Get our free extension to see links to code for papers anywhere online!Free add-on: code for papers everywhere!Free add-on: See code for papers anywhere!
Billy Mazotti
Twilight SLAM: A Comparative Study of Low-Light Visual SLAM Pipelines
Apr 27, 2023Authors:Surya Pratap Singh, Billy Mazotti, Sarvesh Mayilvahanan, Guoyuan Li, Dhyey Manish Rajani, Maani Ghaffari
Figures and Tables:
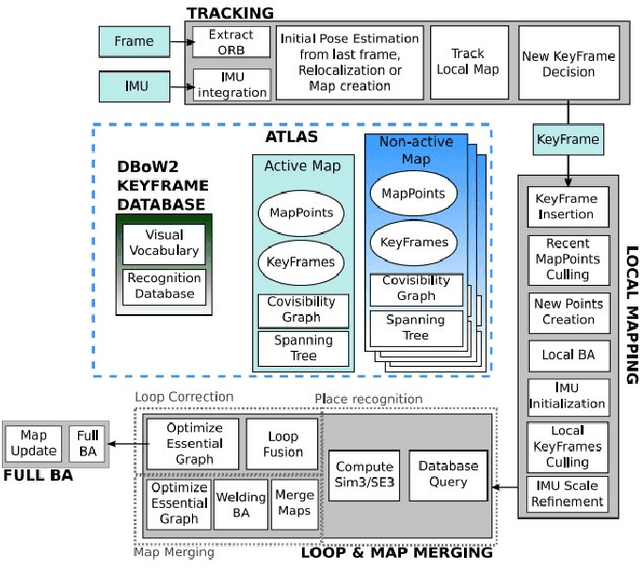
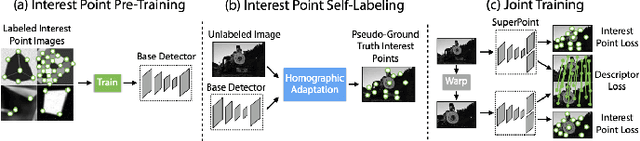
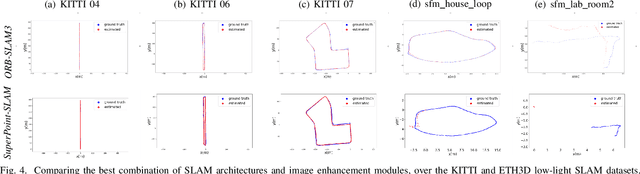




Abstract:This paper presents a comparative study of low-light visual SLAM pipelines, specifically focusing on determining an efficient combination of the state-of-the-art low-light image enhancement algorithms with standard and contemporary Simultaneous Localization and Mapping (SLAM) frameworks by evaluating their performance in challenging low-light conditions. In this study, we investigate the performance of several different low-light SLAM pipelines for dark and/or poorly-lit datasets as opposed to just partially dim-lit datasets like other works in the literature. Our study takes an experimental approach to qualitatively and quantitatively compare the chosen combinations of modules to enhance the feature-based visual SLAM.
Via
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge