement, automatically selects the operating point of a VPR system to maximise recall. The method uses a small calibration traversal with known correspondences and transfers thresholds to deployment via quantile normalisation of similarity score distributions. This quantile transfer ensures that thresholds remain stable across calibration sizes and query subsets, making the method robust to sampling variability. Experiments with multiple state-of-the-art VPR techniques and datasets show that the proposed approach consistently outperforms the state-of-the-art, delivering up to 25% higher recall in high-precision operating regimes. The method eliminates manual tuning by adapting to new environments and generalising across operating conditions. Our code will be released upon acceptance.
Twilight SLAM: A Comparative Study of Low-Light Visual SLAM Pipelines
Apr 27, 2023
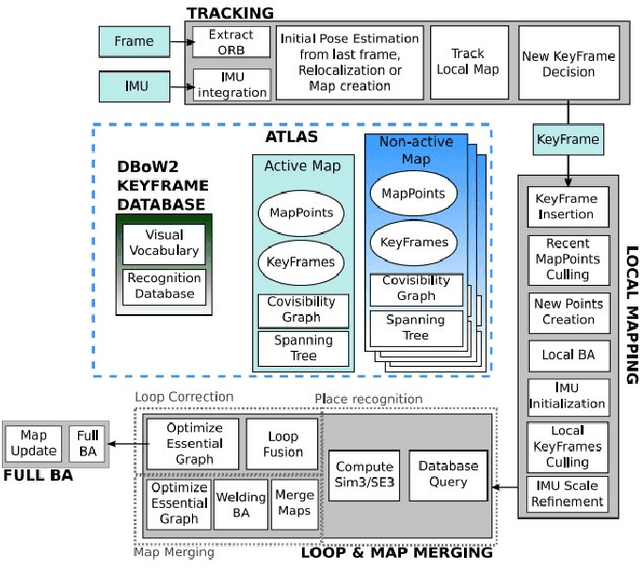
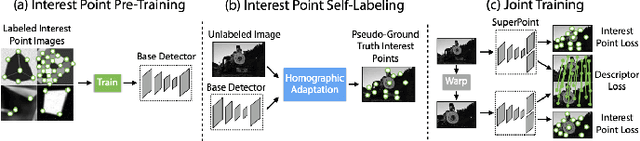
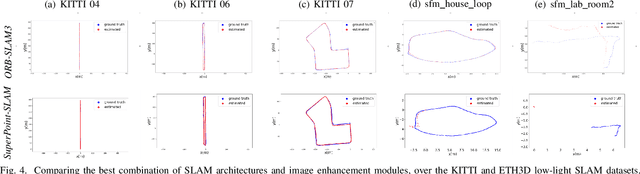
Abstract:This paper presents a comparative study of low-light visual SLAM pipelines, specifically focusing on determining an efficient combination of the state-of-the-art low-light image enhancement algorithms with standard and contemporary Simultaneous Localization and Mapping (SLAM) frameworks by evaluating their performance in challenging low-light conditions. In this study, we investigate the performance of several different low-light SLAM pipelines for dark and/or poorly-lit datasets as opposed to just partially dim-lit datasets like other works in the literature. Our study takes an experimental approach to qualitatively and quantitatively compare the chosen combinations of modules to enhance the feature-based visual SLAM.
OriCon3D: Effective 3D Object Detection using Orientation and Confidence
Apr 27, 2023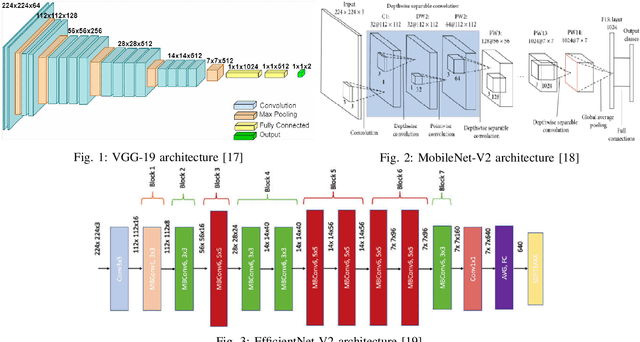
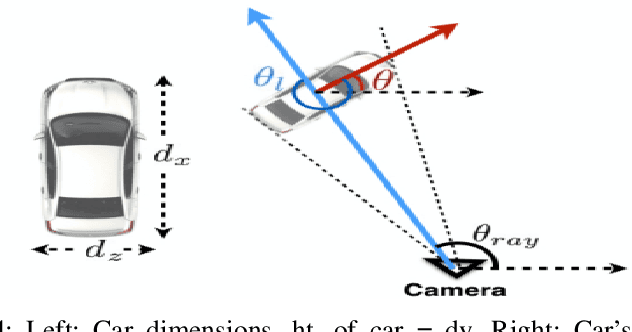
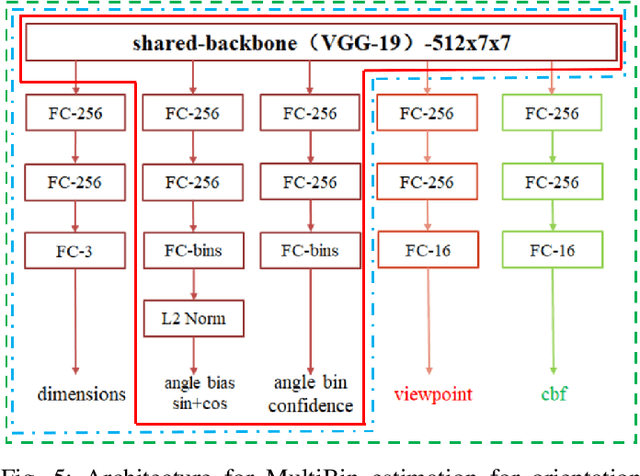
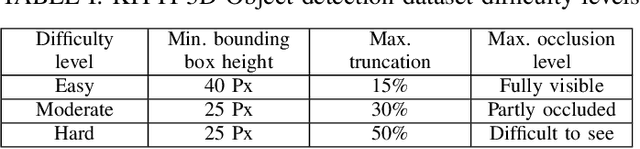
Abstract:We introduce a technique for detecting 3D objects and estimating their position from a single image. Our method is built on top of a similar state-of-the-art technique [1], but with improved accuracy. The approach followed in this research first estimates common 3D properties of an object using a Deep Convolutional Neural Network (DCNN), contrary to other frameworks that only leverage centre-point predictions. We then combine these estimates with geometric constraints provided by a 2D bounding box to produce a complete 3D bounding box. The first output of our network estimates the 3D object orientation using a discrete-continuous loss [1]. The second output predicts the 3D object dimensions with minimal variance. Here we also present our extensions by augmenting light-weight feature extractors and a customized multibin architecture. By combining these estimates with the geometric constraints of the 2D bounding box, we can accurately (or comparatively) determine the 3D object pose better than our baseline [1] on the KITTI 3D detection benchmark [2].
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge